Question: Specific aid in substituting the correct numbers with new information provided in attachments. d.) What is Computron's net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT)? What are
Specific aid in substituting the correct numbers with new information provided in attachments.
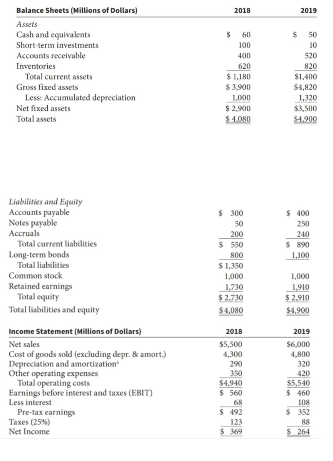
d.) What is Computron's net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT)? What are operating current assets? What are operating current liabilities? How much net operating working capital and total net operating capital does Computron have?
NOPAT = EBIT (1 - tax rate)
Current year:
NOPAT = 17,440 (1-0.4) = $10,464
Previous year:
NOPAT = $125,460
Operating currents assets are cash, inventory and receivables.
Operating current liabilities are accounts payable and accruals.
Net operating working capital = operating current assets - operating current liabilities.
Current year:
NOWC = (7,282 + 632,160 + 1,287,360) - (324,000 + 284,960) = $1,317,842
Previous year:
NOWC = $793,800
Total operating working capital = Net operating working capital + net fixed assets.
Current year:
TOWC = 1,317,842 + 939,790 = $2,257,632
Previous year:
TOWC = $1,138,600
e.) What is Computron's free cash flow? What are Computron's "net uses" of its FCF?
FCF = NOPAT - Net investment in capital
FCF = 10,464 - (2,257,632 - 1,138,600)
FCF = $1,108,568
Net uses = combine after-tax interest (AFI), net debt repayments (NDR), dividends (Div.), net stock repurchases (NSR), net purchases of short-term investments (NPSTI)
AFI = 105,600
NDR = -1,196,568
Div. = 11,000
NSR = 0
NPSTI = -28,600
Total uses of FCF = - $1,108,568
f.) Calculate Computron's return on invested capital (ROIC). Computron has a 10% cost of capital (WACC). What caused the decline in the ROIC? Was it due to operating profitability or capital utilization? Do you think Computron's growth added value?
ROIC = NOPAT / Total Net Operating Capital
Current year:
ROIC = 10,464 / 2,257,632 = 0.5%
Previous year:
ROIC = 11.0%
Operating Profit = NOPAT / Sales
Current year:
OP = 10,464 / 5,834,400 = 0.18%
Previous year:
OP = 2.15%
Capital Requirement = Total net operating capital / Sales
Current year:
CR = 2,257,632 / 5,834,400 = 38.7%
Previous year:
CR = 19.5%
For ROIC there was a decline from 0.5% to 11%. This decrease was due to both, the operating profit and the capital requirement/utilization (ratios are in results above). The ROIC is less than a 10% cost of capital, which means high growth occurred. Gathering from the chapter, growth occurring usually means a negative effect on free cash flow, however when the ROIC is less than the 10% cost of capital this is not the case.

2013 2019 $ 60 100 400 Balance Sheets (Millions of dollars Assets Cash and equivalents Short term investments Accounts receivable Inventores Tocal current assets Gross the assets Les Accumulated depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets SLISO $ 3.900 1.000 $ 2.900 $ 4 000 $1,400 SERO 1.320 SK SOO 54.900 $ 300 $ 100 240 $ 550 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Notes payable Accruals Total current liabilities Long-term bonds Total liabilities Common stock Retained earnings Total equity Total liabilities and equity $ 890 1,100 $ 1.350 1.000 1,730 $2.730 1910 $2.910 54,900 SCONO 2018 $5.500 2019 6.000 00 10 Income Statement Millions of Dollars) Net sales Cost of woods sold excluding depr. & amort) Depreciation and amortization Other operating expenses Total operating costs Earnings before interest and tas (EBIT Les mest Pretax carming Taxes 02 ) Net Income 54.9 40 $ 560 2019 2018 $50.00 $30.00 Other Data Stock price Shares outstanding (millions) Common dividends (millions) Tax rate Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) 25% 10.00% 10.00% 2019 $ 264 320 Statement of Cash Flows (Millions of dollars) Operating Activities Net income before preferred dividends Nonadh Adjustments Depreciation and amortization Due to Changes Working Capital Change in accounts receivable Change in inventories Change in accounts payable Change in accruals Net cash provided by operating activities (120) (2009 $ 404 $1920) Investing Activities Cash used to acquire fixed assets Change in short-term investments Net cash provided by investing activities S(.30) $ 200 Financing Activities Change in notes payable Change in long-term debt Payment of cash dividends Net cash provided by financing activities 300 $ 416 S (10) Net change in cash and equivalents Cash and securities at beginning of the year Cash and securities at end of the year $ 50 Assume that you are Cochran's assistant and that you must help her answer the fol lowing questions: A. What effect did the expansion have on sales and net income? What effect did the expansion have on the asset side of the balance sheet? What effect did it have on liabilities and equity? b. What do you conclude from the statement of cash flows? c. What is free cash flow? Why is it important? What are FCF's five uses? d. What is Computron's net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT)? What are operat- ing current assets? What are operating current liabilities? How much net operating working capital and total net operating capital does Computron have? e. What is Computron's free cash flow What are Computron's "net uses" of its FCF? f. Calculate Computron's return on invested capital (ROIC). Computron has a 10% cost of capital (WACC). What caused the decline in the ROIC? Was it due to operating profitability or capital utilization? Do you think Computron's growth ackled value? g Cochran also has asked you to estimate Computron's Economic Value Added (EVA) She estimates that the after tax cost of capital was 10% in both years. h. What happened to Computron's Market Value Added (MVA)? i. The Tax Cut and Jobs Act (TCIA) was signed into law in 2017. Briefly describe its key provisions for corporate taxes Assume that a corporation has $87 million of taxable income from operations. It also received interest income of $8 million and dividend income of $10 million. The federal tax rate is 21%, and the dividend exclusion rate is 50%. What is its taxable income and federal tax liability? k. Briefly describe the TCIA'S key provisions for personal taxes. I Assume that you are in the 25% marginal tax bracket and that you have $20,000 to invest. You have narrowed your investment choices down to municipal bonds vield ing 7% or equally risky corporate bonds with a yield of 10%. Which one should you choose and why? At what marginal tax rate would you be indifferent? 2013 2019 $ 60 100 400 Balance Sheets (Millions of dollars Assets Cash and equivalents Short term investments Accounts receivable Inventores Tocal current assets Gross the assets Les Accumulated depreciation Net fixed assets Total assets SLISO $ 3.900 1.000 $ 2.900 $ 4 000 $1,400 SERO 1.320 SK SOO 54.900 $ 300 $ 100 240 $ 550 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Notes payable Accruals Total current liabilities Long-term bonds Total liabilities Common stock Retained earnings Total equity Total liabilities and equity $ 890 1,100 $ 1.350 1.000 1,730 $2.730 1910 $2.910 54,900 SCONO 2018 $5.500 2019 6.000 00 10 Income Statement Millions of Dollars) Net sales Cost of woods sold excluding depr. & amort) Depreciation and amortization Other operating expenses Total operating costs Earnings before interest and tas (EBIT Les mest Pretax carming Taxes 02 ) Net Income 54.9 40 $ 560 2019 2018 $50.00 $30.00 Other Data Stock price Shares outstanding (millions) Common dividends (millions) Tax rate Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) 25% 10.00% 10.00% 2019 $ 264 320 Statement of Cash Flows (Millions of dollars) Operating Activities Net income before preferred dividends Nonadh Adjustments Depreciation and amortization Due to Changes Working Capital Change in accounts receivable Change in inventories Change in accounts payable Change in accruals Net cash provided by operating activities (120) (2009 $ 404 $1920) Investing Activities Cash used to acquire fixed assets Change in short-term investments Net cash provided by investing activities S(.30) $ 200 Financing Activities Change in notes payable Change in long-term debt Payment of cash dividends Net cash provided by financing activities 300 $ 416 S (10) Net change in cash and equivalents Cash and securities at beginning of the year Cash and securities at end of the year $ 50 Assume that you are Cochran's assistant and that you must help her answer the fol lowing questions: A. What effect did the expansion have on sales and net income? What effect did the expansion have on the asset side of the balance sheet? What effect did it have on liabilities and equity? b. What do you conclude from the statement of cash flows? c. What is free cash flow? Why is it important? What are FCF's five uses? d. What is Computron's net operating profit after taxes (NOPAT)? What are operat- ing current assets? What are operating current liabilities? How much net operating working capital and total net operating capital does Computron have? e. What is Computron's free cash flow What are Computron's "net uses" of its FCF? f. Calculate Computron's return on invested capital (ROIC). Computron has a 10% cost of capital (WACC). What caused the decline in the ROIC? Was it due to operating profitability or capital utilization? Do you think Computron's growth ackled value? g Cochran also has asked you to estimate Computron's Economic Value Added (EVA) She estimates that the after tax cost of capital was 10% in both years. h. What happened to Computron's Market Value Added (MVA)? i. The Tax Cut and Jobs Act (TCIA) was signed into law in 2017. Briefly describe its key provisions for corporate taxes Assume that a corporation has $87 million of taxable income from operations. It also received interest income of $8 million and dividend income of $10 million. The federal tax rate is 21%, and the dividend exclusion rate is 50%. What is its taxable income and federal tax liability? k. Briefly describe the TCIA'S key provisions for personal taxes. I Assume that you are in the 25% marginal tax bracket and that you have $20,000 to invest. You have narrowed your investment choices down to municipal bonds vield ing 7% or equally risky corporate bonds with a yield of 10%. Which one should you choose and why? At what marginal tax rate would you be indifferent
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


