Question: The figure describes the basic elements of an LLM ( Large Language Model ) pipeline, showing the use of both open and closed source LLM
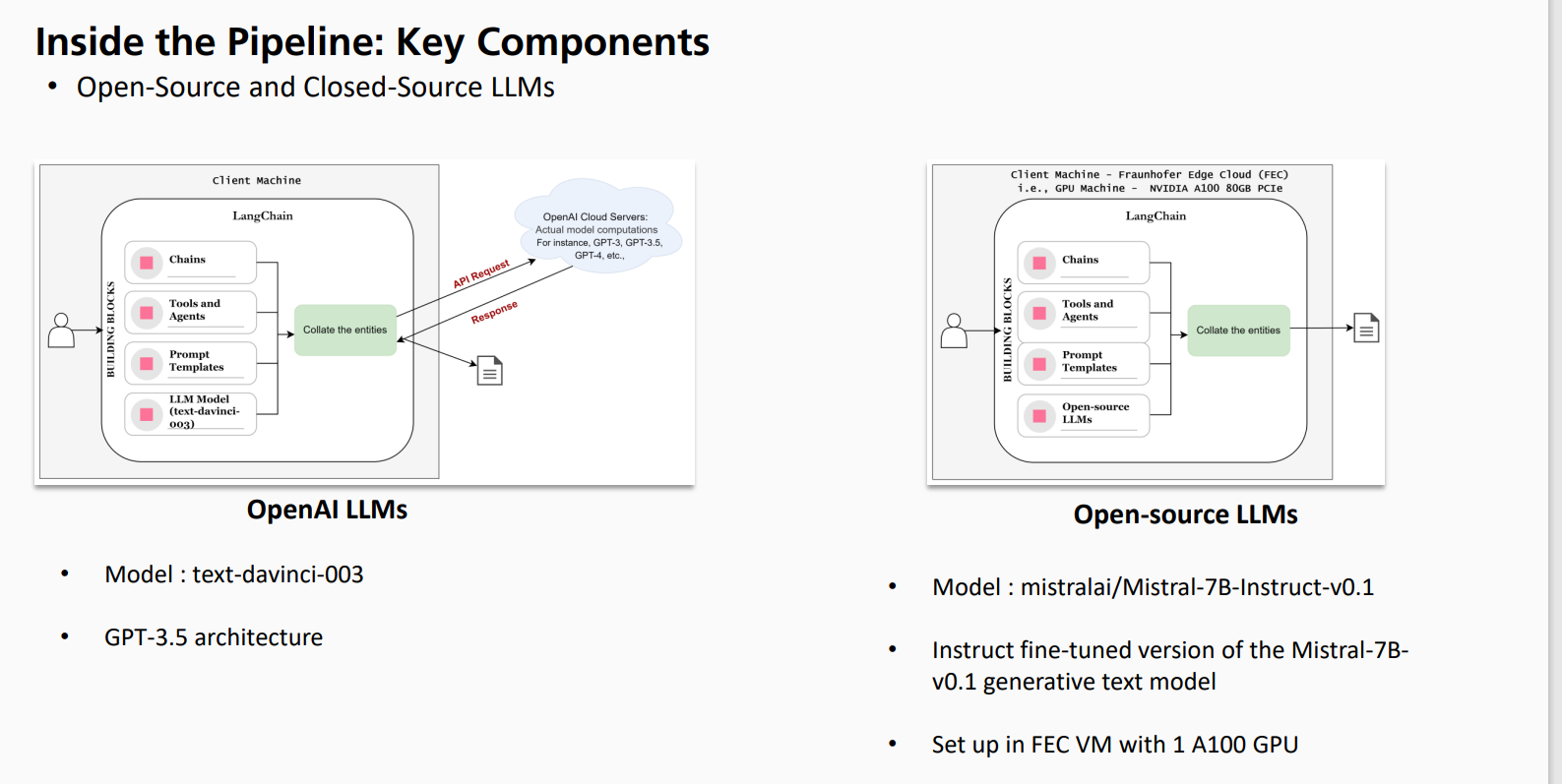
The figure describes the basic elements of an LLM Large Language Model pipeline, showing the use of both open and closed source LLM An analysis of the diagram follows:
Pipeline structure
Client machine: This is the user device where the LangChain framework operates. It interacts with both OpenAI cloud servers for closedsource models and a Fraunhofer Edge Machine FEC equipped with an NVIDIA A GPU for opensource models
LangChain: this framework is the backbone of the pipeline. It provides the necessary tools and functions for interacting with LLMs managing chains and agents, and handling prompts and templates.
LLM models: the pipeline supports two types of LLMs:
OpenAI LLMs closed source: in this case, the pipeline uses the "textdavinci model, which is based on the GPT architecture. The actual computation of the model is performed on the OpenAI cloud servers.
LLM open source: Here, the pipeline uses the model "mistralaiMistralBInstructv a finetuned version of the MistralB model for instruction tracking. This model runs on the FEC engine with an NVIDIA A GPU.
Building blocks: Both types of LLM use similar building blocks:
Chains: These are sequences of calls to LLMs or other utilities that enable complex interactions.
Tools and agents: These elements help to enhance the capabilities of LLMs by allowing them to interact with external systems and perform specific tasks.
Templates: these provide structured prompts to guide LLMs text production.
Output: Both pipelines produce a response that is sent back to the client machine. The response is based on the processing of the input by the LLM and the applied building blocks.
Key differences
Model location: OpenAI's LLMs are hosted on cloud servers, while the open source LLM is built on a local GPU machine FEC
Model type: The OpenAI model is a closedsource, proprietary model, while the opensource model is available for public use and modification.
Computing Environment: The OpenAI models are optimized for their cloud infrastructure, while the open source model is optimized to run on a specific GPU configuration.
Overall
This pipeline offers a flexible and modular approach to using LLMs for various applications. By supporting both open and closed source models, it caters to different needs and preferences. The use of LangChain, chains, agents and templates further enhances the functionality and customization of the pipeline. Identify the problematic points of this proposal by documenting your proposal in detail then submit your own new proposal differentiated from this one to include new schemas. The figure describes the basic elements of an LLM Large Language Model pipeline, showing the use of both open and closed source LLM An analysis of the diagram follows:
Pipeline structure
Client machine: This is the user device where the LangChain framework operates. It interacts with both OpenAI cloud servers for closedsource models and a Fraunhofer Edge Machine FEC equipped with an NVIDIA A GPU for opensource models
LangChain: this framework is the backbone of the pipeline. It provides the necessary tools and functions for interacting with LLMs managing chains and agents, and handling prompts and templates.
LLM models: the pipeline supports two types of LLMs:
OpenAI LLMs closed source: in this case, the pipeline uses the "textdavinci model, which is based on the GPT architecture. The actual computation of the model is performed on the OpenAI cloud servers.
LLM open source: Here, the pipeline uses the model "mistralaiMistralBInstructv a finetuned version of the MistralB model for instruction tracking. This model runs on the FEC engine with an NVIDIA A GPU.
Building blocks: Both types of LLM use similar building blocks:
Chains: These are sequences of calls to LLMs or other utilities that enable complex interactions.
Tools and agents: These elements help to enhance the capabilities of LLMs by allowing them to interact with external systems and perform specific tasks.
Templates: these provide structured prompts to guide LLMs text production.
Output: Both pipelines produce a response that is sent back to the client machine. The response is based on the processing of the input by the LLM and the applied building blocks.
Key differences
Model location: OpenAI's LLMs are hosted on cloud servers, while the open source LLM is built on a local GPU machine FEC
Model type: The OpenAI model is a closedsource, proprietary model, while the opensource model is available for public use and modification.
Computing Environment: The OpenAI models are optimized for their cloud infrastructure, while the open source model is optimi
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


