Question: Step 1: Using the Apportion Method, create a budget (Fig 5.1) to send to Ava. Total Budget = $85,000 Initial Design Work = 10% Ventilation
 Step 1: Using the Apportion Method, create a budget (Fig 5.1) to send to Ava.
Step 1: Using the Apportion Method, create a budget (Fig 5.1) to send to Ava.
Total Budget = $85,000
- Initial Design Work = 10%
- Ventilation System = 35% (Parts = 20%; Labor = 15%)
- New Racks = 20% (Parts = 15%; Labor = 5%)
- Power Supplies and Cables = 25% (Parts = 15%; Labor = 10%)
- Switchover Ops Checks = 10%
Step 2: Given the budget and schedule details, create a Time Phased Budget (like the one in Fig 8.16). Assume the cost of parts is paid in the first unit of time, and the labor is equally spread out over the units of time.
Total Budget = $85,000
- Initial design Work = 10%
- Ventilation System = 35% (Parts = 20%; labor = 15%)
- New Racks = 20% (Parts = 15%; labor = 5%)
- Power Supplies and Cables = 25% (Parts = 15%; labor = 10%)
- Switchover Ops Checks = 10%
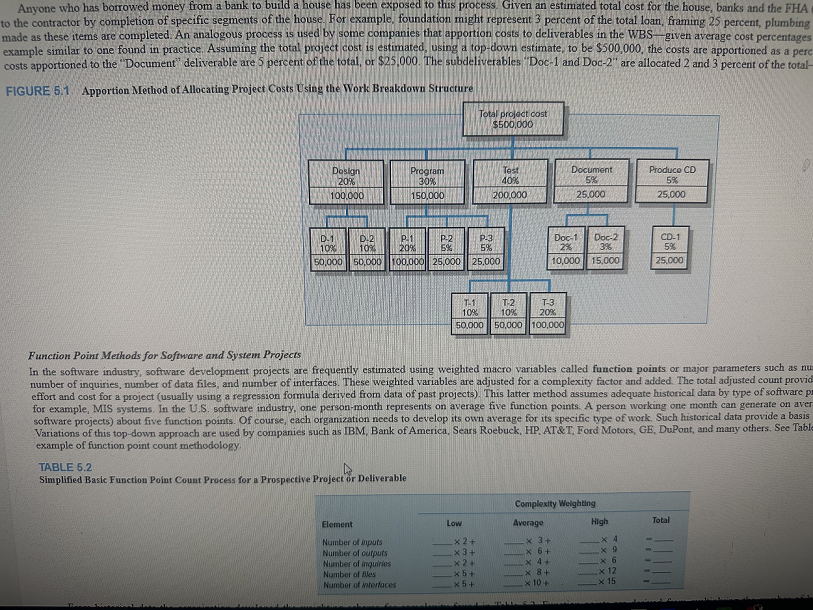
Anyone who has borrowed money from a bank to build a house has been exposed to this process. Given an estimated total cost for the house, banks and the FHA to the contractor by completion of specific segments of the house. For example, foundation might represent 3 percent of the total loan, framing 25 percent, plumbing made as these items are completed. An analogous process is used by some companies that apportion costs to deliverables in the WBS-given average cost percentages example similar to one found in practice. Assuming the total project cost is estimated, using a top-down estimate, to be $500,000, the costs are apportioned as a pere costs apportioned to the "Document" deliverable are 5 percent of the total, or $25,000. The subdeliverables "Doc-1 and Doc-2" are allocated 2 and 3 percent of the totalFIGURE 5.1 Apportion Method of Allocating Project Costs Using the Work Breakdown Structure Function Point Methods for Software and System Projects In the software industry, software development projects are frequently estimated using weighted macro variables called function points or major parameters such as nu number of inquiries, number of data files, and number of interfaces. These weighted variables are adjusted for a complexity factor and added. The total adjusted count provid effort and cost for a project (usually using a regression formula derived from data of past projects). This latter method assumes adequate historical data by type of software p. for example, MIS systems. In the U.S. software industry, one person-month represents on average five function points. A person working one month can generate on aver software projects) about five function points. Of course, each organization needs to develop its own average for its specific type of work. Such historical data provide a basis Variations of this top-down approach are used by companies such as IBM, Bank of America, Sears Roebuck, HP. AT\&T. Ford Motors, GE, DuPont, and many others. See Tabl example of function point count methodology. TABLE 5.2 Simplified Basic Function Point Count Process for a Prospective Project or Deliverable Anyone who has borrowed money from a bank to build a house has been exposed to this process. Given an estimated total cost for the house, banks and the FHA to the contractor by completion of specific segments of the house. For example, foundation might represent 3 percent of the total loan, framing 25 percent, plumbing made as these items are completed. An analogous process is used by some companies that apportion costs to deliverables in the WBS-given average cost percentages example similar to one found in practice. Assuming the total project cost is estimated, using a top-down estimate, to be $500,000, the costs are apportioned as a pere costs apportioned to the "Document" deliverable are 5 percent of the total, or $25,000. The subdeliverables "Doc-1 and Doc-2" are allocated 2 and 3 percent of the totalFIGURE 5.1 Apportion Method of Allocating Project Costs Using the Work Breakdown Structure Function Point Methods for Software and System Projects In the software industry, software development projects are frequently estimated using weighted macro variables called function points or major parameters such as nu number of inquiries, number of data files, and number of interfaces. These weighted variables are adjusted for a complexity factor and added. The total adjusted count provid effort and cost for a project (usually using a regression formula derived from data of past projects). This latter method assumes adequate historical data by type of software p. for example, MIS systems. In the U.S. software industry, one person-month represents on average five function points. A person working one month can generate on aver software projects) about five function points. Of course, each organization needs to develop its own average for its specific type of work. Such historical data provide a basis Variations of this top-down approach are used by companies such as IBM, Bank of America, Sears Roebuck, HP. AT\&T. Ford Motors, GE, DuPont, and many others. See Tabl example of function point count methodology. TABLE 5.2 Simplified Basic Function Point Count Process for a Prospective Project or Deliverable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


