Question: Stack canaries and non - executable stacks make stack exploitation difficult. Such techniques, however, do not protect against return - oriented programming where only the
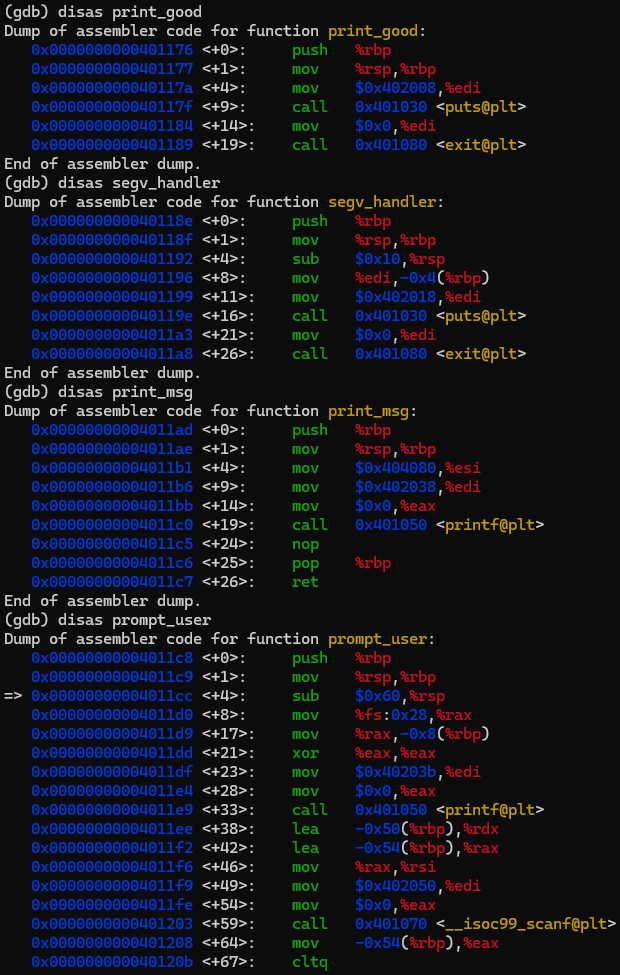
Stack canaries and nonexecutable stacks make stack exploitation difficult. Such techniques, however, do not protect against returnoriented programming where only the return addresses on the stack are targeted. In this level, you control a single write into a vulnerable buffer in the function promptuser. Overflow the buffer to modify the return address beyond the stack canary so that it points to a function of your choice. The level will prompt you with an offset in decimal from the beginning of the buffer that will be written into followed by a hexadecimal value that will be written there eg scanfd x; The program will then write the hexadecimal value to a location computed using the offset. To determine how close you are, examine the pointer being used to write into the stack and how far away it is from the value of $rsp when the retq instruction at the end of promptuser is reached.
The c file:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define USERDEF
char msg
"Stack canaries and nonexecutable stacks make stack exploitation difficult. Such
"techniques, however, do not protect against returnoriented programming where
"only the return addresses on the stack are targeted. In this level, you control
"a single write into a vulnerable buffer in the function promptuser. Overflow
"the buffer to modify the return address beyond the stack canary so that it
"points to a function of your choice. The level will prompt you with an offset
in decimal from the beginning of the buffer that will be written into followed
by a hexadecimal value that will be written there eg scanfd x;
"The program will then write the hexadecimal value to a location computed
"using the offset. To determine how close you are, examine the pointer
"being used to write into the stack and how far away it is from the value
of $rsp when the retq instruction at the end of promptuser is reached.
;
void printgood
printfGood Job.
;
exit;
void segvhandlerint sig
printfSegmentation fault. Try again.
;
exit;
void printmsg
printfsmsg;
void promptuser
char buffer;
int offset;
char useraddr;
char overaddr;
printfEnter the password: ;
scanfd lx &offset, unsigned long &useraddr;
overaddr char buffer offset;
overaddr useraddr;
int mainint argc, char argv
signalSIGSEGV segvhandler;
printmsg;
promptuser;
printfTry again.
;
return ;
I've tried x and x and x and x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


