Question: subject is biochemistry. please do all its only one question they are all connected. if you cannot do all please dont answer. please and thank
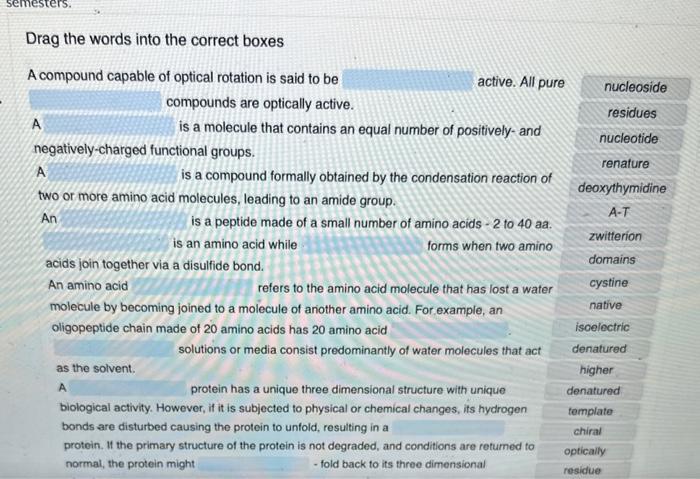
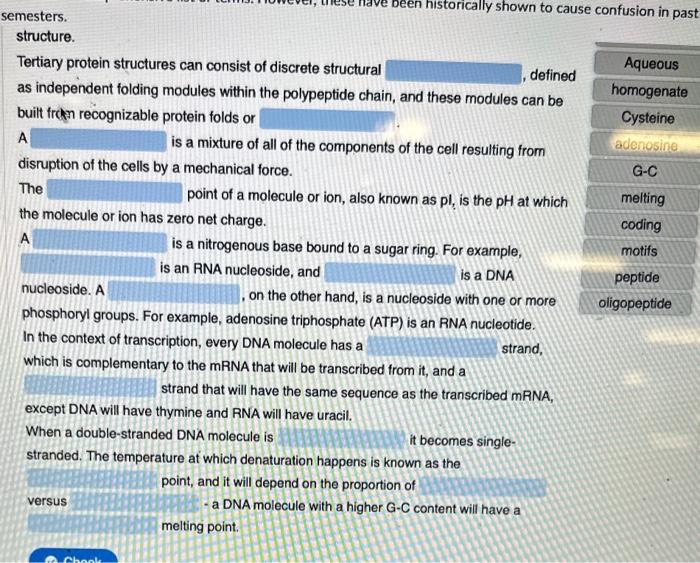
A compound capable of optical rotation is said to be active. All pure compounds are optically active. A is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively-and negatively-charged functional groups. A is a compound formally obtained by the condensation reaction of two or more amino acid molecules, leading to an amide group. An is a peptide made of a small number of amino acids - 2 to 40 aa. is an amino acid while forms when two amino acids join together via a disulfide bond. An amino acid refers to the amino acid molecule that has lost a water molecule by becoming joined to a molecule of another amino acid. For example, an oligopeptide chain made of 20 amino acids has 20 amino acid solutions or media consist predominantly of water molecules that act as the solvent. A protein has a unique three dimensional structure with unique biological activity. However, if it is subjected to physical or chemical changes, its hydrogen bonds are disturbed causing the protein to unfold, resulting in a protein. It the primary structure of the protein is not degraded, and conditions are returned to normal, the protein might - fold back to its three dimensional structure. Tertiary protein structures can consist of discrete structural defined as independent folding modules within the polypeptide chain, and these modules can be built fran recognizable protein folds or A is a mixture of all of the components of the cell resulting from disruption of the cells by a mechanical force. The point of a molecule or ion, also known as pl, is the pH at which the molecule or ion has zero net charge. A is a nitrogenous base bound to a sugar ring. For example, is an RNA nucleoside, and is a DNA nucleoside. A ,on the other hand, is a nucleoside with one or more phosphoryl groups. For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an RNA nucleotide. In the context of transcription, every DNA molecule has a strand, which is complementary to the mRNA that will be transcribed from it, and a strand that will have the same sequence as the transcribed mRNA, except DNA will have thymine and RNA will have uracil. When a double-stranded DNA molecule is it becomes singlestranded. The temperature at which denaturation happens is known as the point, and it will depend on the proportion of versus - a DNA molecule with a higher G-C content will have a melting point
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


