Question: Technique Ascertaining Supply Analyzing Movement Internal movement is hard to track accuratelymostly because of the ripple effect that simple transfers can cause across the organization.
Technique Ascertaining Supply Analyzing Movement
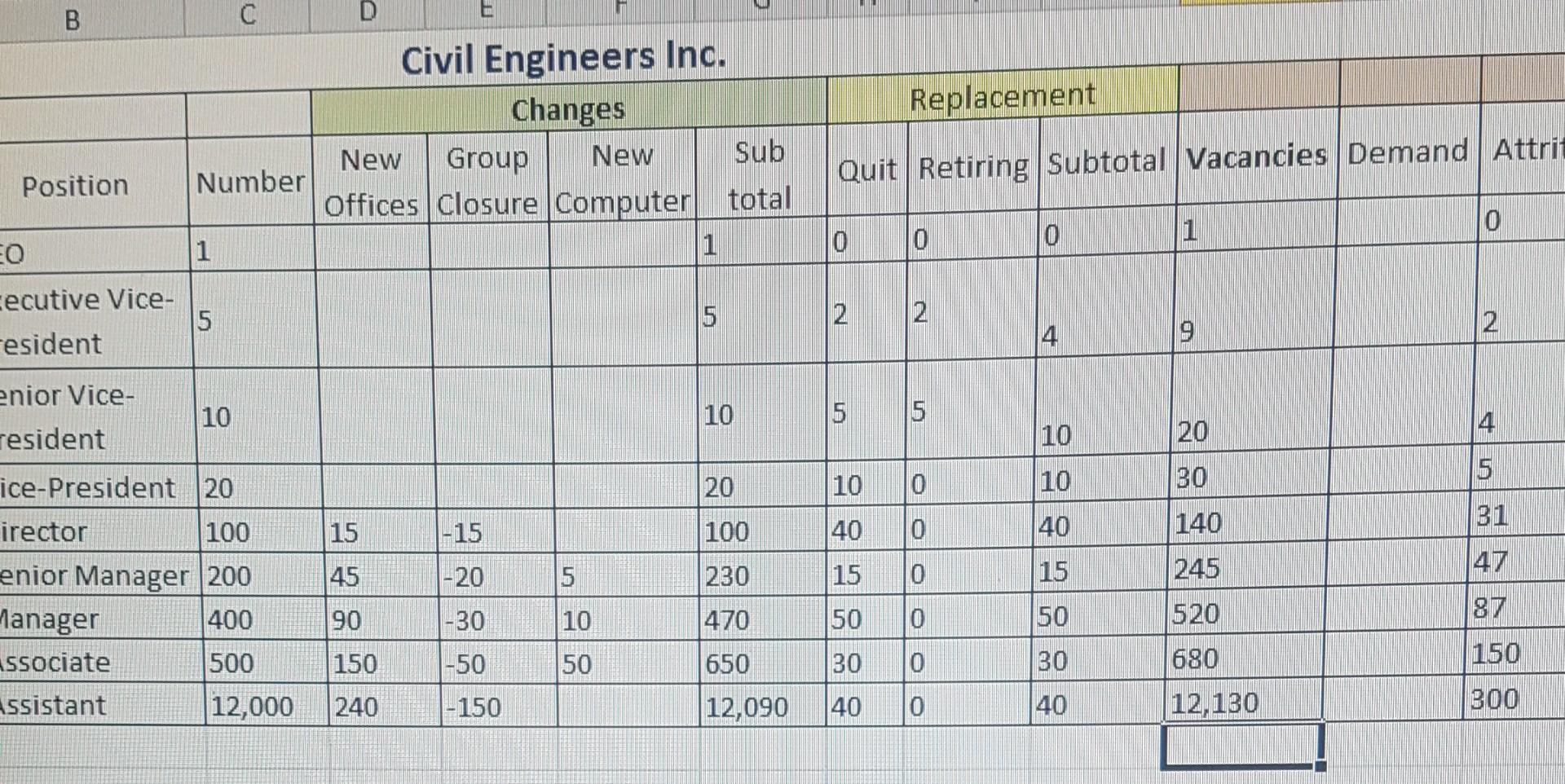
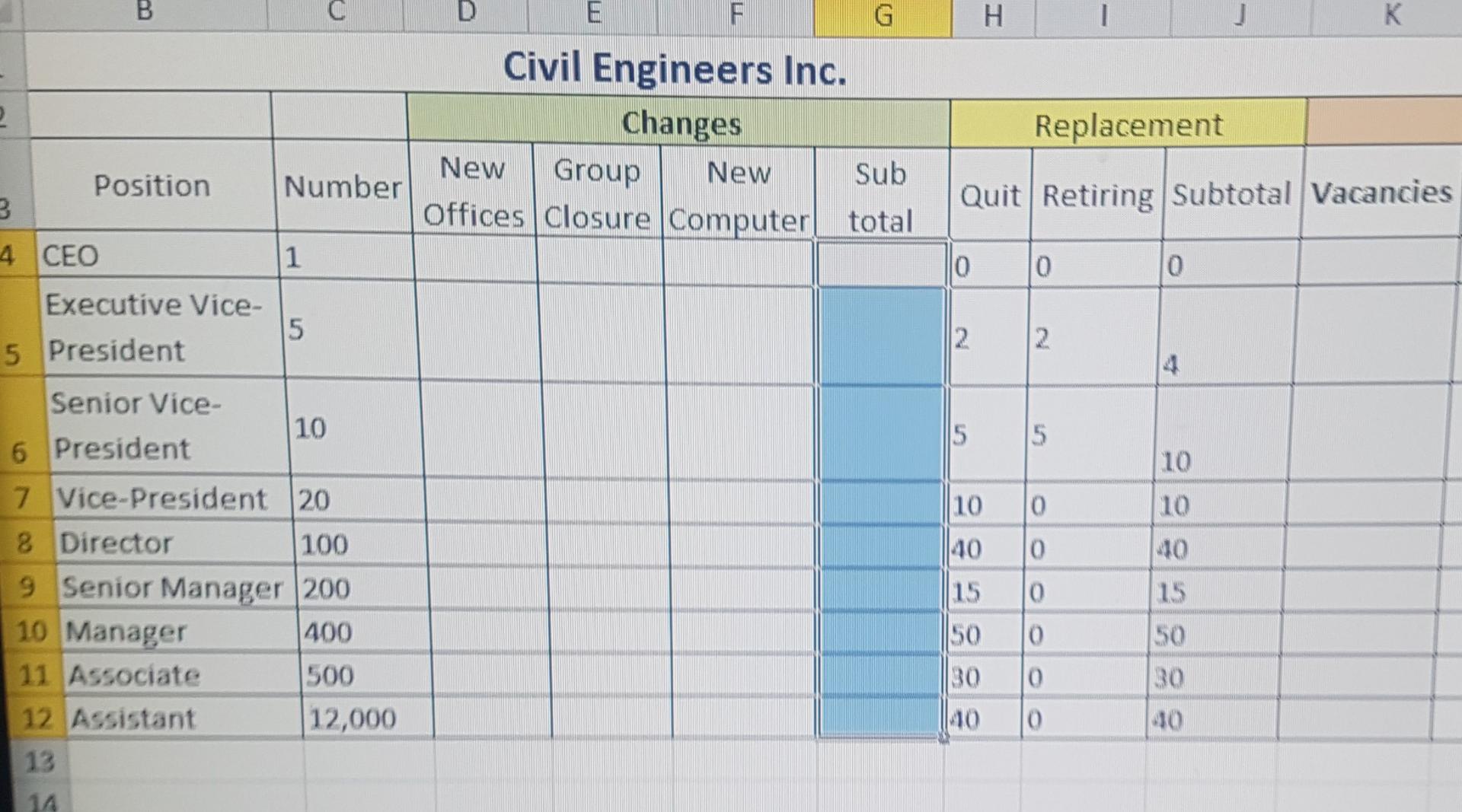
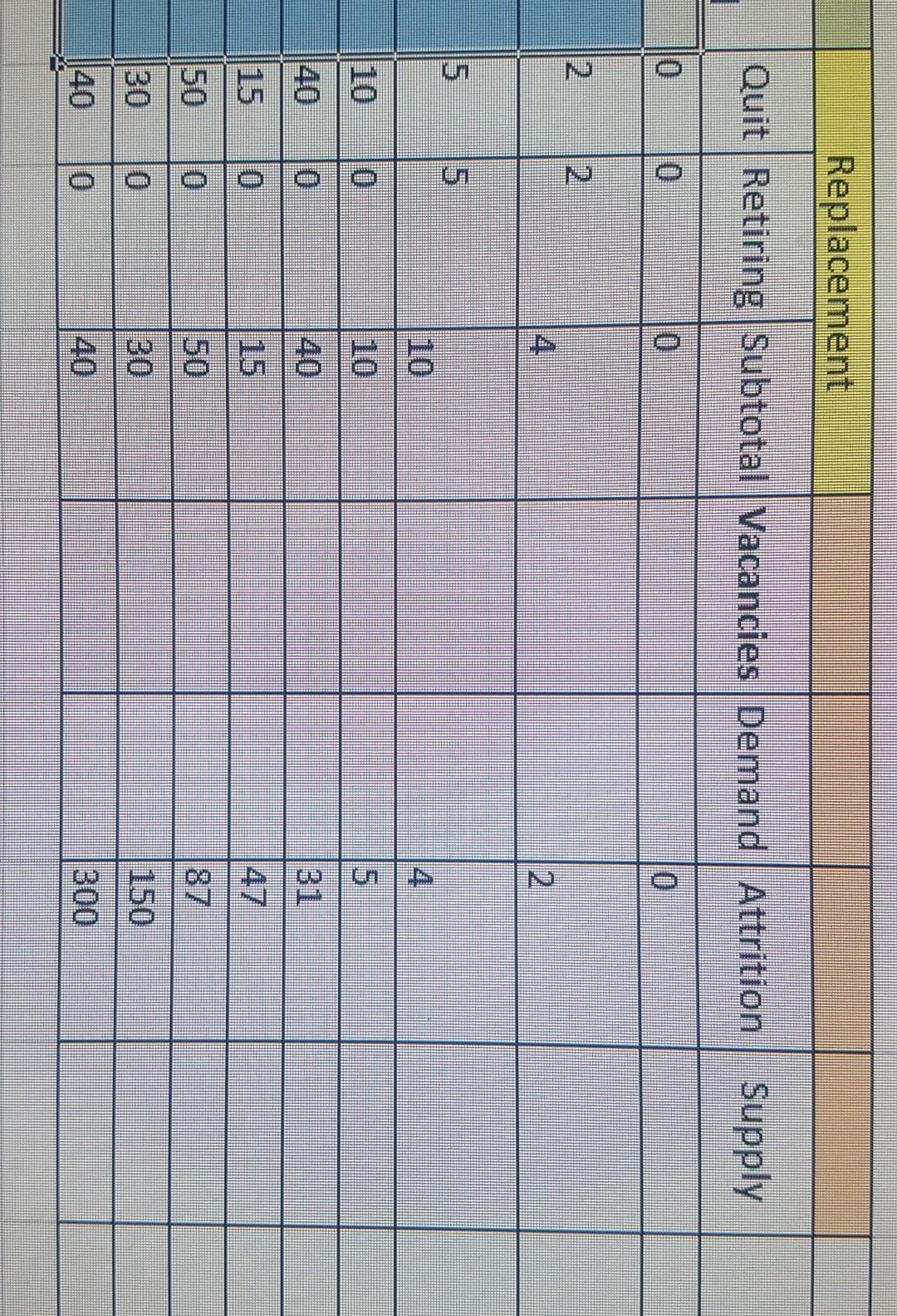
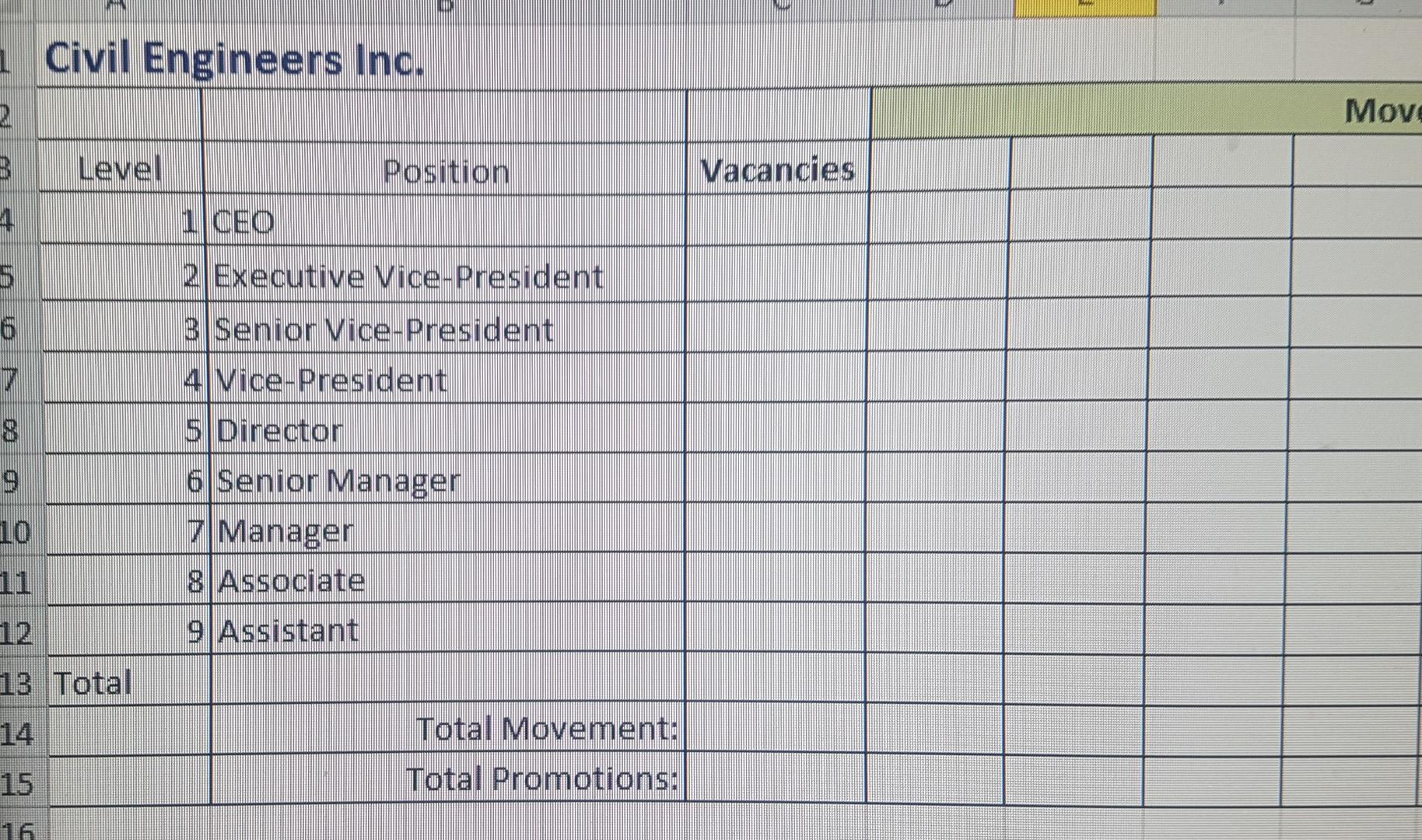
Internal movement is hard to track accuratelymostly because of the ripple effect that simple transfers can cause across the organization. One solution is to use Markov Analysis to determine the number of positions you need to fill over the coming year and identify the other positions that will shift as a result. The outcome is a separate table for each situation that lets you analyze the change visually. In this technique, you will make a series of simple calculations to determine the probability of an event happening then plot those changes into the tables for Positions to Fill and Position Movement. Use the staffing table below as your starting point for the current complement of employees. Then factor in the changes anticipated for the coming year. For your calculations, click the Civil Engineers Inc. link and the use the spreadsheet provided.
Scenario
The company has the following goals for next year:
Open three new offices across the country. Each office requires 5 directors, 15 senior managers, 30 managers, 50 associates, and 80 assistants.
Discontinue the Highway Signage group, which is loosing money. This will decrease staffing by 15 directors, 20 senior managers, 30 managers, 50 associates, and 150 assistants.
Introduce a new computer system to increase efficiency. This system requires 5 senior managers, 10 managers, and 50 associates.
Tip: If you are not sure how to perform the calculations, review the explanation for using Markov Analysis on the Commentary page.
Instructions
To complete your calculations:
Click the link above to open the spreadsheet and save a copy to your local computer.
Fill out the table on the Positions to Fill tab of the worksheet provided.
Fill out the table on the Position Movement tab of the worksheet provided.
Analyze the results to answer the questions below.
Questions
Answer these questions in your journal:
What is the number of promotions if the organization uses a promote from within policy?
What is the number of employee movements if the organization uses a promote from within policy?
Provide a Positions to Fill and a Position Movement table for each condition to prove your answer.
Criteria
For this technique, points are assigned to each of the following categories:
The Positions to Fill table shows the correct staffing Changes (2 points).
The Positions to Fill table shows the correct staffing Replacements (2 points).
The Position Movement table shows the correct number of employee movements (2 points).
The Position Movement table shows the correct number of promotions (2 points).
Both tables include a written note to explain your conclusions (2 points).
B C D Replacement Civil Engineers Inc. Changes New Group New Sub Offices Closure Computer total 1 Position Number Quit Retiring Subtotal Vacancies Demand Attrit 0 1 0 O 0 15 2 2 2 9 4 10 5 5 4 20 4 10 EO 1 cecutive Vice- 5 resident enior Vice- 10 resident ice-President 20 irector 100 enior Manager 200 Manager 400 Associate 500 ssistant 12,000 20 10 0 10 30 15 81 1-15 100 40 0 40 140 45 47 -20 5 230 15 0 15 245 90 -30 87 10 470 50 0 50 520 150 -50 50 650 30 0 30 680 150 240 - 150 12,090 40 0 40 12,130 300 C F G H 1 K Replacement Civil Engineers Inc. Changes New Group New Sub Number Offices Closure Computer total 1 Position 3 Quit Retiring Subtotal Vacancies 10 0 0 4 CEO Executive Vice- 5 President 5 2 2 5 5 10 10 0 10 1410 0 40 Senior Vice- 10 6 President 7 Vice-President 20 8 Director 100 9 Senior Manager 200 10 Manager 400 11 Associate 500 12 Assistant 12,000 15 0 15 50 0 50 30 0 30 410 0 410 13 14 Replacement Quit | Retiring |Subtotal Vacancies Demand Attrition Supply 0 0 2. 2 4 2 15 LOM 15 10 10 0 5 40 0 2 1 0 150 0 0 150 0 40 300 1 Civil Engineers Inc. 2 Move 3 Level Position Vacancies 4 1 CEO 5 2 Executive Vice-President 3 Senior Vice-President 6 7 4 Vice-President 10 5 Director 6 Senior Manager 7 Manager 8 Associate 9 Assistant 12 13 Total 14 Total Movement: Total Promotions: 15 16. Movement Vacancies Personnel w ent: ons: B C D Replacement Civil Engineers Inc. Changes New Group New Sub Offices Closure Computer total 1 Position Number Quit Retiring Subtotal Vacancies Demand Attrit 0 1 0 O 0 15 2 2 2 9 4 10 5 5 4 20 4 10 EO 1 cecutive Vice- 5 resident enior Vice- 10 resident ice-President 20 irector 100 enior Manager 200 Manager 400 Associate 500 ssistant 12,000 20 10 0 10 30 15 81 1-15 100 40 0 40 140 45 47 -20 5 230 15 0 15 245 90 -30 87 10 470 50 0 50 520 150 -50 50 650 30 0 30 680 150 240 - 150 12,090 40 0 40 12,130 300 C F G H 1 K Replacement Civil Engineers Inc. Changes New Group New Sub Number Offices Closure Computer total 1 Position 3 Quit Retiring Subtotal Vacancies 10 0 0 4 CEO Executive Vice- 5 President 5 2 2 5 5 10 10 0 10 1410 0 40 Senior Vice- 10 6 President 7 Vice-President 20 8 Director 100 9 Senior Manager 200 10 Manager 400 11 Associate 500 12 Assistant 12,000 15 0 15 50 0 50 30 0 30 410 0 410 13 14 Replacement Quit | Retiring |Subtotal Vacancies Demand Attrition Supply 0 0 2. 2 4 2 15 LOM 15 10 10 0 5 40 0 2 1 0 150 0 0 150 0 40 300 1 Civil Engineers Inc. 2 Move 3 Level Position Vacancies 4 1 CEO 5 2 Executive Vice-President 3 Senior Vice-President 6 7 4 Vice-President 10 5 Director 6 Senior Manager 7 Manager 8 Associate 9 Assistant 12 13 Total 14 Total Movement: Total Promotions: 15 16. Movement Vacancies Personnel w ent: ons
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


