Question: The question : You are required to draw a Mind map For the subject in the pictures its about ORGANAIZATION STRUCTURE Organization structure: formal system




The question : You are required to draw a Mind map For the subject in the pictures its about ORGANAIZATION STRUCTURE
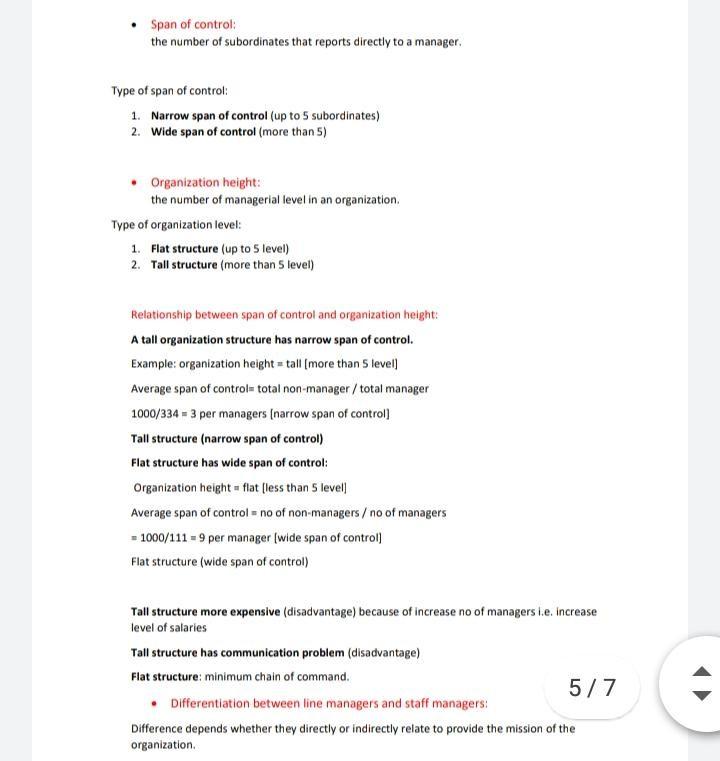
Organization structure: formal system of task, jobs and specifying working relationship. Organizing: process of creating structure of working relationship to achieve organization goals. Organization design: process by which managers make specific choices to choose. Organization steps: Job design Departmentalization Allocation of authority Distribution of authority / power Integration 1. Job design: Process by which managers divide task to be performed job. Dividing task (job) Job simplification: process by which manager reduce the number of tasks of each works that leads to inefficiency due to boredom. Job design approaches: 1. Job enlargement 2. Job enrichment 3. Job characteristics 1. Job enlargement: More task of the same nature and level Adding ticks horizontally 2. Job enrichment: More of different task at higher level Increase the degree of responsibility of an employee Adding tasks vertically 3. Job characteristics approach: Consider 5 characteristics: Skills variety Task identify Task significance Lead to higher motivation + higher performance + higher satisfaction Autonomy feedback Skills variety: for examines the extent to which a job requires an employees to we wider range og different skills, abilities and knowledge. Task identify: for examines the extent to which a job requires a workers to perform au the task from beginning to the end of the process. Task significance: examines the extent to which a worker feel his or her job meaningful because of effect on the outsiders. Feedback: extent to which a workers receives clear and direct information regarding on how well he or she perform the job. Autonomy: degree of freedom in work that an employee have. 2. Departmentalization: Process of grouping jobs (departments) 3/7 Departmentalization bases Functional Divisional Matrix (temporary) Product team (permanent) Hierarchical structure (Level within the org) Team based structure ( 1-3 levels maximum) Hierarchical structure: 1. Functional structure employees doing similar skills / use the same knowledge /tools/ techniches to perform their job are grouped into one department 2. Divisional structure composed of separate business units (divisional A+B+C) within which are the functions (IT and marketing) that work together. Types of divisional: Product: each product line or business is handled by a self-contained department. Customer: each type of a customers is served by a self-contained department. Location: each region of a country (local) or area of the world (international) is served by a self-contained division Hybrid: a structure of large organization that has more divisions and simultaneously uses many different bases of divisional departmentalization. Appropriate for large organization. Advantage of divisional departmentalization: speed up decision Disadvantage: narrow focus on the type. Team based departmentalization: Matrix team: consist of a leader and members They move from one team to another depending on requirement. Most flexible (advantage) Dual reporting relationship lead conflicts (disadvantage) Each team member report to: team leader and functional manager Product team: Consist of a leader and members. Team are permanently working together. Members repots to team leader only 4/7 3. Allocation of authority Sub topics: Authority and hierarchy. Span of control Organization height: Differentiation blow line managers and staff managers. Authority: authority (power + accountability + making decisions) Authority is the power to hold people accountable for their actions and to make decisions concerning the use of organizations resources. Hierarchy of authority: the level of power in an organization. Chain of command line of authority extending the upper level to the lowest level and clarifies who reports to whom Hierarchy of authority: An organization chain of command specifying the authority of each manager. Span of control the number of subordinates that reports directly to a manager, Type of span of control: 1. Narrow span of control (up to 5 subordinates) 2. Wide span of control (more than 5) Organization height: the number of managerial level in an organization. Type of organization level: 1. Flat structure (up to 5 level) 2. Tall structure (more than 5 level) Relationship between span of control and organization height: A tall organization structure has narrow span of control. Example: organization height = tall (more than 5 level) Average span of control total non-manager / total manager 1000/334 - 3 per managers (narrow span of control] Tall structure (narrow span of control) Flat structure has wide span of control: Organization height = flat (less than 5 levell Average span of control = no of non managers / no of managers - 1000/111 - 9 per manager (wide span of controll Flat structure (wide span of control) Tall structure more expensive (disadvantage) because of increase no of managers i.e. increase level of salaries Tall structure has communication problem (disadvantage) Flat structure: minimum chain of command. 5/7 Differentiation between line managers and staff managers: Difference depends whether they directly or indirectly relate to provide the mission of the organization Task force are often called ad hoc committees because they temporary once the task is completed the task force is dismissed. 3) Cross-function teams: Formed by assigning members from different divisions permanently to solve recurring problems 4) Integration roles: It a position /division created to coordinate with other departments. Created for comply need onlyStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


