Question: Solve Posterior probabilities are conditional probabilities based on the outcome of the sample information. These can be computed by developing a table using the following
Solve
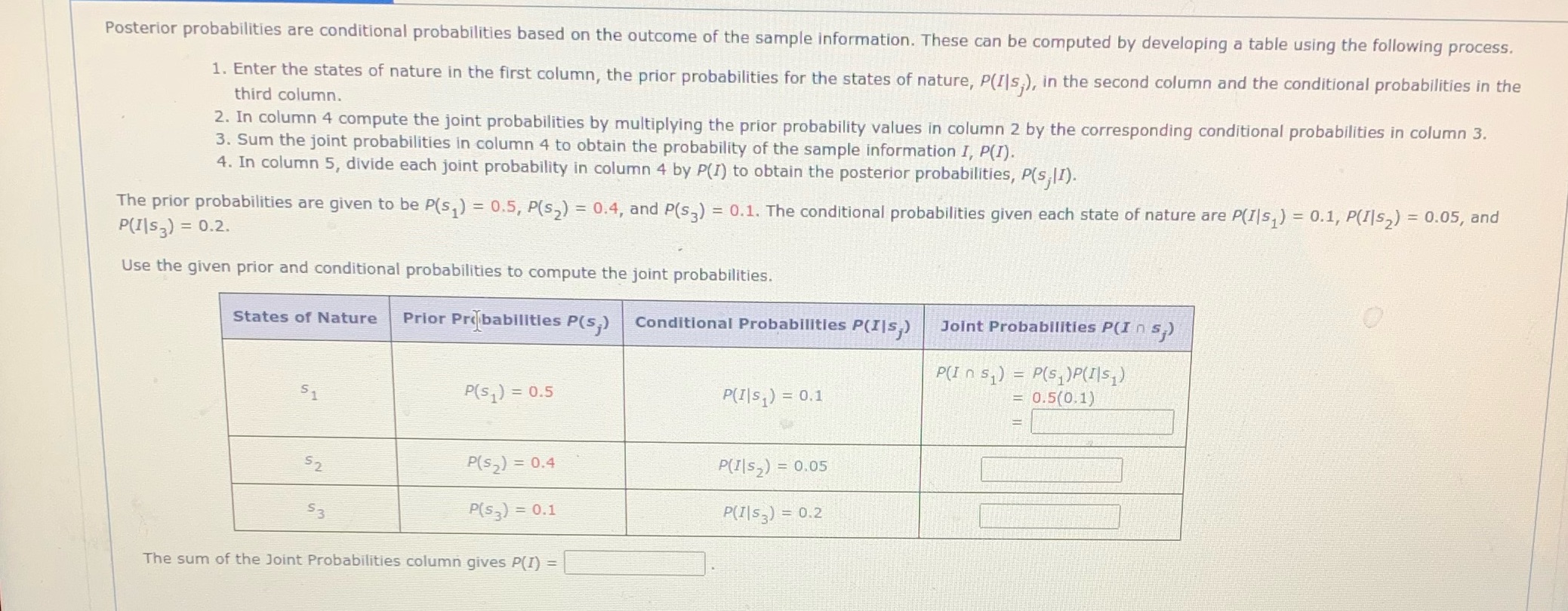
Posterior probabilities are conditional probabilities based on the outcome of the sample information. These can be computed by developing a table using the following process. 1. Enter the states of nature in the first column, the prior probabilities for the states of nature, P(I|s,), in the second column and the conditional probabilities in the third column. 2. In column 4 compute the joint probabilities by multiplying the prior probability values in column 2 by the corresponding conditional probabilities in column 3. 3. Sum the joint probabilities in column 4 to obtain the probability of the sample information I, P(I). 4. In column 5, divide each joint probability in column 4 by P(I) to obtain the posterior probabilities, P(s, |1). The prior probabilities are given to be P(s, ) = 0.5, P(s2) = 0.4, and P(S3) = 0.1. The conditional probabilities given each state of nature are P(I|s, ) = 0.1, P(I|s, ) = 0.05, and P(I|S? ) = 0.2. Use the given prior and conditional probabilities to compute the joint probabilities. States of Nature Prior Probabilities P(s,) Conditional Probabilities P(IIs,) Joint Probabilities P(I n s,) P( I n s. ) = P(5, ) P(I)s, ) 5 1 P(s ) = 0.5 P(I|s ) = 0.1 = 0.5(0,1) 52 P(S,) = 0.4 P(I|S,) = 0.05 P(s?) = 0.1 P(I|S) = 0.2 The sum of the Joint Probabilities column gives P(I) =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


