Question: Subject. Data structure Use java I have the question & answer. But I am not sure which p e is the beet. Please help me
Subject. Data structure
Use java
I have the question & answer. But I am not sure which p e is the beet.
Please help me to find the correct answer please.
if any addition need please do it and send me a correct answer.
If you know data structure then only answer please.
Promise to give you thumbs up.
Question: 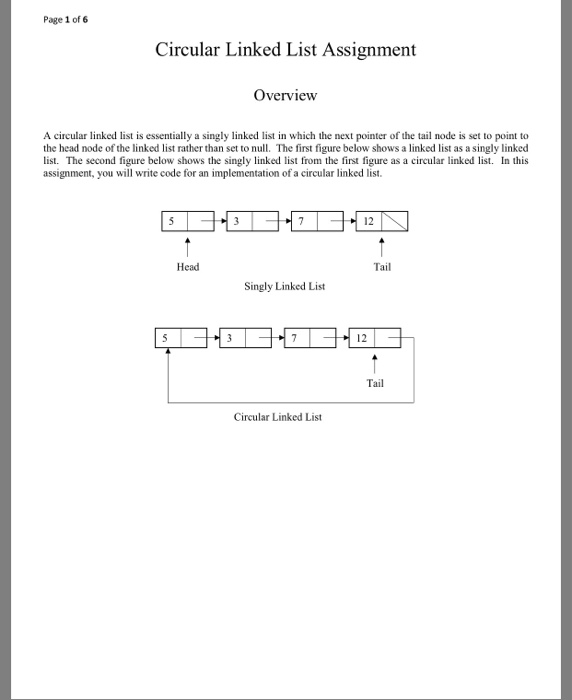





Here. The list. Java is.

& circular link list is.


I got few answer. By reviewing all please send me a new code with java. Please.
1)
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ConcurrentModificationException;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class CircularLinkedList implements List
{
private static class Node
{
private AnyType data;
private Node next;
public Node(AnyType d, Node n)
{
setData(d);
setNext(n);
}
public AnyType getData() { return data; }
public void setData(AnyType d) { data = d; }
public Node getNext() { return next; }
public void setNext(Node n) { next = n; }
}
private int theSize;
private int modCount;
private Node tail;
public CircularLinkedList()
{
}
public void clear()
{
(List)this.clear();
}
public int size()
{
return (List)this.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if((list)this.isEmpty())
return true;
else
return false;
}
public AnyType get(int index)
{
return (List)this.get(index).getData();
}
public AnyType set(int index, AnyType newValue)
{
AnyType tempData = (List)this.get(index).getData();
(List)this.get(index).setData();
return tempData;
}
public boolean add(AnyType newValue)
{
add(size(), newValue);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, AnyType newValue)
{
List tempList = (List)this;
Node current = temp.get(index-1);
Node sNode = new Node(newValue, current.getNext());
current.setNext(sNode);
int pos = tempList.size()-1;
list.add(tempList.get(pos));
while(pos!=index){
tempList.set(pos,tempList.get(pos-1));
}
}
public AnyType remove(int index)
{
List tempList = (List)this;
Node current = temp.get(index);
tempList.remove(index);
return current;
}
public void rotate()
{
List tempList = (List)this;
Node tempFirst = tempList.get(0);
Node tempLast = tempList.get(tempList.size()-1);
tempFirst.setNext(tempLast);
tempFirst.setData(tempLast.getData());
tempLast.setNext(tempList.get(0).getNext);
tempLast.setData(tempList.get(0).getData());
tempList.set(0,tempLast);
tempList.set(tempList.size()-1,tempFirst);
tail = tempFirst;
}
public Iterator iterator()
{
return new LinkedListIterator();
}
private Node getNode(int index)
{
return (getNode(index, 0, size()-1));
}
private Node getNode(int index, int lower, int upper)
{
return (List)this.get(index);
}
private class LinkedListIterator implements Iterator
{
private Node previous;
private Node current;
private int expectedModCount;
private boolean okToRemove;
LinkedListIterator()
{
current = tail.getnext();
}
public boolean hasNext()
{
if(current.getnext()==null)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public AnyType next()
{
return current.next();
}
public void remove()
{
current = null;
}
}
}
2))
#include
using namespace std;
class CircularLinkedList
{
class node
{
int data;
node *next;
};
int theSize;
node *tail = NULL;
int modCount;
node* create(int val)
{
node *newnode;
newnode = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
public:
void clear()
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
node *ptr=tail;
node *temp;
while(ptr->next!=tail)
{
temp=ptr;
ptr=ptr->next;
free(temp);
}
free(ptr);
tail=NULL;
return;
}
}
int size()
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
node *ptr=tail;
int count=1;//1st ptr
while(ptr->next!=tail)
{
ptr=ptr->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
bool isEmpty()
{
if(tail==NULL)
{
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
node *getNode(int index)
{
int i=1;
node *ptr=tail->next;
while(i!=index)
{
ptr=ptr->next;
i++;
}
return ptr;
}
int get(int index)
{
node *ptr=getNode(index);
return ptr->data;
}
int set(int index,int newValue)
{
node *ptr=getNode(index);
int oldValue=ptr->data;
ptr->data=newValue;
return oldValue;
}
node *getPrevPtr(int index)
{
int i=1;
node *ptr=tail->next;
node *temp=tail;
while(i!=index)
{
temp=ptr;
ptr=ptr->next;
i++;
}
return temp;
}
void add(int index,int newValue)
{
node *prev=getPrevPtr(index);
node *ptr=create(newValue);
node *temp=prev->next;
prev->next=ptr;
ptr->next=temp;
}
int remove(int index)
{
node *prev=getPrevPtr(index);
node *temp=prev->next->next;
int data=prev->next->data;
free(prev->next);
return data;
}
void rotate()
{
tail=tail->next;
}
}ll;
3)
#include
#include
#include
/* structure containing a data part and link part */
struct node
{
int data ;
struct node * link ;
} ;
void addcirq ( struct node **, struct node **, int ) ;
int delcirq ( struct node **, struct node ** ) ;
void cirq_display ( struct node * ) ;
void main( )
{
struct node *front, *rear ;
front = rear = NULL ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 10 ) ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 17 ) ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 18 ) ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 5 ) ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 30 ) ;
addcirq ( &front, &rear, 15 ) ;
clrscr( ) ;
printf ( "Before deletion: " ) ;
cirq_display ( front ) ;
delcirq ( &front, &rear ) ;
delcirq ( &front, &rear ) ;
delcirq ( &front, &rear ) ;
printf ( " After deletion: " ) ;
cirq_display ( front ) ;
}
/* adds a new element at the end of queue */
void addcirq ( struct node **f, struct node **r, int item )
{
struct node *q ;
/* create new node */
q = malloc ( sizeof ( struct node ) ) ;
q -> data = item ;
/* if the queue is empty */
if ( *f == NULL )
*f = q ;
else
( *r ) -> link = q ;
*r = q ;
( *r ) -> link = *f ;
}
/* removes an element from front of queue */
int delcirq ( struct node **f, struct node **r )
{
struct node *q ;
int item ;
/* if queue is empty */
if ( *f == NULL )
printf ( "queue is empty" ) ;
else
{
if ( *f == *r )
{
item = ( *f ) -> data ;
free ( *f ) ;
*f = NULL ;
*r = NULL ;
}
else
{
/* delete the node */
q = *f ;
item = q -> data ;
*f = ( *f ) -> link ;
( *r ) -> link = *f ;
free ( q ) ;
}
return ( item ) ;
}
return NULL ;
}
/* displays whole of the queue */
void cirq_display ( struct node *f )
{
struct node *q = f, *p = NULL ;
/* traverse the entire linked list */
while ( q != p )
{
printf ( "%d\t", q -> data ) ;
q = q -> link ;
p = f ;
}
}
4)
public class LinkedList {
private class Node {
int data;
Node next;
/ext will point to next node
/ode consist of data and the value of next node
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
/ode consist of two parts that is head and tail
//head part is the starting of the node
//tail is the end part of the linked list
private int size;
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public LinkedList() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.size = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
//if list is empty then head and tail part will be the same
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size() == 0;
}
//adding in the head part of the list and then make the previous head to next
public void addFirst(int item) {
Node node = new Node(item, this.head);
this.head = node;
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.tail = node;
}
this.size++;
}
//adding in the last part of the list and then take the previous tail node and point it to the new tail part
public void addLast(int item) {
Node node = new Node(item, null);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this.size++;
}
//this will get the node
private Node getNode(int index) throws Exception {
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
Node temp = this.head;
int counter = 0;
while (counter
temp = temp.next;
counter++;
}
return temp;
}
//calling the function get node where user want to add the node and then after calling that node add the node
public void addAt(int index, int item) throws Exception {
if (index this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
if (index == 0) {
this.addFirst(item);
} else if (index == this.size()) {
this.addLast(item);
} else {
Node temp = getNode(index - 1);
Node node = new Node(item, temp.next);
temp.next = node;
this.size++;
}
}
//getting the first node of the list
public int getFirst() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
return this.head.data;
}
//getting the last node of the list
public int getLast() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
return this.tail.data;
}
public int getAt(int index) throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
Node temp = this.getNode(index);
return temp.data;
}
public int removeFirst() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node rv = this.head;
if (this.size() == 1) {
this.tail = null;
this.head = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
public int removeLast() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node rv = this.tail;
if (this.size() == 1) {
this.tail = null;
this.head = null;
} else {
Node temp = this.getNode(this.size() - 2);
temp.next = null;
this.tail = temp;
}
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
//removing the element from where the user wants to remove
public int removeAt(int index) throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
if (index == 0) {
return this.removeFirst();
} else if (index == this.size() - 1) {
return this.removeLast();
} else {
Node rv = this.getNode(index);
Node temp = this.getNode(index - 1);
temp.next = temp.next.next;
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
}
//triverse the list from first node to last and display the data and stops when list becomes empty
public void display() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node temp = this.head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "=>");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("END");
System.out.println("*************************************");
}
5)
public class LinkedList {
private class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
private int size;
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public LinkedList() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.size = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size() == 0;
}
public void addFirst(int item) {
Node node = new Node(item, this.head);
this.head = node;
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.tail = node;
}
this.size++;
}
public void addLast(int item) {
Node node = new Node(item, null);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this.size++;
}
private Node getNode(int index) throws Exception {
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
Node temp = this.head;
int counter = 0;
while (counter
temp = temp.next;
counter++;
}
return temp;
}
public void addAt(int index, int item) throws Exception {
if (index this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
if (index == 0) {
this.addFirst(item);
} else if (index == this.size()) {
this.addLast(item);
} else {
Node temp = getNode(index - 1);
Node node = new Node(item, temp.next);
temp.next = node;
this.size++;
}
}
public int getFirst() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
return this.head.data;
}
public int getLast() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
return this.tail.data;
}
public int getAt(int index) throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is Empty");
}
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
Node temp = this.getNode(index);
return temp.data;
}
public int removeFirst() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node rv = this.head;
if (this.size() == 1) {
this.tail = null;
this.head = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
public int removeLast() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node rv = this.tail;
if (this.size() == 1) {
this.tail = null;
this.head = null;
} else {
Node temp = this.getNode(this.size() - 2);
temp.next = null;
this.tail = temp;
}
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
public int removeAt(int index) throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
if (index = this.size()) {
throw new Exception("Index out of Range");
}
if (index == 0) {
return this.removeFirst();
} else if (index == this.size() - 1) {
return this.removeLast();
} else {
Node rv = this.getNode(index);
Node temp = this.getNode(index - 1);
temp.next = temp.next.next;
this.size--;
return rv.data;
}
}
public void display() throws Exception {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Exception("List is empty");
}
Node temp = this.head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + "=>");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println("END");
System.out.println("*************************************");
}
public void reverseDI() throws Exception {
int si = 0, li = this.size - 1;
while (si
Node left = this.getNode(si);
Node right = this.getNode(li);
int temp = left.data;
left.data = right.data;
right.data = temp;
si++;
li--;
}
}
public void reversePI() {
Node prev = this.head;
Node curr = prev.next;
while (curr != null) {
Node tempPrev = prev;
Node tempCurr = curr;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
tempCurr.next = tempPrev;
}
Node temp = this.head;
this.head = this.tail;
this.tail = temp;
this.tail.next = null;
}
public void reversePR() {
reverse(this.head);
Node temp = this.head;
this.head = this.tail;
this.tail = temp;
this.tail.next = null;
}
private void reverse(Node node) {
if (node == this.tail) {
return;
}
reverse(node.next);
node.next.next = node;
}
}
6)*************************************
public class CircularList {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private Node current;
private int size; // total items in the list
public CircularList getCurrent;
public CircularList() {
first = null;
last = null;
current = null;
size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public void step() {
current = current.next;
}
public Node getCurrent() {
return current;
}
public boolean get(int x) {
Node search = first;
int y = 0;
while (search.iData != x && y
search = search.next;
y++;
}
}
public boolean set(int x, E element ) {
Entry e = entry(index);
E oldVal = e.element;
e.element = element;
return oldVal;
}
public void add(int x) {
Node newNode = new Node(x);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = newNode;
current = first;
} else {
current.next = newNode;
}
newNode.next = first;
last = newNode;
step();
size++;
}
public void remove(int x) {
Node prev = first;
Node curr = first.next;
while (curr.iData != x) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
if (size == 1) {
first = null;
size--;
} else if (curr == first) {
prev.next = curr.next;
first = curr.next;
size--;
} else {
prev.next = curr.next;
size--;
}
}
public void displayList() {
int x = 0;
Node printer = first;
while (x
printer.displayNode();
printer = printer.next;
x++;
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
java code for iterator class
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Itr extends CircularLinkedList implements Iterator
{
/** the size of the list */
private int size = 0;
/** for the hasNext() method for Iterator */
private int nextNode = 0;
/** two Nodes used for next() method for Iterator */
private Node lastReturned = null;
private Node nextUp;
/** part of the Iterator implementation */
public boolean hasNext()
{
return nextNode
}
/** part of the Iterator implementation */
public E next()
{
lastReturned = nextUp;
nextUp = nextUp.getNext();
nextNode++;
return lastReturned.data;
}
/** part of the Iterator implementation */
public void remove()
{
Node lastNext = lastReturned.getNext();
if (lastReturned == null)
nextUp = lastNext;
else
nextNode--;
lastReturned = null;
}
}
7)************************************
8) ********************************************************
I spotted a discrepancy in your insert method. Posting the same, but with correct insert method.
---------------------------------------------------
/* adds a new element at the end of queue */
void addcirq ( struct node **f, struct node **r, int item )
{
struct node *q ;
/* create new node */
q = malloc ( sizeof ( struct node ) ) ;
q -> data = item ;
/* if the queue is empty */
if ( *f == NULL )
*f = q ;
else
( *q ) -> link = *f ; //Changed -- See correction
*f = q ; //Changed -- See correction
( *r ) -> link = *f ;
}
9)***********************************************************
I'm assuming that your delete method is incorrect. Since the ask is in Java, allow me to post a snippet of the code. You may only concentrate on the delete method. You should ideally add an last.next = firstbefore you return the temporary (temp) node. Your add and display methods are correct.
Here, I'm writing three classes to simplify the understanding -
1. Node class (Object of this class has the data and the next node)
2. CircularList class
3. Driver class which acts as the driver for running the code and contains the main() method
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class Node {
public long data;
public Node next;
public Node(long val) {
data = val;
next = null;
}
public void displayNode() {
System.out.print(data + " ");
}
}
/* ---------end of class Node--------- */
public class CircularList {
Node first;
Node last;
public CircularList() {
first = null;
last = null;
}
public Node find(long key) {
Node current = first;
while(current.data != key) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
public Node delete() {
if(first.next == null)
last = null;
Node temp = first;
first = first.next;
if(last != null)
last.next = first; //This is where you should look to correct your delcirq() method
return temp;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { return (first == null); }
public void insert(long val) {
Node newNode = new Node(val);
if(isEmpty())
last = newNode;
newNode.next = first;
first = newNode;
last.next = first;
}
public void displayData(int n) {
Node current = first;
while(n>0) {
current.displayNode();
current = current.next;
n--;
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
/* ------- end of class CircularList ------- */
public class Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularList cl = new CircularList();
cl.insert(5);
cl.insert(6);
cl.insert(7);
cl.insert(8);
cl.displayData(6);
cl.delete();
cl.displayData(6);
}
}
10)*********************************************
1. void insertion_at_beginning()
2.
3. {
4.
5. x = head;
6.
7. y = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
8.
9. printf(" Enter the data:");
10.
11. scanf("%d", &y->data);
12.
13. while (x->link != head)
14.
15. {
16.
17. x = x->link;
18.
19. }
20.
21. x->link = y;
22.
23. y->link = head;
24.
25. head = y;
26.
27. }
28.
29.
30.
31.
32. /*Function to insert an element at any position the list*/
33.
34.
35.
36.
37. void ins_at_pos()
38.
39. {
40.
41. struct node *ptr;
42.
43. int c = 1, pos, count = 1;
44.
45. y = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
46.
47. if (head == NULL)
48.
49. {
50.
51. printf("cannot enter an element at this place");
52.
53. }
54.
55. printf(" Enter the data:");
56.
57. scanf("%d", &y->data);
58.
59. printf(" Enter the position to be inserted:");
60.
61. scanf("%d", &pos);
62.
63. x = head;
64.
65. ptr = head;
66.
67. while (ptr->link != head)
68.
69. {
70.
71. count++;
72.
73. ptr = ptr->link;
74.
75. }
76.
77. count++;
78.
79. if (pos > count)
80.
81. {
82.
83. printf("OUT OF BOUND");
84.
85. return;
86.
87. }
88.
89. while (c
90.
91. {
92.
93. z = x;
94.
95. x = x->link;
96.
97. c++;
98.
99. }
100.
101. y->link = x;
102.
103. z->link = y;
104.
105. }
106.
107.
108.
109.
110. /*Function to delete an element at begining of the list*/
111.
112. void del_at_beg()
113.
114. {
115.
116. if (head == NULL)
117.
118. printf(" List is empty");
119.
120. else
121.
122. {
123.
124. x = head;
125.
126. y = head;
127.
128. while (x->link != head)
129.
130. {
131.
132. x = x->link;
133.
134. }
135.
136. head = y->link;
137.
138. x->link = head;
139.
140. free(y);
141.
142. }
143.
144. }
145.
146. /*Function to delete an element at any position the list*/
147.
148. void del_at_pos()
149.
150. {
151.
152. if (head == NULL)
153.
154. printf(" List is empty");
155.
156. else
157.
158. {
159.
160. int c = 1, pos;
161.
162. printf(" Enter the position to be deleted:");
163.
164. scanf("%d", &pos);
165.
166. x = head;
167.
168. while (c
169.
170. {
171.
172. y = x;
173.
174. x = x->link;
175.
176. c++;
177.
178. }
179.
180. y->link = x->link;
181.
182. free(x);
183.
184. }
185.
186. }
187.
188.
189.
190.
191. /*Function to display the elements in the list*/
192.
193. void traverse()
194.
195. {
196.
197. if (head == NULL)
198.
199. printf(" List is empty");
200.
201. else
202.
203. {
204.
205. x = head;
206.
207. while (x->link != head)
208.
209. {
210.
211. printf("%d->", x->data);
212.
213. x = x->link;
214.
215. }
216.
217. printf("%d", x->data);
218.
219. }
220.
221. }
222.
223.
224.
225.
226. /*Function to search an element in the list*/
227.
228. void search()
229.
230. {
231.
232. int search_val, count = 0, flag = 0;
233.
234. printf(" enter the element to search ");
235.
236. scanf("%d", &search_val);
237.
238. if (head == NULL)
239.
240. printf(" List is empty nothing to search");
241.
242. else
243.
244. {
245.
246. x = head;
247.
248. while (x->link != head)
249.
250. {
251.
252. if (x->data == search_val)
253.
254. {
255.
256. printf(" the element is found at %d", count);
257.
258. flag = 1;
259.
260. break;
261.
262. }
263.
264. count++;
265.
266. x = x->link;
267.
268. }
269.
270. if (x->data == search_val)
271.
272. {
273.
274. printf("element found at postion %d", count);
275.
276. }
277.
278. if (flag == 0)
279.
280. {
281.
282. printf(" element not found");
283.
284. }
285.
286. }
287.
288. }
289.
290. /*Function to sort the list in ascending order*/
291.
292. void sort()
293.
294. {
295.
296. struct node *ptr, *nxt;
297.
298. int temp;
299.
300. if (head == NULL)
301.
302. {
303.
304. printf("empty linkedlist");
305.
306. }
307.
308. else
309.
310. {
311.
312. ptr = head;
313.
314. while (ptr->link != head)
315.
316. {
317.
318. nxt = ptr->link;
319.
320. while (nxt != head)
321.
322. {
323.
324. if (nxt != head)
325.
326. {
327.
328. if (ptr->data > nxt->data)
329.
330. {
331.
332. temp = ptr->data;
333.
334. ptr->data = nxt->data;
335.
336. nxt->data = temp;
337.
338. }
339.
340. }
341.
342. else
343.
344. {
345.
346. break;
347.
348. }
349.
350. nxt = nxt->link;
351.
352. }
353.
354. ptr = ptr->link;
355.
356. }
357.
358. }
359.
360. }
361.
362.
363.
364.
365. /*Function to update an element at any position the list*/
366.
367. void update()
368.
369. {
370.
371. struct node *ptr;
372.
373. int search_val;
374.
375. int replace_val;
376.
377. int flag = 0;
378.
379. if (head == NULL)
380.
381. {
382.
383. printf(" empty list");
384.
385. }
386.
387. else
388.
389. {
390.
391. printf("enter the value to be edited ");
392.
393. scanf("%d", &search_val);
394.
395. fflush(stdin);
396.
397. printf("enter the value to be replace ");
398.
399. scanf("%d", &replace_val);
400.
401. ptr = head;
402.
403. while (ptr->link != head)
404.
405. {
406.
407. if (ptr->data == search_val)
408.
409. {
410.
411. ptr->data = replace_val;
412.
413. flag = 1;
414.
415. break;
416.
417. }
418.
419. ptr = ptr->link;
420.
421. }
422.
423. if (ptr->data == search_val)
424.
425. {
426.
427. ptr->data = replace_val;
428.
429. flag = 1;
430.
431. }
432.
433. if (flag == 1)
434.
435. {
436.
437. printf(" UPdate sucessful");
438.
439. }
440.
441. else
442.
443. {
444.
445. printf(" update not successful");
446.
447. }
448.
449. }
450.
451. }
452.
226
/*Function to count the number of elements in the list*/
void count()
{
if (head == NULL)
printf(" List is empty");
else
{
x = head;
int cou=0;
while (x->link != head)
{
c++;
x = x->link;
}
printf("%d",c);
}
}
Page 1 of 6 Circular Linked List Assignment Overview A circular linked list is essentially a singly linked list in which the next pointer of the tail node is set to point to the head node of the linked list rather than set to nul. The first figure below shows a linked list as a singly linked list. The second figure below shows the singly linked list from the first figure as a circular linked list. In this assignment, you will write code for an implementation of a circular linked list 12 Head Tail Singly Linked List 12 Tail Circular Linked List
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


