Question: The fzero function The Roots package provides the fzero function that implements the bisection method, only a bit more carefully. The MTH229 package loads this
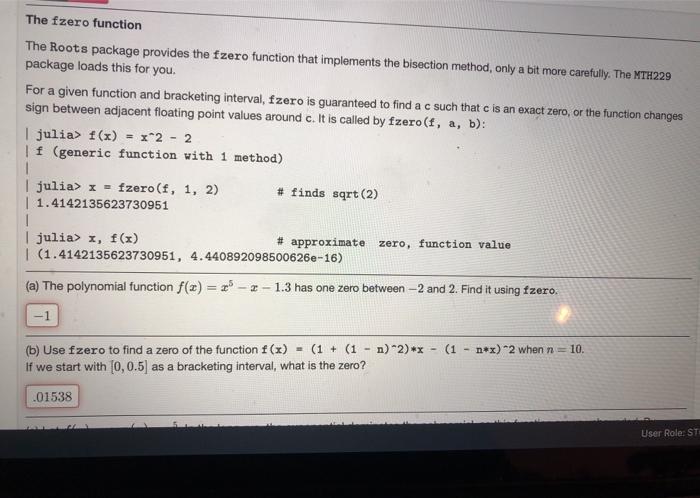
The fzero function The Roots package provides the fzero function that implements the bisection method, only a bit more carefully. The MTH229 package loads this for you. For a given function and bracketing interval, fzero is guaranteed to find a c such that c is an exact zero, or the function changes sign between adjacent floating point values around c. It is called by fzero(f, a, b): | julia) f(x) = x^2 - 2 | f (generic function with 1 method) 1 | julia> x = fzero (f, 1, 2) # finds sqrt(2) | 1.4142135623730951 | julia> x, f(x) # approximate zero, function value I (1.4142135623730951, 4.440892098500626e-16) (a) The polynomial function f(x) = **-*-1.3 has one zero between-2 and 2. Find it using fzero. -1 n*x)2 when n = 10 (b) Use fzero to find a zero of the function f(x) = (1 + (1 - 1)*2)** - (1 If we start with (0,0.5) as a bracketing interval, what is the zero? .01538 User Role: ST
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


