Question: Simulation Trial range is 1-1000 Model Production Quantity 60,000 Simulation Trial Demand Net Profit Summary Statistics 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9

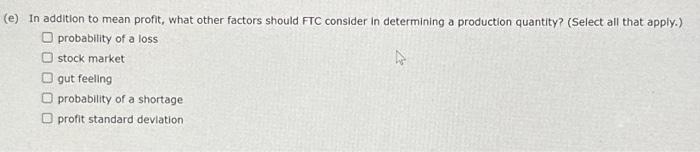
Model Production Quantity 60,000 Simulation Trial Demand Net Profit Summary Statistics 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Mean Net Profit HDIV/O! St. Dev. Net Profit HDIV/O! In preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dovgle that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is \$100,000. The variable cost, which includes materlal, labor, and shipping costs, is $29 per doll. During the hollday seliling season, FTC wal sell the dolls for $37 esch, If FiC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in lanuary through a distributor who has agreed to poy fre $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the hollday selling season is extremely. uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000 . The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. ETC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (o) Determine the equation for computing fTCs profit for given values of the reievant parameters (e. g. demand, production quantity, etc.). Using this equation, compute frC's profit (in dollars) when realited demand is equal to 60,000 (the average demand). (b) Modeling demsid as a normal random variable with a mean of 60,000 and a standard deviation of 15,000 , simulate the sales of the Dougie doll using a production quantity of 60,000 units. What is the estimate of the averdge profit (in dollars) assoclated with the production quantity of 60,000 dolls? (Use at least 1,000 trials. Round your answer to the nearest integer. 3 (c) Compare the average profit ectimated by simulation in part (b) to the profit calculation in part (a). The average profit from the simulation is greater than the profit computed in part (o) The aveiage profit from the simulation is tess than the profit computed in part (o): Explain why they differ. since the Semand is being inodeied os a normal random vaiable, the sample mean pront will always tend to be lower than the true mean proft. Profit is amined by the production quantay, so hagher than average demand does not correspond to higher profits, but lower demand wul lead to lower aronis. Since the demand is being moceled as a normal random variable, the sample mean prof will always tend to be higher than the true inean profit. Profit is lemged by the production quantay, so lower than average demand does not correspond to lower profits, but higher demand will lead to higher pronts. (d) Before making a final decision on the preduction quantity, management wants an analysis of a more a9gressive 70,000 unit production quantity and a more conservative 50,000 -unit production quartity. Ran your simulatian with these two production quantales. (Use at least 1,000 trials. Round your answers to the nearest integer.) What is the mean profit (in dollars) associated with 50,000 units? What is the mean grofit (in dollars) associated with 70,000 units? (e) In addition to mean profit, what other factors should FTC consider in determining a production quantity? (Select all that apply.) probability of a loss stock market gut feeling probability of a shortage profit standard devlation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


