Question: Start with the default settings. For each trial, you are given the mass of the star and the distance of the satellite. 1. Calculate
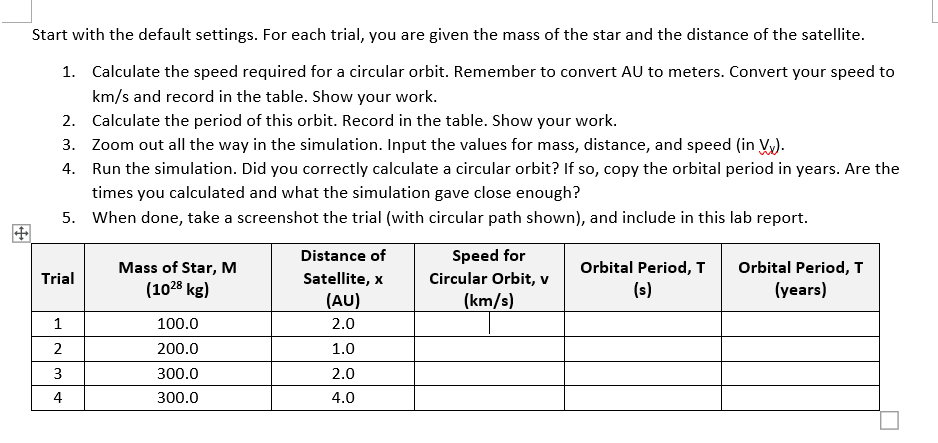
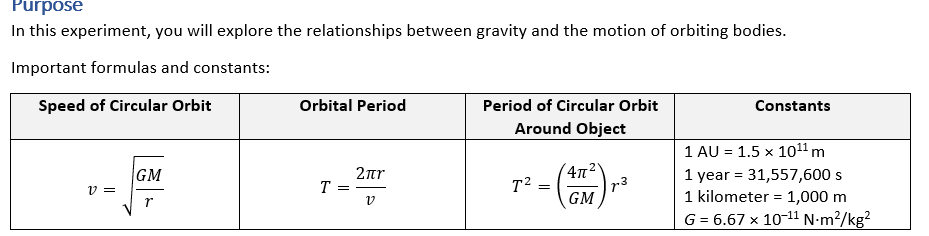
Start with the default settings. For each trial, you are given the mass of the star and the distance of the satellite. 1. Calculate the speed required for a circular orbit. Remember to convert AU to meters. Convert your speed to km/s and record in the table. Show your work. 2. Calculate the period of this orbit. Record in the table. Show your work. 3. Zoom out all the way in the simulation. Input the values for mass, distance, and speed (in V). 4. Run the simulation. Did you correctly calculate a circular orbit? If so, copy the orbital period in years. Are the times you calculated and what the simulation gave close enough? 5. When done, take a screenshot the trial (with circular path shown), and include in this lab report. Mass of Star, M Trial Distance of Satellite, x Speed for Circular Orbit, v (1028 kg) Orbital Period, T (s) Orbital Period, T (years) (AU) (km/s) 1 100.0 2.0 2 200.0 1.0 3 300.0 2.0 4 300.0 4.0 Purpose In this experiment, you will explore the relationships between gravity and the motion of orbiting bodies. Important formulas and constants: Speed of Circular Orbit Orbital Period Period of Circular Orbit Around Object 2r T = T r v GM = 42 73 Constants 1 AU = 1.5 x 10 m = 1 year 31,557,600 s 1 kilometer 1,000 m = G = 6.67 10-11 N-m/kg v = GM
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


