Question: the equilibria. de C. Carry out a phase-line analysis for the case s = n - 72 = 1, and characterize the stability of P=0
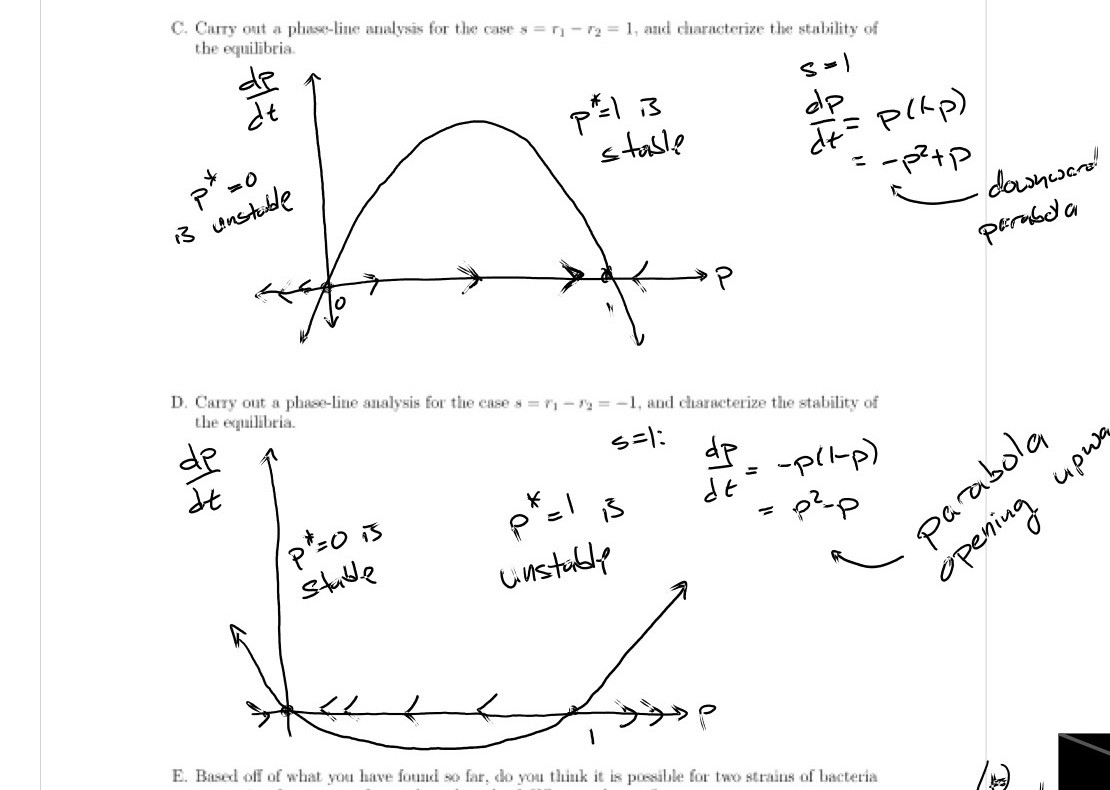



the equilibria. de C. Carry out a phase-line analysis for the case s = n - 72 = 1, and characterize the stability of P=0 S =) 13 unstable stable elp If = P ( RP ) - p2 + p downward - P the equilibria. D. Carry out a phase-line analysis for the case s = ry - ry = -1, and characterize the stability of It s=1: P"= 0 15 * ap P = 3 de -p ( 1- p ) stable unstable = parabola opening upwe R E. Based off of what you have found so far, do you think it is possible for two strains of bacteriagoes extinct & the entire population comekis only of stroin 2. whichever strain grows more slowly goes extinct. coexistence is not possible.PS10 Due April 12, 2024 Student Name: Student #: report all answers to 3 significant digits Problem 1: In Problem Set 8, you derived the following equation which appears in population genetics: dp = 1p), 0) = pog. o = p(L=p), p(0) =po In the original problem in PS8, you considered two strains of a bacteria population, and p represented the proportion of the population that belonged to strain 1. The constant term s represented the difference in growth rates. The initial proportion at time t = 0 is py. Now, we will solve this equation for the full time-dependent solution. Employing separation of variables, we can re- write this equation as 1 dp p(ipydt Then, we can integrate each side of the equation with respect to t: /(%) dt:/sdt. According to the substitution rule, this is equivalent to /mdp:/sdt. A. Solve the integrals above to obtain the solution, p(t), to the initial value problem. Don't forget to use the intitial condition. (Hint: 57 =+ &, and [ 1dv = In(|z]) + .) PS10 Due April 12, 2024 B. Make a sketch of your solution, p(t), for po = 0.01 and s = 2 for 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


