Question: ### testing computeHomography # # NOTE: make sure you don't try to estimate a homography for cases where three or # four of the points
### testing computeHomography # # NOTE: make sure you don't try to estimate a homography for cases where three or # four of the points are in a line since this will lead to an underdetermined # linear system #
# # If you compute the homography between a set of points and itself, you should get back the identity matrix #
#I need to write a function that will assert true for below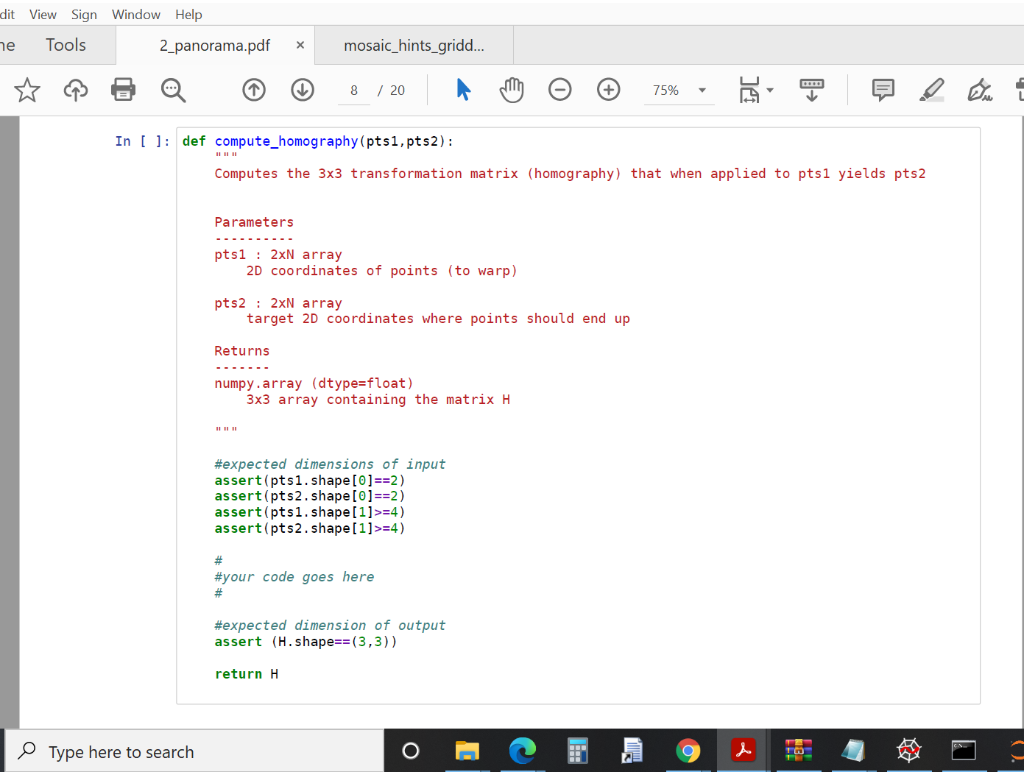 pts1 = np.array([ [0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1, 0] ]) pts2 = pts1 H = compute_homography(pts1,pts2) identityM = np.array([[1.,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]) assert(H.all()==identityM.all())
pts1 = np.array([ [0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1, 0] ]) pts2 = pts1 H = compute_homography(pts1,pts2) identityM = np.array([[1.,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]) assert(H.all()==identityM.all())
dit View Sign Window Help ne Tools 2_panorama.pdf X mosaic_hints_gridd... 8 / 20 o 75% 5 In [ ]: def compute_homography (pts1, pts2): Computes the 3x3 transformation matrix (homography) that when applied to pts1 yields pts2 Parameters pts1 : 2xN array 2D coordinates of points (to warp) pts2 : 2xN array target 2D coordinates where points should end up Returns numpy.array (dtype=float) 3x3 array containing the matrix H #expected dimensions of input assert(ptsi. shape [0]==2) assert(pts2. shape [0]==2) assert(pts 1. shape[1]>=4) assert(pts2.shape[1]>=4) # #your code goes here # #expected dimension of output assert (H.shape==(3,3)) return H Type here to search E
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


