Question: ------- Some example code for an XOR encryption function ------- #include #include #include int encrypt_data(FILE *); int main (void) { FILE *file_ptr; int return_code; ....add!


------- Some example code for an XOR encryption function ------- #include #include #include
int encrypt_data(FILE *); int main (void) { FILE *file_ptr; int return_code; ....add! //get file name from user, then do fopen( ...) for reading & writing ....add! return_code = encrypt_data( file_ptr ); ....add fclose(file_ptr); return 0; }
int encrypt_data(FILE *disk_file_ptr) { int i; // Used to index through file_buffer unsigned long int file_size; // Holds number of bytes in the file int key_length; // Holds length of encryption key
char *file_buffer = NULL;
char key[] = ABCDEF; //default encryption key, you can change to //something else if you //want ( e.g. key[] = 12Ygh9sss; ) key_length = strlen(key);
fseek(disk_file_ptr, 0, SEEK_END); // Move file_pointer to end of file. file_size = ftell(disk_file_ptr); // Get current file pointer location // (which will be the size of the file // in bytes)
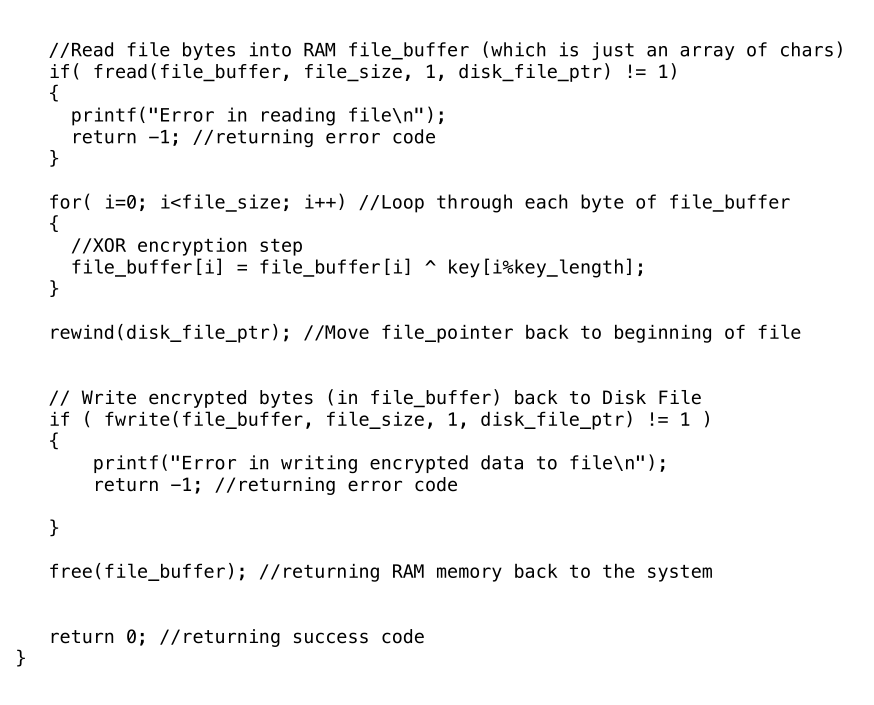
rewind(disk_file_ptr); //Move file_pointer back to beginning of file //Next step is to allocate RAM memory to hold all the bytes that are //currently stored on the HardDisk
file_buffer = malloc(file_size); //Read file bytes into RAM file_buffer (which is just an array of chars) if( fread(file_buffer, file_size, 1, disk_file_ptr) != 1) { printf("Error in reading file "); return -1; //returning error code } for( i=0; i { //XOR encryption step file_buffer[i] = file_buffer[i] ^ key[i%key_length]; } rewind(disk_file_ptr); //Move file_pointer back to beginning of file // Write encrypted bytes (in file_buffer) back to Disk File if ( fwrite(file_buffer, file_size, 1, disk_file_ptr) != 1 ) { printf("Error in writing encrypted data to file "); return -1; //returning error code } free(file_buffer); //returning RAM memory back to the system return 0; //returning success code }
r this extra credit assignment, you need to create a program that reads in a text-file (specified by the user), performs a "bit-level Exclusive-OR" on each byte of the text-file (as a method of encryption), then writes the encrypted file data back out to disk and gives the encrypted file the same name as the input file (i.e. so it overwrites the original file). XOR encryption is a symmetric encryption algorithm, which means, the encrypted file can also be decrypted with the same XOR algorithm (as long as you use the same encryption key, which you will, because the encryption key is hard-coded - a variation of this program would be to ask the user to enter the encryption key) So when testing your program (keep a backup copy of the file to be encrypted), then do the following: (1) Create a text file (make a backup copy) and encrypt it (2) Use cat or vi to view the text file to see that it's encrypted (3) Run the encryption again on the encrypted file, and then see if it's decrypted Below is the description of the (User/Application) interaction: DESCRIPTION 1. Usertypes lextra5 2. Application Asks user to enter name of file to be encrypted 3. UserEnters name of file (this file should be in the same directory as the executable file "extra5") 4. Application Encrypts each byte of the input file and writes encrypted data back to the same file, over writing the original data You will need to refer to pages 603-604(5th edition), or 678-680 (6th edition) of the textbook for information on the bit-level Exclusive-OR operator , which you will need for the encryption process. You can also search the web for "XOR encryption" to see code examples and more information
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


