Question: The extended Euclidean algorithm is used for efficiently finding the multiplicative inverse (when it exists; Note that when we are looking for the multiplicative inverse
The extended Euclidean algorithm is used for efficiently finding the multiplicative inverse (when it exists; Note that when we are looking for the multiplicative inverse of a mod n, gcd(a,n) needs to be 1.) We run the Euclidean algorithm as before but in addition to q1,q2,...r1,r2,... we also compute si and ti where;
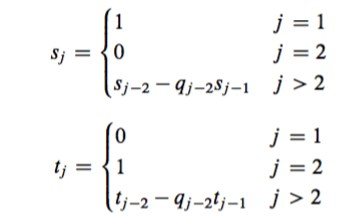
Write a C++ program that takes two positive integers as input. First, it checks if the
gcd of them is 1, if so, then it should return the multiplicative inverse of the
second input argument. You need to print a trace of your program as well. For
example, if your input values are 28; 75, the multiplicative inverse of 28 mod 75
is -8 =75 67 and the trace table looks like the following.
| i | qi | ri | ri + 1 | ri +2 | si | ti |
| 1 | 2 | 75 | 28 | 19 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 28 | 19 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 19 | 9 | 1 | 1 | -2 |
| 4 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | -8 |
9-2-qj-29-1 J >2 6-2-%-2tj-1 J >2 122 122 10 01
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


