Question: The main reasons for using pointers to arrays are ones of notational convenience and of program efficiency, Pointers to arrays generally result in code that
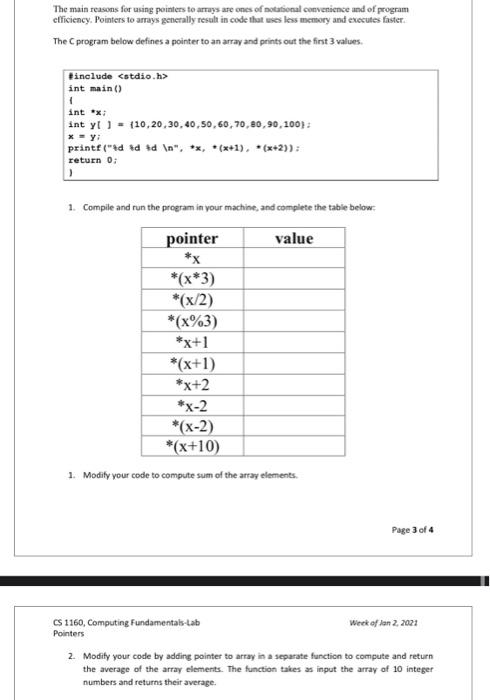
The main reasons for using pointers to arrays are ones of notational convenience and of program efficiency, Pointers to arrays generally result in code that uses less memory and executes faster The program below defines a pointer to an array and prints out the first 3 values. tinclude
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


