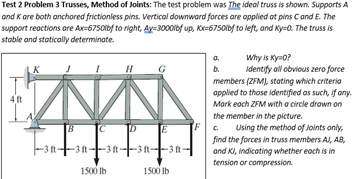
Question: Test 2 Problem 3 Trusses, Method of Joints: The test problem was The ideal truss is shown, Supports A and ( K )
Test Problem Trusses, Method of Joints: The test problem was The ideal truss is shown, Supports A and K are both anchored frictionless pins. Vertical downword forces are opplied of pins C and E The support reoctions are A xmathrmbf to right, mathrmAgmathrmf up K xmathrmf to left, and K y The truss is stable and statically determinate.
a Why is K y
b Identify oll obvious zero force members ZFM stoting which criterio applied to those identified os such, if any. Mork each ZFM with a circle drown on the member in the picture.
c Using the method of Joints only, find the forces in truss members A A B and Kl indicating whether each is in tension or compression. Test Problem Trusses, Method of Joints: The test problem was The ideal truss is shown, Supports A and K are both anchored frictionless pins. Vertical downword forces are opplied of pins C and E The support reoctions are A xmathrmbf to right, mathrmAgmathrmf up K xmathrmf to left, and K y The truss is stable and statically determinate.
a Why is K y
b Identify oll obvious zero force members ZFM stoting which criterio applied to those identified os such, if any. Mork each ZFM with a circle drown on the member in the picture.
c Using the method of Joints only, find the forces in truss members A A B and Kl indicating whether each is in tension or compression.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


