Question: the dataset is: 1. Create Python functions logistic_objective(x,y), dlogistic_objective(x,y). d2logisitic_objective (x,y) satisfying the following specifications . All functions expect two arraysumpy arrays x and y

the dataset is:
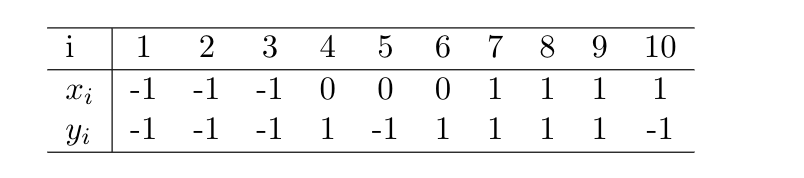
1. Create Python functions logistic_objective(x,y), dlogistic_objective(x,y). d2logisitic_objective (x,y) satisfying the following specifications . All functions expect two arraysumpy arrays x and y where x [1]-xi, y [1]-yi, and { (zi,Vi)}} , C R x,1 are training data for logistic regression logistic_objective(x,y) returns a function f satisfying the following specifications f expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0] = 0 and b [1] 1 for some logistic model parameters (30190 f (b) computes the negative log-likelihood of the parameters (o,1). That is, f (b) = 1(3) =log (1 + e-m(Ao+31") . dlogistic_objective(x,y) returns a function df satisfying the following specifications df expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0] = and b [1] = 1 for some logistic model parameters (A,A) df (b) computes the gradient of negative log-likelihood at (Bo, B1). That is, d2logistic-objective (x,y) returns a function d2f satisfying the following specifications d2f expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0]-A) and b [1]-A for some logistic model parameters (A,A) d2f (b) computes the Hessian of negative log-likelihood at (30,A). That is. Use these implementations and the data from Exercise 2 in Homework 05 to perform backtracking with both gradient descent and Newton increments. For the Newton increments, note that the computation of e() Vt() is carried out by the command dx_newt - numpy.linalg.solve (d2f (b), df (b)) For each type of increment, initialize with Bo) , run 30 steps of backtracking and provide a y- semilog plot of the point residuals { (k+1) For backtracking, use a - 0.2 and 3-0.8 (k) } 1 and the function residuals { E((k+1)) 1(8(k))) 1 1. Create Python functions logistic_objective(x,y), dlogistic_objective(x,y). d2logisitic_objective (x,y) satisfying the following specifications . All functions expect two arraysumpy arrays x and y where x [1]-xi, y [1]-yi, and { (zi,Vi)}} , C R x,1 are training data for logistic regression logistic_objective(x,y) returns a function f satisfying the following specifications f expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0] = 0 and b [1] 1 for some logistic model parameters (30190 f (b) computes the negative log-likelihood of the parameters (o,1). That is, f (b) = 1(3) =log (1 + e-m(Ao+31") . dlogistic_objective(x,y) returns a function df satisfying the following specifications df expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0] = and b [1] = 1 for some logistic model parameters (A,A) df (b) computes the gradient of negative log-likelihood at (Bo, B1). That is, d2logistic-objective (x,y) returns a function d2f satisfying the following specifications d2f expects a single arrayumpy array b such that b [0]-A) and b [1]-A for some logistic model parameters (A,A) d2f (b) computes the Hessian of negative log-likelihood at (30,A). That is. Use these implementations and the data from Exercise 2 in Homework 05 to perform backtracking with both gradient descent and Newton increments. For the Newton increments, note that the computation of e() Vt() is carried out by the command dx_newt - numpy.linalg.solve (d2f (b), df (b)) For each type of increment, initialize with Bo) , run 30 steps of backtracking and provide a y- semilog plot of the point residuals { (k+1) For backtracking, use a - 0.2 and 3-0.8 (k) } 1 and the function residuals { E((k+1)) 1(8(k))) 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


