Question: The figure below provides the schematic description of a continuous stirred tank reactor. The reactor operates at constant temperature and its content is well-mixed. The
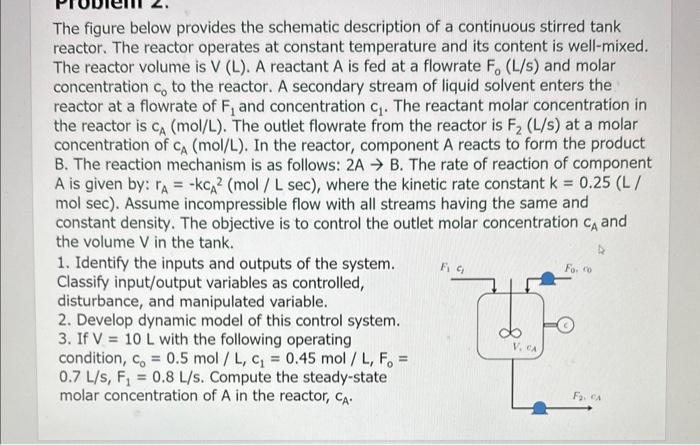
The figure below provides the schematic description of a continuous stirred tank reactor. The reactor operates at constant temperature and its content is well-mixed. The reactor volume is V(L). A reactant A is fed at a flowrate F0(L/s) and molar concentration c0 to the reactor. A secondary stream of liquid solvent enters the reactor at a flowrate of F1 and concentration c1. The reactant molar concentration in the reactor is CA(mol/L). The outlet flowrate from the reactor is F2(L/s) at a molar concentration of CA(mol/L). In the reactor, component A reacts to form the product B. The reaction mechanism is as follows: 2AB. The rate of reaction of component A is given by: rA=kcA2 (mol / L sec), where the kinetic rate constant k=0.25 (L / mol sec). Assume incompressible flow with all streams having the same and constant density. The objective is to control the outlet molar concentration CA and the volume V in the tank. 1. Identify the inputs and outputs of the system. Classify input/output variables as controlled, disturbance, and manipulated variable. 2. Develop dynamic model of this control system. 3. If V=10L with the following operating condition, C0=0.5mol/L,c1=0.45mol/L,F0= 0.7L/s,F1=0.8L/s. Compute the steady-state molar concentration of A in the reactor, CA
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


