Question: Task 6 : Adsorption ( 1 3 P ) Methanol is removed from a carrier gas stream ( ( V ) = 6 0 0
Task : Adsorption P
Methanol is removed from a carrier gas stream with the help of adsorption on
activated carbon. The initial loading content of methanol in the gas stream equals The
final loading contents of the outlet gas stream should not be higher than There are
three fixed bed adsorbers bulk density Schttdichte available, which operate alternately
every minutes.
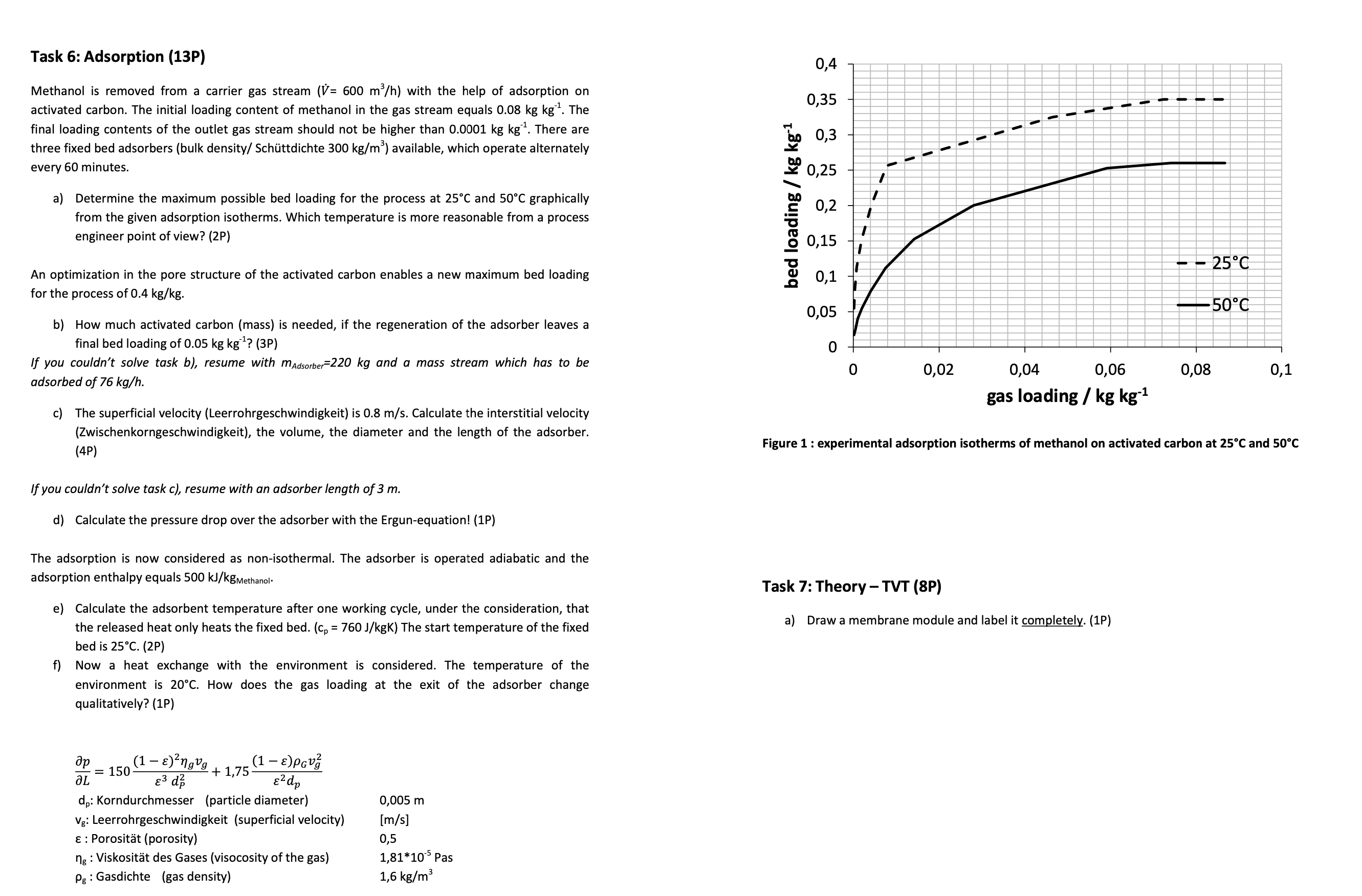
a Determine the maximum possible bed loading for the process at and graphically
from the given adsorption isotherms. Which temperature is more reasonable from a process
engineer point of view? P
An optimization in the pore structure of the activated carbon enables a new maximum bed loading
for the process of
b How much activated carbon mass is needed, if the regeneration of the adsorber leaves a
final bed loading of P
If you couldn't solve task b resume with and a mass stream which has to be
adsorbed of
c The superficial velocity Leerrohrgeschwindigkeit is Calculate the interstitial velocity
Zwischenkorngeschwindigkeit the volume, the diameter and the length of the adsorber.
P
If you couldn't solve task c resume with an adsorber length of
d Calculate the pressure drop over the adsorber with the Ergunequation! P
The adsorption is now considered as nonisothermal. The adsorber is operated adiabatic and the
adsorption enthalpy equals
e Calculate the adsorbent temperature after one working cycle, under the consideration, that
the released heat only heats the fixed bed. The start temperature of the fixed
bed is P
f Now a heat exchange with the environment is considered. The temperature of the
environment is How does the gas loading at the exit of the adsorber change
qualitatively? P
: Korndurchmesser diameter
: Leerrohrgeschwindigkeit velocity
: Porosit
: Viskosit des Gases the gas Pas
: Gasdichte density
Figure : experimental adsorption isotherms of methanol on activated carbon at and
Task : Theory TVT P
a Draw a membrane module and label it completely. P
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


