Question: The first step in analyzing the pay data is to generate the weighted means for each benchmark job. Weighted means, as compared to simple means,
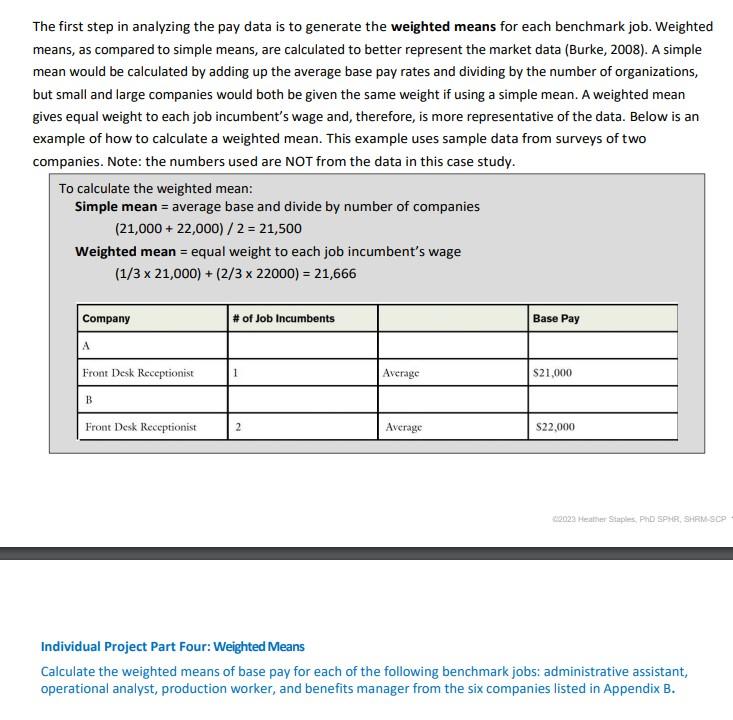
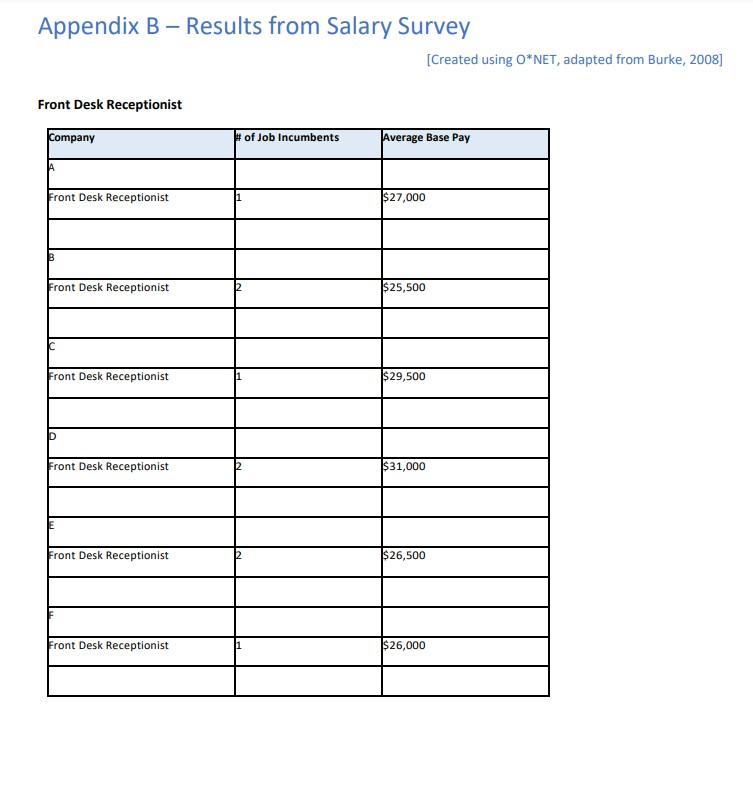
The first step in analyzing the pay data is to generate the weighted means for each benchmark job. Weighted means, as compared to simple means, are calculated to better represent the market data (Burke, 2008). A simple mean would be calculated by adding up the average base pay rates and dividing by the number of organizations, but small and large companies would both be given the same weight if using a simple mean. A weighted mean gives equal weight to each job incumbent's wage and, therefore, is more representative of the data. Below is an example of how to calculate a weighted mean. This example uses sample data from surveys of two companies. Note: the numbers used are NOT from the data in this case study. To calculate the weighted mean: Simple mean = average base and divide by number of companies (21,000+22,000)/2=21,500 Weighted mean = equal weight to each job incumbent's wage (1/321,000)+(2/322000)=21,666 Individual Project Part Four: Weighted Means Calculate the weighted means of base pay for each of the following benchmark jobs: administrative assistant, operational analyst, production worker, and benefits manager from the six companies listed in Appendix B. Appendix B - Results from Salary Survey [Created using O*NET, adapted from Burke, 2008] Front Desk Receptionist
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


