Question: Table 1 Cell Type Lithium-iodine Operating Cell Potential for Commercial Batteries, E (V) +2.80 +1.35 Zinc mercury Table 2 Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) -1.20
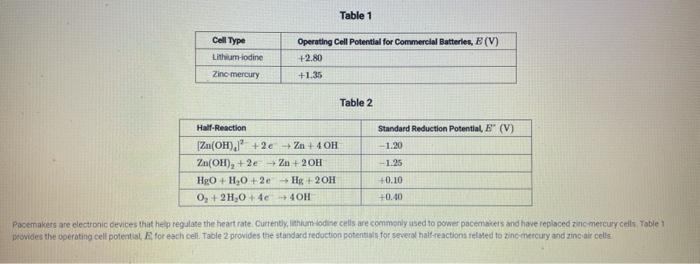

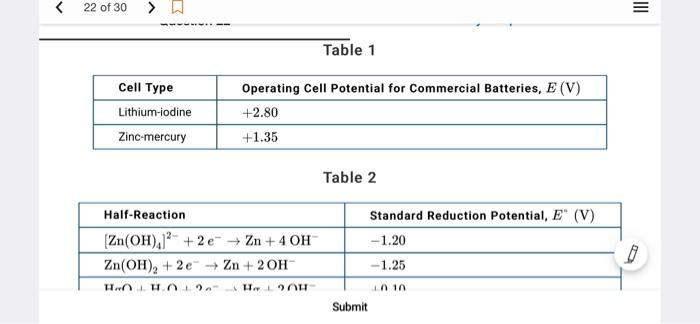
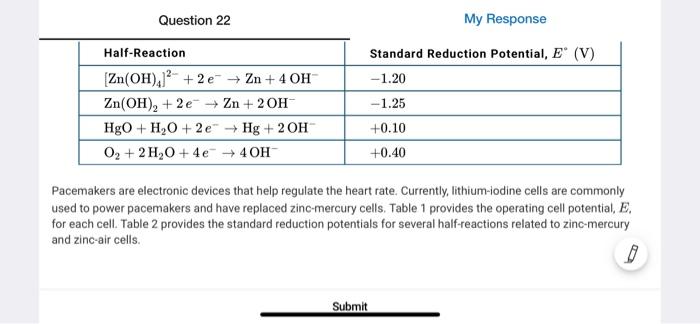


Table 1 Cell Type Lithium-iodine Operating Cell Potential for Commercial Batteries, E (V) +2.80 +1.35 Zinc mercury Table 2 Standard Reduction Potential, E" (V) -1.20 Half-Reaction Zn(OH)./' + 2 + Zn + 4 OH Zn(OH), +2e-2n+20H HgO+H.0 +2e + H+ 2OH 0, +2,04c-40H -1.25 +0.10 +0.00 Pacemakers are electronic devices that help regulate the heart rate Currently, lithium-.lodine cells are commonly used to power pacemakers and have replaced zinc mercury cells Table 1 provides the operating cell potential for each cell. Table 2 provides the standard reduction potential for several half-reactions reled to ino mercury and zinc air cells Pacemakers are electronic devices that help regulate the heart rate. Currently, lithium-iodine cells are commonly used to power pacemakers and have replaced in mercury cells Table 1 provides the operating cell potential. E for each cell. Toble 2 provides the standard reduction potentials for several hall reactions related to inc mercury and zinc air cells. The use of zinc mercury cells in hearing aids tas been replaced by zinc-air cells that operate using the cuidation of 2 by O, from the air, generating a potential of +1,00 V Table 2 provides the Standard reduction potentials for the half reactions used in zno mercury and zinc-oir cells which of the following best explains the modification to the cell design that is mostly responsible for the difference in standard cell potentials for sine mercury and zinc-air cells? The greater standard cell potential of the Zo-air cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically more tovorable reduction of O, compared to HO The greater standard cell potential of the Zair celt compared to that of the mine mercury cell most likely results from the greater rumber ot moles of e roured to reduceo, compared to HEO The greater standard cell potential of the Zu-nir cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically less favorable reduction of O, compared to Heo D The greater standard cell potential of the Zu-air cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell motely results from the greater number of moles of hydroxide fons required to reduce Zn(OH), compared to Zn(OH), Pacemakers are electronic devices that help regulate the heart rate. Currently, lithium-iodine cells are commonly used to power pacemakers and have replaced in mercury cells Table 1 provides the operating cell potential. E for each cell. Toble 2 provides the standard reduction potentials for several hall reactions related to inc mercury and zinc air cells. The use of zinc mercury cells in hearing aids tas been replaced by zinc-air cells that operate using the cuidation of 2 by O, from the air, generating a potential of +1,00 V Table 2 provides the Standard reduction potentials for the half reactions used in zno mercury and zinc-oir cells which of the following best explains the modification to the cell design that is mostly responsible for the difference in standard cell potentials for sine mercury and zinc-air cells? The greater standard cell potential of the Zo-air cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically more tovorable reduction of O, compared to HO The greater standard cell potential of the Zair celt compared to that of the mine mercury cell most likely results from the greater rumber ot moles of e roured to reduceo, compared to HEO The greater standard cell potential of the Zu-nir cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically less favorable reduction of O, compared to Heo D The greater standard cell potential of the Zu-air cell compared to that of the zinc mercury cell motely results from the greater number of moles of hydroxide fons required to reduce Zn(OH), compared to Zn(OH), Question 22 My Response Half-Reaction Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) -1.20 -1.25 (Zn(OH)2 +2e Zn + 4 OH Zn(OH)2 +2e Zn +20H HgO + H2O +2e Hg + 2 OH O2 + 2H2O + 4e + 40H +0.10 +0.40 Pacemakers are electronic devices that help regulate the heart rate. Currently, lithium-iodine cells are commonly used to power pacemakers and have replaced zinc-mercury cells. Table 1 provides the operating cell potential, E. for each cell. Table 2 provides the standard reduction potentials for several half-reactions related to zinc-mercury and zinc-air cells Submit Table 1 Cell Type Lithium-iodine Operating Cell Potential for Commercial Batteries, E (V) +2.80 +1.35 Zinc mercury Table 2 Standard Reduction Potential, E" (V) -1.20 Half-Reaction Zn(OH)./' + 2 + Zn + 4 OH Zn(OH), +2e-2n+20H HgO+H.0 +2e + H+ 2OH 0, +2,04c-40H -1.25 +0.10 +0.00 Pacemakers are electronic devices that help regulate the heart rate Currently, lithium-.lodine cells are commonly used to power pacemakers and have replaced zinc mercury cells Table 1 provides the operating cell potential for each cell. Table 2 provides the standard reduction potential for several half-reactions reled to ino mercury and zinc air cells mercury and zinc-air cells? A The greater standard cell potential of the Zn-air cell compared to that of the zinc-mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically more favorable reduction of O2 compared to HgO. B The greater standard cell potential of the Zn-air cell compared to that of the zinc-mercury cell most likely results from the greater number of moles of e required to reduce O2 compared to HgO The greater standard cell potential of the Zn-air cell compared to that of the zinc-mercury cell most likely results from the thermodynamically less favorable reduction of O, compared to HgO. D The greater standard cell potential of the Zn-air cell compared to that of the zinc-mercury cell most likely results from the greater number of moles of hydroxide ions required to reduce Zn(OH),]? compared to Zn(OH)2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


