Question: The program to be written should read some numbers any number of those on a single line and store them in an ArrayList. The numbers


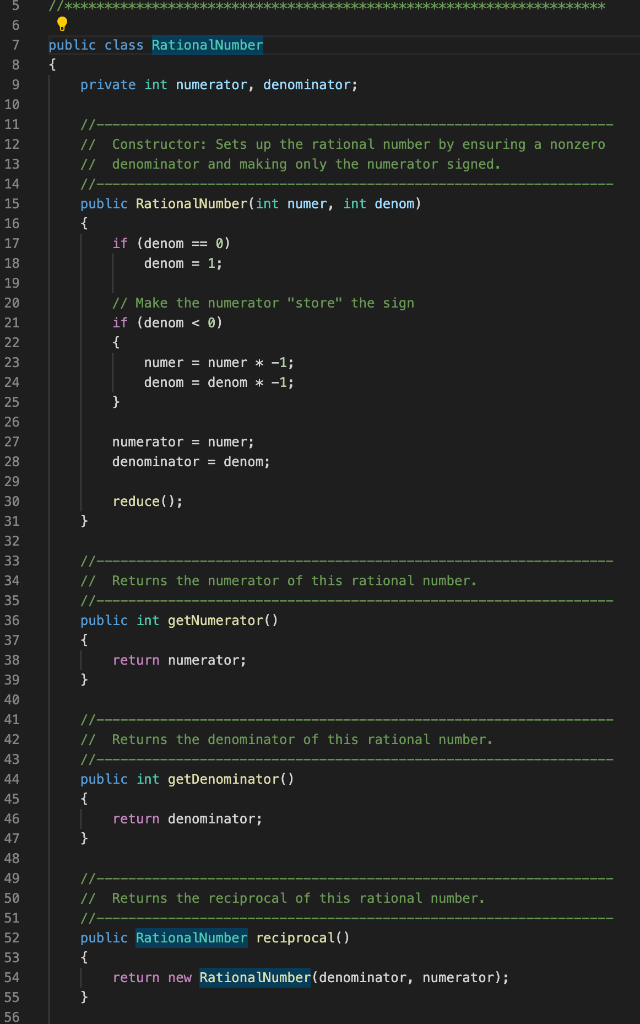
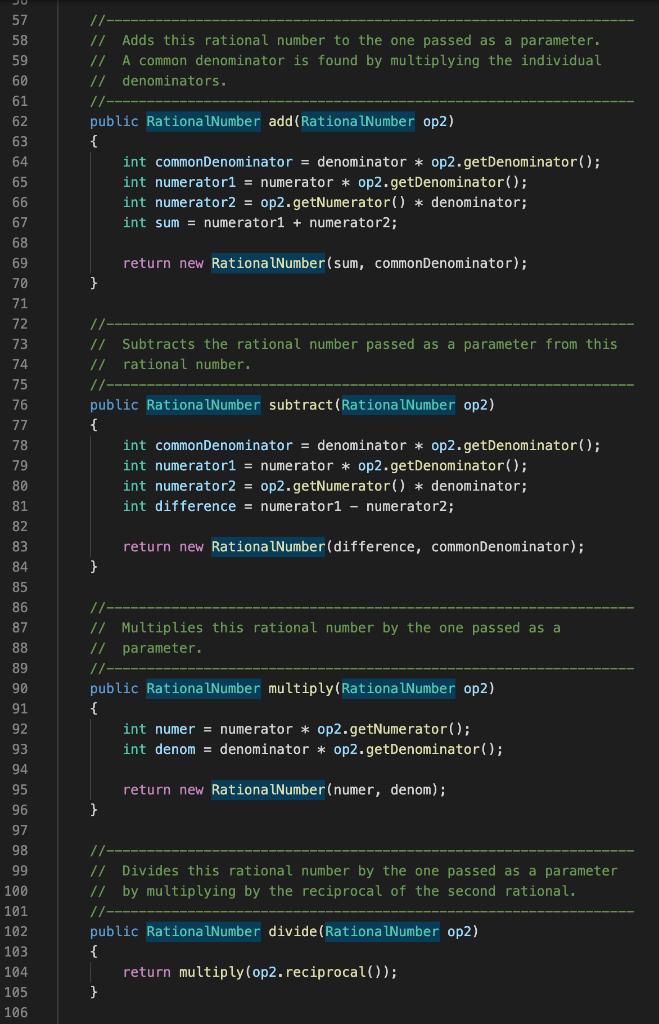
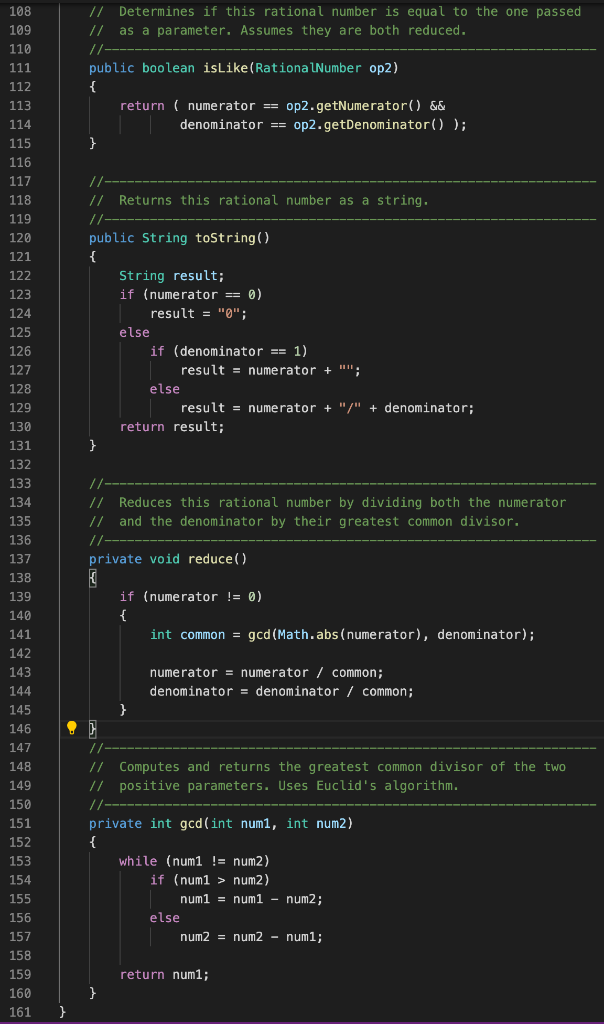
The program to be written should read some numbers any number of those on a single line and store them in an ArrayList. The numbers read could be integers, doubles, and rational numbers. Then, it should go through each element of that list, printing each on a single line and add it (as a double) into a sum. This sum should be printed at the end. Here is an example of what the input/output should look like (the second line, in bold, is what the user enters): Enter a list of numbers separated by a space: 3 5.5 10 4/5 The list is: 3 5.5 10 4/5 The sum is: 19.3 This assignment can be done incrementally, over 6 steps. Step 1: Read the input line, and decompose each part (i.e., number but still as a String) into an array using the split method in the String class. You can print each element of your array to confirm what you got (as strings) but do not do any sum yet. Step 2: When looping over each number, have the code to check which type it is. Hint: if the number contains a ., it is a double. If the number contains a /, it is a rational number. Otherwise it is an int. In the case of an int or a double, parse them properly to an int variable or double variable, using the parsing method of the corresponding Wrapper class. In the case of a rational number, use the split method again to separate the numerator and the denominator. Parse each of these 2 numbers (as int), and create an object of type RationalNumber using these 2 values. Use the RationalNumber class provided to you. Step 3: At the beginning of your program, create an ArrayList of integers. As you are looping over all numbers read (array in Step 1), when the number is an integer (as determined in Step 2), add it to the ArrayList. Of course, use the parsed number for this, not the original string. Step 4: In a separate loop (after the one you have from the steps above), create another loop to go over all elements of your ArrayList, printing each of these elements and adding them up into the sum. Note: the sum at this point will be for the int values only. For example, if the example input above was provided, the list would be only 3 and 10, and the sum would be 13. Step 5: Handle the doubles as well (i.e., adding them to the ArrayList). Of course, the type of objects the ArrayList contains will have to change, so that you can put both ints and doubles in it. Use a class that both Integer and Double are inheriting from (but do not use the Object class). Then modify your program so that it handles both integers and doubles (i.e., storing the numbers in the first loop, and printing them / doing the sum in the second loop). In particular, for adding up each number in the second loop, you will need to access the numbers in a common way (hint: there is a common method you can use that will extract the value as a double). Step 6: Finally, handle the rational numbers as well (i.e., adding the objects created in Step 2 into the ArrayList). Now since this class (RationalNumber) does not inherit from the same class as Integer and Double, you will not be able to use it as is, as a valid type for your ArrayList. Modify the RationalNumber class so that it can be used in the ArrayList (i.e., make it inherit from the same class as the one currently used for your ArrayList and add all the code necessary so that such inheritance is properly implemented). Then modify the rest of your program so that it handles all 3 types of input (similar modifications as for Step 5).
Tasks: The program to be written should read some numbers - any number of those - on a single line and store them in an ArrayList. The numbers read could be integers, doubles, and rational numbers. Then, it should go through each element of that list, printing each on a single line and add it (as a double) into a sum. This sum should be printed at the end. Here is an example of what the input/output should look like (the second line, in bold, is what the user enters): Enter a list of numbers separated by a space: 3 5.5 10 4/5 The list is: 3 5.5 10 4/5 The sum is: 19.3 This assignment can be done incrementally, over 6 steps. Step 1: Read the input line, and decompose each part (i.e., number but still as a String) into an array using the split method in the String class. You can print each element of your array to confirm what you got (as strings) but do not do any sum yet. Step 2: When looping over each number, have the code to check which type it is. Hint: if the number contains a ".", it is a double. If the number contains a l", it is a rational number. Otherwise it is an int. In the case of an int or a double, parse them properly to an int variable or double variable, using the parsing method of the corresponding Wrapper class. In the case of a rational number, use the split method again to separate the numerator and the denominator. Parse each of these 2 numbers (as int), and create an object of type Rational Number using these 2 values. Use the RationalNumber class provided to you. Step 3: At the beginning of your program, create an ArrayList of integers. As you are looping over all numbers read (array in Step 1), when the number is an integer (as determined in Step 2), add it to the ArrayList. Of course, use the parsed number for this, not the original string. Step 4: In a separate loop (after the one you have from the steps above), create another loop to go over all elements of your ArrayList, printing each of these elements and adding them up into the sum. Note: the sum at this point will be for the int values only. For example, if the example input above was provided, the list would be only 3 and 10, and the sum would be 13. Step 5: Handle the doubles as well (i.e., adding them to the ArrayList). Of course, the type of objects the ArrayList contains will have to change, so that you can put both ints and doubles in it. Use a class that both Integer and Double are inheriting from (but do not use the "Object" class). Then modify your program so that it handles both integers and doubles (i.e., storing the numbers in the first loop, and printing them / doing the sum in the second loop). In particular, for adding up each number in the second loop, you will need to access the numbers in a common way (hint: there is a common method you can use that will extract the value as a double). Step 6: Finally, handle the rational numbers as well (i.e., adding the objects created in Step 2 into the ArrayList). Now since this class (Rational Number) does not inherit from the same class as Integer and Double, you will not be able to use it as is, as a valid type for your ArrayList. Modify the RationalNumber class so that it can be used in the ArrayList (i.e., make it inherit from the same class as the one currently used for your ArrayList - and add all the code necessary so that such inheritance is properly implemented). Then modify the rest of your program so that it handles all 3 types of input (similar modifications as for Step 5). //******* ********************* * ******************* ******** 7 8 public class RationalNumber private int numerator, denominator; //------- // Constructor: Sets up the rational number by ensuring a nonzero // denominator and making only the numerator signed. public RationalNumber(int numer, int denom), { if (denom == 0) denom = 1; // Make the numerator "store" the sign if (denom num2) num1 = num1 - num2; else num2 = num2 - numi; 159 return num1; 160
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


