Question: Suppose an engineer wanted to determine whether the gas mixture used increases gas mileage. He constructed a Mix 1 Mix 2 Mix 3 randomized block
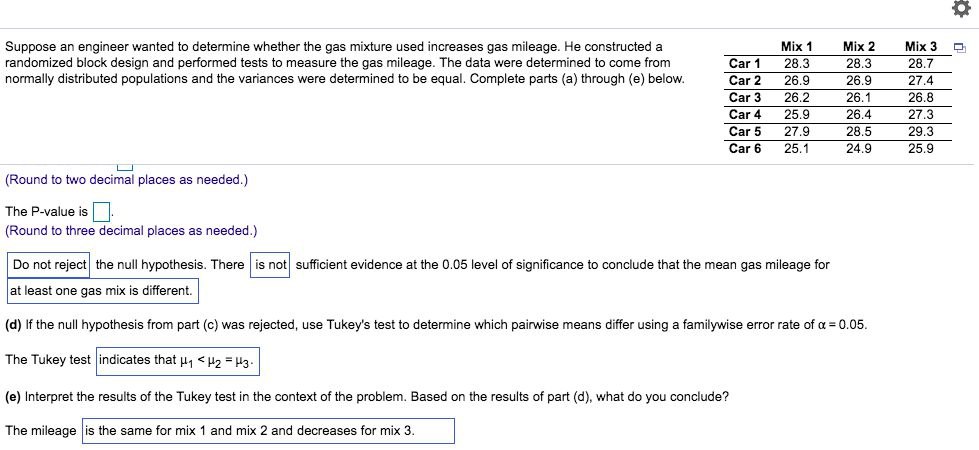
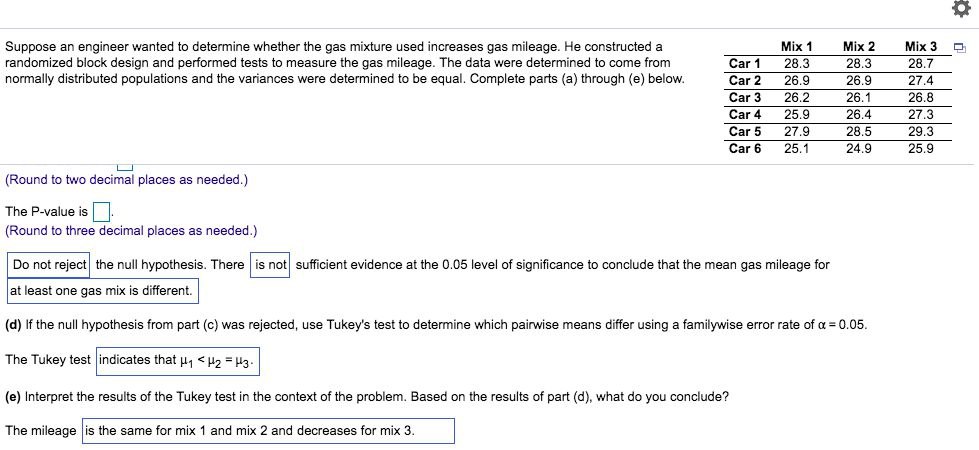
Suppose an engineer wanted to determine whether the gas mixture used increases gas mileage. He constructed a Mix 1 Mix 2 Mix 3 randomized block design and performed tests to measure the gas mileage. The data were determined to come from Car 1 28.3 28.3 28.7 normally distributed populations and the variances were determined to be equal. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. Car 2 26.9 26.9 27.4 Car 3 26.2 26.1 26.8 Car 4 25.9 26.4 27.3 Car 5 27.9 28.5 29.3 Car 6 25.1 24.9 25.9 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Do not reject the null hypothesis. There | is not sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level of significance to conclude that the mean gas mileage for at least one gas mix is different. (d) If the null hypothesis from part (c) was rejected, use Tukey's test to determine which pairwise means differ using a familywise error rate of a = 0.05. The Tukey test | indicates that H1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


