Question: The problem: Use the Molecular Dynamics program as the below code for a two-dimensional Lennard-Jones system to calculate the pair distribution function for two different
The problem: Use the Molecular Dynamics program as the below code for a two-dimensional Lennard-Jones system to calculate the pair distribution function for two different state points. Choose a relatively low density (or a relatively high temperature) state point so that g(r) has a shape similar to that in a dilute gas and a higher density (or a lower temperature) state point with a liquid-like g(r). For each state point you should plot g(r) and, in addition, the dependence of the kinetic, potential and total energy (all per particle) on time. For each state point indicate the initial equilibration period and the part of the trajectory used to calculate the pair correlation function. * Use the code as the below, modify this code to solve the problem as the above. Here is the example as someone has solved the similar problem with the Monte Carlo program as the following:
finalU - the energy in each step (1 by Nstep matrix) finalConfigurations - the coordinates of all particles in each step (2 by N by Nstep matrix) finalDistances - the pair distances of all particles in each step (N by N by Nstep matrix) moveCount - counts accepted moves
the potential of Lennard-Jonse in reduced units: U = 4*[(1/r)^12 - (1/r)^6] (you can change the 6 with the optional input 'm')
the potential of Lennard-Jonse in non-reduced units: U = 4*epsilon*[(sigma/r)^12 - (sigma/r)^6]
reduced units: T(reduced) = kT/epsilon | r(reduced) = r/sigma | U(reduced) = U/epsilon
usage examples:
create an initial configuration of 100 particles in a 100*100 box: N = 100; L = 100; initialConfig = L*rand(2,N); rho = N/L^2;
choose simulation parameters: T = 1; Nsteps = 1000; maxdr = 1; rCutoff = 2.5;
calculate the pair distances: initialDistances = sqrt(bsxfun(@(x1,x2) (x1-x2).^2 ,... initialConfig(1,:),initialConfig(1,:)')... +bsxfun(@(x3,x4) (x4-x3).^2 ,... initialConfig(2,:),initialConfig(2,:)'));
calculate the initial energy (up to the cutoff): d = initialDistances(and(initialDistances 0)); initialU = 4*sum(sum(d.^(-12)-d.^(-6)));
calculate energy [finalU,~,~,finalConfiguration,finalDistances,moveCount] = ... MonteCarlo2DLJHeart(N,T,rho,Nsteps,maxdr,initialConfig,rCutoff... ,initialDistances,initialU)
also calculate the pressure. first calculate the initial virial: virial = -(2*rho/N)*(sum(sum(6*d.^(-6) - 12*d.^(-12))));
now calculate the energy and pressure using monte carlo [finalU,finalVirial,finalPressure,finalConfiguration,finalDistances,moveCount] = ... MonteCarlo2DLJHeart(N,T,rho,Nsteps,maxdr,initialConfig,rCutoff... ,initialDistances,initialU,'virial',virial);

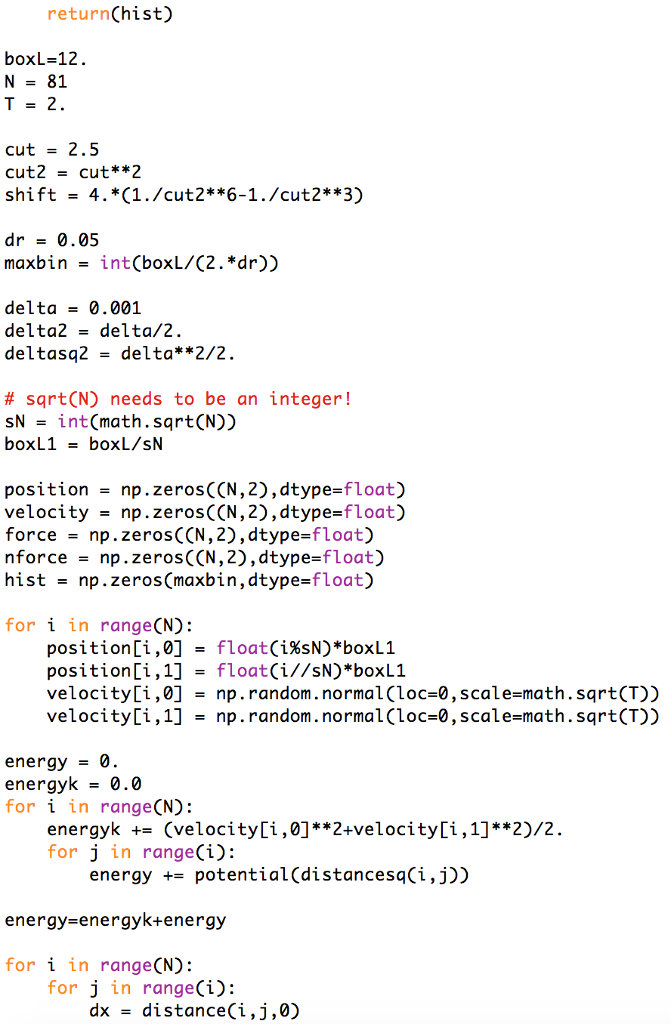


mport numpy as np import math def ff(dx, dy, i): if d2 > cut2 return 0. else: return fff*dx if i == 1: return fff*dy def distance(i,j,k): distancex - position[i,0]-position[j,0] distancex -- boxL*round(distancex/boxL) return distancex ifk== 1: distancey = position [i,1]-position[j,1] distancey -- boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancey def potential(d2): if d2 > cut2: return 0 else: return 4.*(di6**2-di6)-shift def distancesq(i,j): distancex position [i ,0]-position [j,0] distancex -- boxL*round(distancex/boxL) distancey = position [1,1]-position [j,1] distancey -- boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancex**2+distancey**2 def gr(hist): for i in rangeCN): for j in range(i): bin = round(math. sqrt(distancesq(i,j))/dr) if( bin cut2 return 0. else: return fff*dx if i == 1: return fff*dy def distance(i,j,k): distancex - position[i,0]-position[j,0] distancex -- boxL*round(distancex/boxL) return distancex ifk== 1: distancey = position [i,1]-position[j,1] distancey -- boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancey def potential(d2): if d2 > cut2: return 0 else: return 4.*(di6**2-di6)-shift def distancesq(i,j): distancex position [i ,0]-position [j,0] distancex -- boxL*round(distancex/boxL) distancey = position [1,1]-position [j,1] distancey -- boxL*round(distancey/boxL) return distancex**2+distancey**2 def gr(hist): for i in rangeCN): for j in range(i): bin = round(math. sqrt(distancesq(i,j))/dr) if( bin
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


