Question: solve this solution please 6.1 R. J. Farrauto and C. H. Bartholemew (Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes, p. 127, Blackie, London, 1997) reported the data
solve this solution please

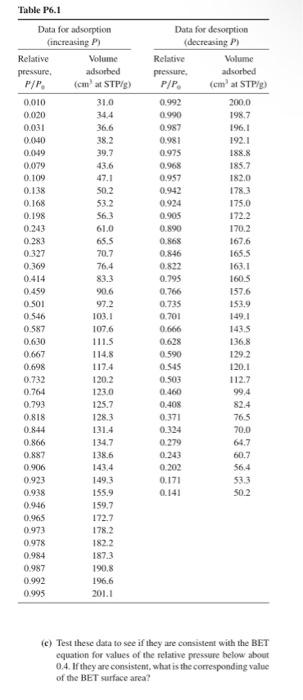
6.1 R. J. Farrauto and C. H. Bartholemew (Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes, p. 127, Blackie, London, 1997) reported the data in Table P6.1 for the adsorption of nitrogen at 77K on a bayerite alumina sample. (a) Use these data to prepare plots of the adsorption and desorption branches of the adsorption isotherm. Comment. (b) Test these data to see if they can be fit by an isotherm of the Langmuir form for relative pressures up to about 0.4. Use the Langmuir equation in the form vPA=vmK1+vmPA where PA is the pressure of adsorbate and v is the corresponding equivalent volume of adsorbed material. Comment. (c) Test these data to see if they are consistent with the BET cquation for values of the relative pressure helowa about 0.4. If they are consistent, what is the corresponding valoe of the BEI surface area? 6.1 R. J. Farrauto and C. H. Bartholemew (Fundamentals of Industrial Catalytic Processes, p. 127, Blackie, London, 1997) reported the data in Table P6.1 for the adsorption of nitrogen at 77K on a bayerite alumina sample. (a) Use these data to prepare plots of the adsorption and desorption branches of the adsorption isotherm. Comment. (b) Test these data to see if they can be fit by an isotherm of the Langmuir form for relative pressures up to about 0.4. Use the Langmuir equation in the form vPA=vmK1+vmPA where PA is the pressure of adsorbate and v is the corresponding equivalent volume of adsorbed material. Comment. (c) Test these data to see if they are consistent with the BET cquation for values of the relative pressure helowa about 0.4. If they are consistent, what is the corresponding valoe of the BEI surface area
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


