Question: Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) is one of the most popular term-weighting schemes today, and 83% of text-based recommender systems in digital
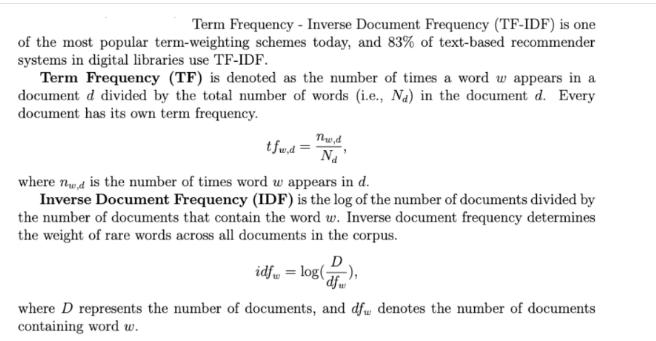
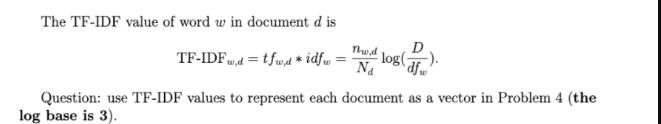

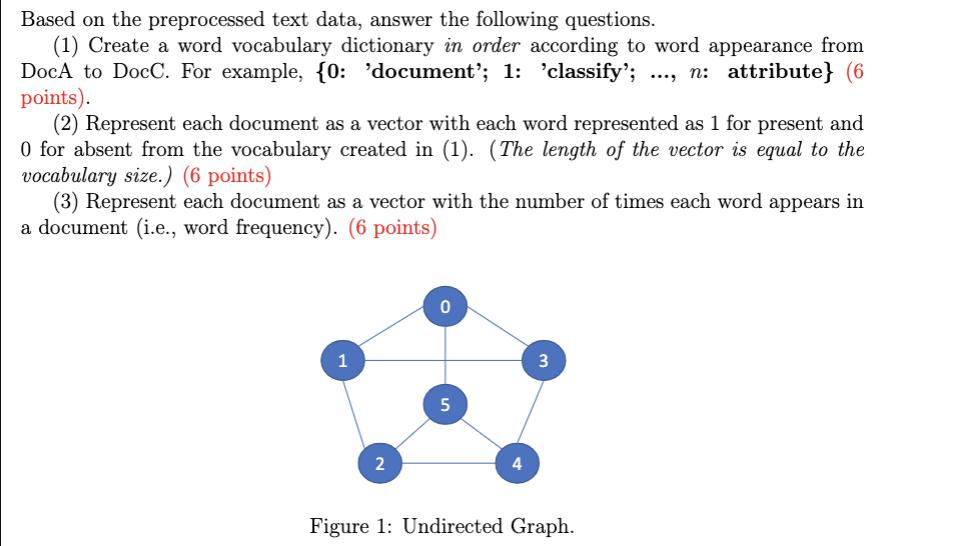
Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) is one of the most popular term-weighting schemes today, and 83% of text-based recommender systems in digital libraries use TF-IDF. Term Frequency (TF) is denoted as the number of times a word w appears in a document d divided by the total number of words (i.e., Na) in the document d. Every document has its own term frequency. tfw.d = Thw,d Na where nd is the number of times word w appears in d. Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) is the log of the number of documents divided by the number of documents that contain the word w. Inverse document frequency determines the weight of rare words across all documents in the corpus. D idfw = log(), where D represents the number of documents, and df denotes the number of documents containing word w. The TF-IDF value of word w in document d is Thut Na log df TF-IDFwd = tfwd *idfw= Question: use TF-IDF values to represent each document as a vector in Problem 4 (the log base is 3). Problem 4 (18 points). In a text data corpus, there are three documents DocA= 'Document classification or document categorization is a problem in computer science.' DocB = 'Document classification task is to assign a document to one or more classes or categories.' DocC='Documents may be classified according to their subjects or according to other attributes.' After removing stop words and conducting stemming, we then have three vectors as follows: ['document', 'classify', 'document', 'category', 'problem', 'computer', 'science'] = DocB = ['document', 'classify', 'task', 'assign', 'document', 'class', 'category'] . DocC ['document', 'classify', 'accord', 'subject', 'accord', 'attribute'] = Based on the preprocessed text data, answer the following questions. (1) Create a word vocabulary dictionary in order according to word appearance from DocA to DocC. For example, {0: 'document'; 1: 'classify'; n: attribute} (6 points). (2) Represent each document as a vector with each word represented as 1 for present and 0 for absent from the vocabulary created in (1). (The length of the vector is equal to the vocabulary size.) (6 points) (3) Represent each document as a vector with the number of times each word appears in a document (i.e., word frequency). (6 points) 1 2 0 5 3 .... Figure 1: Undirected Graph.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


