Question: Solve using Excel or Python For the binary n-butane, i-butane, do the following a) Calculate the normal boiling point of each species from Antoine Constants
Solve using Excel or Python
For the binary n-butane, i-butane, do the following
a) Calculate the normal boiling point of each species from Antoine Constants in Table B.4
Calculate the percent error from the values tabulated in App. F.
b) Prepare the Txy diagram to be used in the design of a distillation process at 15 psig . Tabulate and plot the results. You may assume the Antoine constants in Table B.4 for normal and Iso butane are valid up to the boiling points at the pressure given in the problem statement.
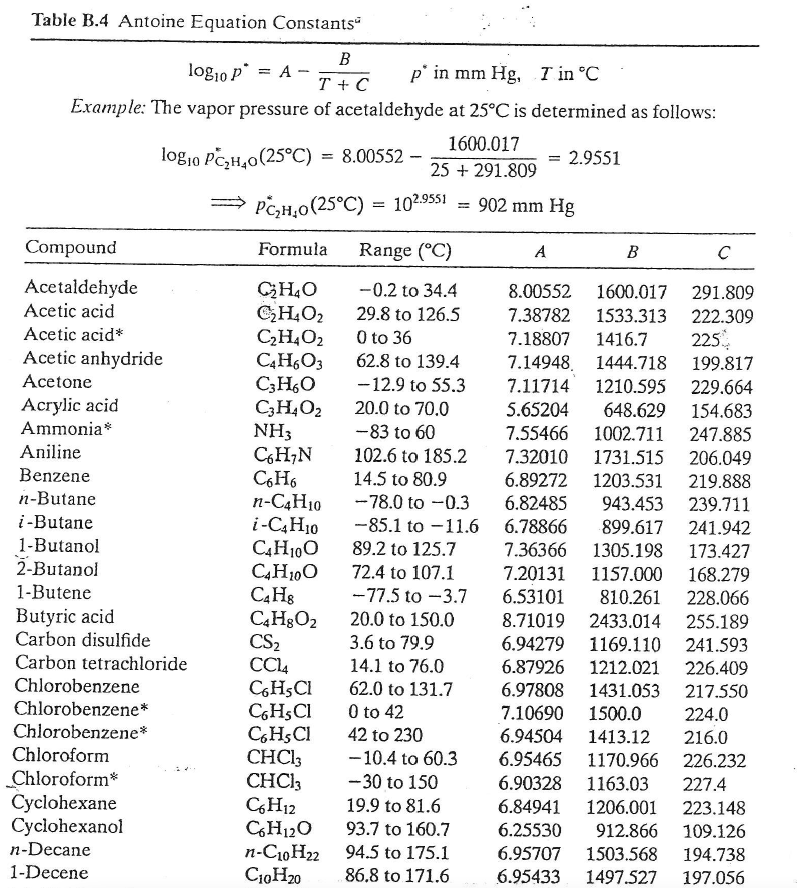
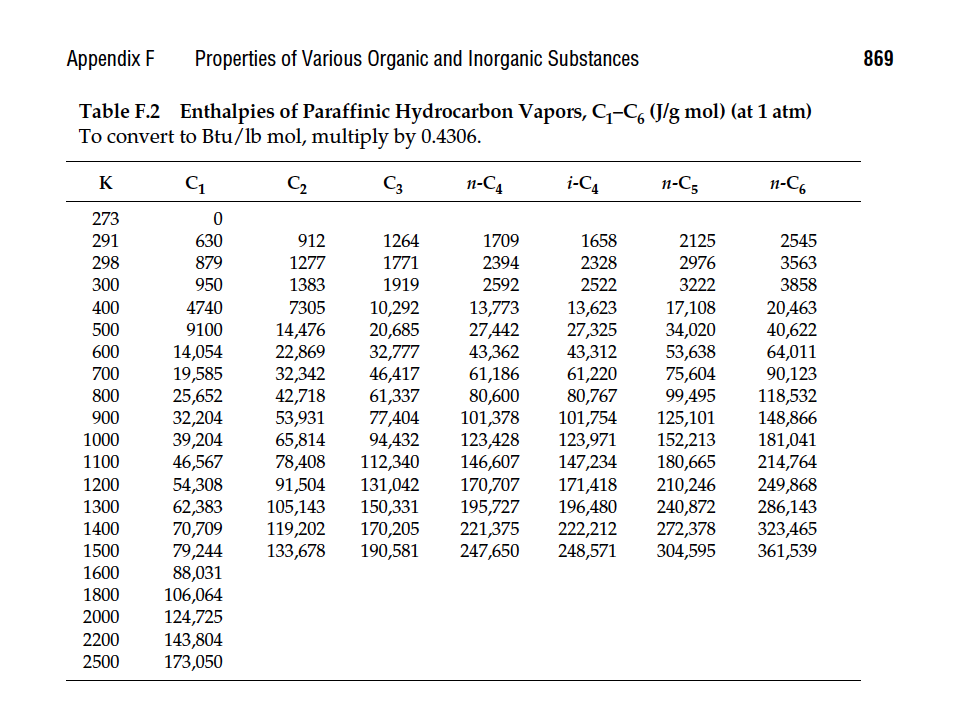
Table B.4 Antoine Equation Constantsu B logio p* = A - p' in mm Hg, I inC T +C Example: The vapor pressure of acetaldehyde at 25C is determined as follows: 1600.017 logio PC2H40(25C) = 8.00552 - = 2.9551 25 + 291.809 PCH,0(25C) = 102.9551 902 mm Hg Compound Formula Range (C) A B Acetaldehyde Acetic acid Acetic acid Acetic anhydride Acetone Acrylic acid Ammonia Aniline Benzene n-Butane i-Butane 1-Butanol 2-Butanol 1-Butene Butyric acid Carbon disulfide Carbon tetrachloride Chlorobenzene Chlorobenzene* Chlorobenzene* Chloroform Chloroform* Cyclohexane Cyclohexanol n-Decane 1-Decene CHO -0.2 to 34.4 C2H4O2 29.8 to 126.5 C2H4O2 0 to 36 C4H603 62.8 to 139.4 CzHO -12.9 to 55.3 C2H4O2 20.0 to 70.0 NH3 -83 to 60 C.HN 102.6 to 185.2 C6H6 14.5 to 80.9 n-C4H10 -78.0 to -0.3 i-C Hjo -85.1 to -11.6 C4H100 89.2 to 125.7 CH100 72.4 to 107.1 C4H8 --77.5 to -3.7 CH02 20.0 to 150.0 CS2 3.6 to 79.9 CC4 14.1 to 76.0 C.HSCI 62.0 to 131.7 CGHSCI 0 to 42 C.HSCI 42 to 230 CHCl3 -10.4 to 60.3 CHC13 --30 to 150 C6H12 19.9 to 81.6 C6H12O 93.7 to 160.7 n-C10H22 94.5 to 175.1 C10H20 86.8 to 171.6 8.00552 1600.017 291.809 7.38782 1533.313 222.309 7.18807 1416.7 225 7.14948. 1444.718 199.817 7.11714 1210.595 229.664 5.65204 648.629 154.683 7.55466 1002.711 247.885 7.32010 1731.515 206.049 6.89272 1203.531 219.888 6.82485 943.453 239.711 6.78866 899.617 241.942 7.36366 1305.198 173.427 7.20131 1157.000 168.279 6.53101 810.261 228.066 8.71019 2433.014 255.189 6.94279 1169.110 241.593 6.87926 1212.021 226.409 6.97808 1431.053 217.550 7.10690 1500.0 224.0 6.94504 1413.12 216.0 6.95465 1170.966 226.232 6.90328 1163.03 227.4 6.84941 1206.001 223.148 6.25530 912.866 109.126 6.95707 1503.568 194.738 6.95433 1497.527 197.056 Appendix F Properties of Various Organic and Inorganic Substances 869 Table F.2 Enthalpies of Paraffinic Hydrocarbon Vapors, G-C (J/g mol) (at 1 atm) To convert to Btu/lb mol, multiply by 0.4306. K G C2 n-C4 i-C4 n-C5 n-Co 2125 273 291 298 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1800 2000 2200 2500 0 630 879 950 4740 9100 14,054 19,585 25,652 32,204 39,204 5,567 54,308 62,383 70,709 79,244 88,031 106,064 124,725 143,804 173,050 912 1277 1383 7305 14,476 22,869 32,342 42,718 53,931 65,814 78,408 91,504 105,143 119,202 133,678 1264 1771 1919 10,292 20,685 32,777 46,417 61,337 77,404 94,432 112,340 131,042 150,331 170,205 190,581 1709 2394 2592 13,773 27,442 43,362 61,186 80,600 101,378 123,428 146,607 170,707 195,727 221,375 247,650 1658 2328 2522 13,623 27,325 43,312 61,220 80,767 101,754 123,971 147,234 171,418 196,480 222,212 248,571 2976 3222 17,108 34,020 53,638 75,604 99,495 125,101 152,213 180,665 210,246 240,872 272,378 304,595 2545 3563 3858 20,463 40,622 64,011 90,123 118,532 148,866 181,041 214,764 249,868 286,143 323,465 361,539
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


