Question: Solutions to linear differential equations can be written using convolutions as y = yIVP + (h(t) f(t))y = yIVP + (h(t) f(t)) yIVPyIVP is the
Solutions to linear differential equations can be written using convolutions as
y = yIVP + (h(t) f(t))y = yIVP + (h(t) f(t))
yIVPyIVP is the solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation with the given initial values (ignore the forcing function, keep initial values). h(t)h(t) is the impulse response (ignore the initial values and forcing function). f(t)f(t) is the forcing function. (ignore the initial values and differential equation).
Use the form above to write the solution to the differential equation
y+3y+2y=7t2etwithy(0)=2,y(0)=2y+3y+2y=7t2etwithy(0)=2,y(0)=2
y = y = +(+( )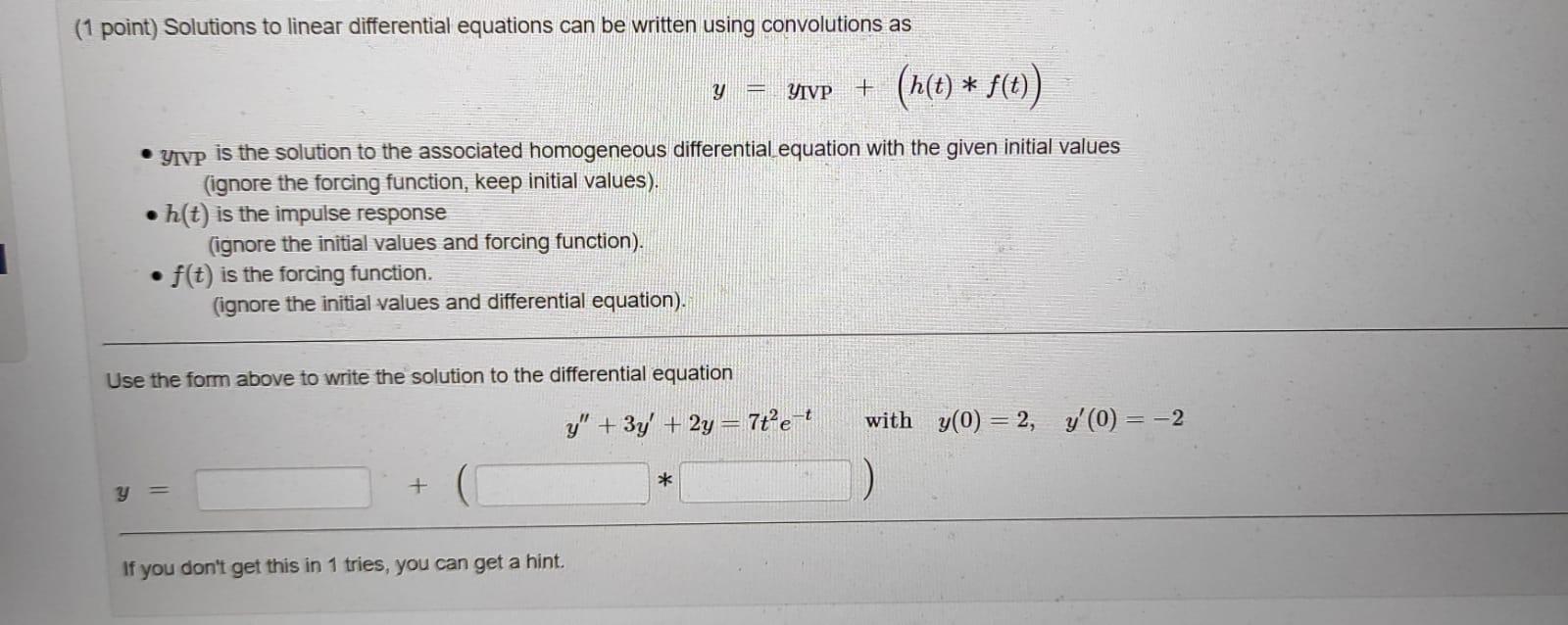
(1 point) Solutions to linear differential equations can be written using convolutions as y YIVP + (h(t) * f(t)) YIvp is the solution to the associated homogeneous differential equation with the given initial values (ignore the forcing function, keep initial values). h(t) is the impulse response (ignore the initial values and forcing function). f(t) is the forcing function. (ignore the initial values and differential equation). Use the form above to write the solution to the differential equation y" + 3y + 2y = 7tet with y(0) = 2, 7(0) = -2 y + * If you don't get this in 1 tries, you can get a hint
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


