Question: The probability of a normally distributed random variable X smaller equal to a value k can be determined by the cumulative distribution function (cdf) which
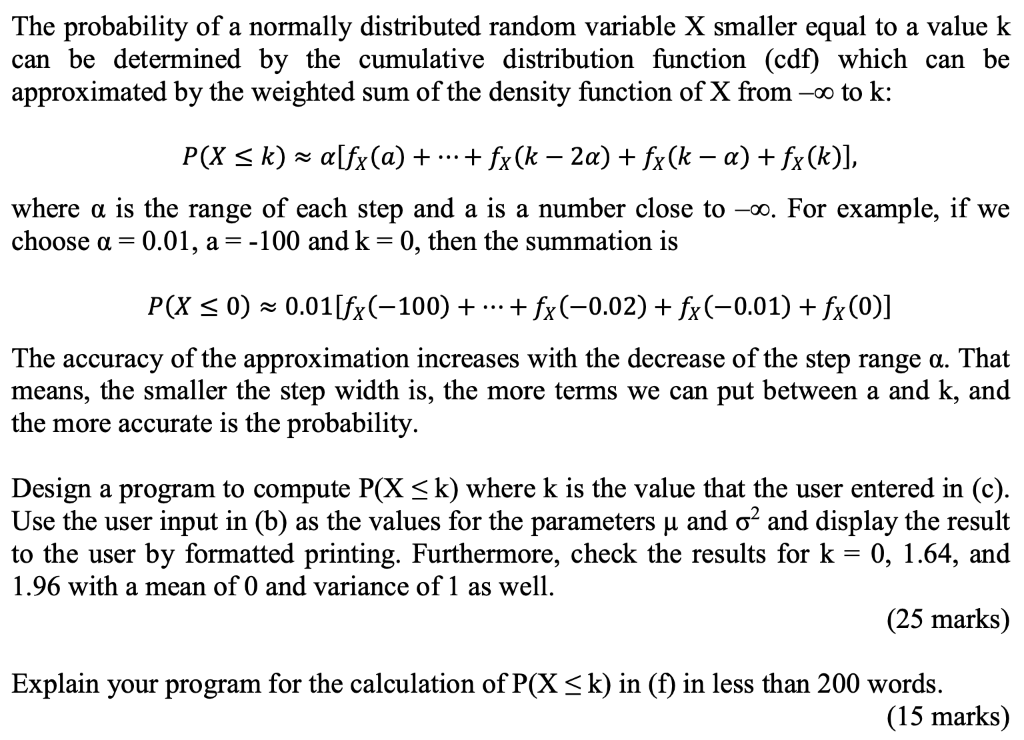
The probability of a normally distributed random variable X smaller equal to a value k can be determined by the cumulative distribution function (cdf) which can be approximated by the weighted sum of the density function of X from 0 to k: P(X = k) = a[fx(a) + + fx (k 2a) + fx(k a) + fx(k)], where a is the range of each step and a is a number close to oo. For example, if we choose a = 0.01, a=-100 and k = 0, then the summation is P(X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


