Question: Students: This content is controlled by your instructor, and is not zyBooks content. Direct questions or concerns about this content to your instructor. If you

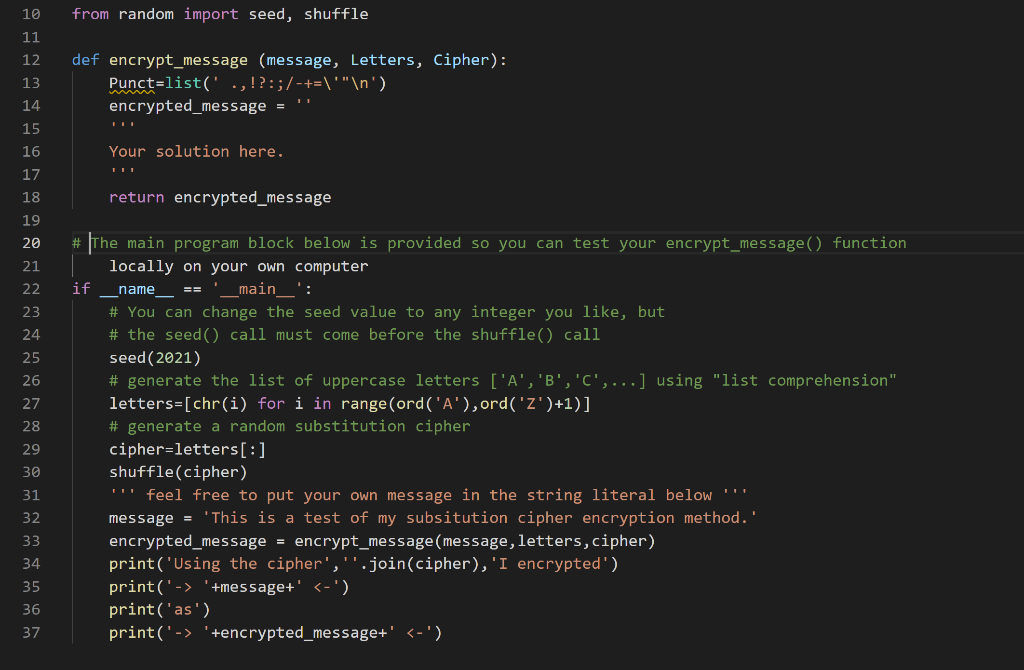
Students: This content is controlled by your instructor, and is not zyBooks content. Direct questions or concerns about this content to your instructor. If you have any technical issues with the zyLab submission system, use the Trouble with lab button at the bottom of the lab. 5.43 Programming Project 1: Substitution Cipher A substitution cipher is a way to encrypt a message by substituting each letter in the message with another. For example, here is a message encrypted using a certain substitution cipher: JES'B LDHN D WEI, VDS!" (Punctuation and spaces are not encrypted.) A random substitution cipher can obtained by shuffling the alphabet. The cipher used to generate the encrypted message above is ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ DZWUNGFLAXOTVSEKCPOBYHIRUM (original characters) (the cipher) For example, an A in the original message is replaced with a D in the encrypted message, B with Z, and so on. (Thus we know that the original unencrypted message has three A's and no B's.) Image credit: Stealth Copter Download the program template provided below, my_cipher.py. You will see that it partially defines a function encrypt_message() that should return the encrypted version of its argument message within a new string named encrypted_message. The argument Letters is a list of all 26 uppercase letters in alphabetical order, and the argument Cipher is a randomly shuffled list of all 26 uppercase letters. (These are generated for you in the __main__ block given.) These two are parallel lists: Cipher[i] is the encrypted form of Letters[i]. You are to complete the definition of encrypt_message(). Nothing given in template should be deleted (except the commented lines). Before encrypting, convert all letters in message to upper case. The local variable Punct (as you can see) is a list of common punctuation characters, which are not to be substituted, but must remain in the encrypted message in the same positions they appear in the original message. Your function encrypt_message ( ) will be tested against random messages using random substitution ciphers. A __main__ code block is provided to (1) generate Letters and Cipher for you, and (2) allow you to run my_cipher.py locally on your own computer to test your implementation of encrypt_message(). It does not matter what is in the __main__block for grading purposes; you are only being graded on what you put in your encrypt_message () function definition. 289182.1728126 10 from random import seed, shuffle 11 12 def encrypt_message (message, Letters, Cipher): Punct=list(' .,!?:;/-+=\"" ') encrypted_message = 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Your solution here. return encrypted_message # 20 21 name 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 # The main program block below is provided so you can test your encrypt_message() function locally on your own computer if _main__': # You can change the seed value to any integer you like, but # the seed() call must come before the shuffle() call seed(2021) # generate the list of uppercase letters ['A', 'B','c',...] using "list comprehension" letters=[chr(i) for i in range (ord('A'),ord('Z')+1)] # generate a random substitution cipher cipher-letters[:] shuffle(cipher) feel free to put your own message in the string literal below "T! message = 'This is a test of my subsitution cipher encryption method.' encrypted_message = encrypt_message (message, letters, cipher) print('Using the cipher',"'.join(cipher), 'I encrypted') print('-> '+message+' '+encrypted_message+'
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


