Question: The triangular wedge shown in Figure 2 resides in air moving at M = 3. Making the assump- tions that (1) the flow separates

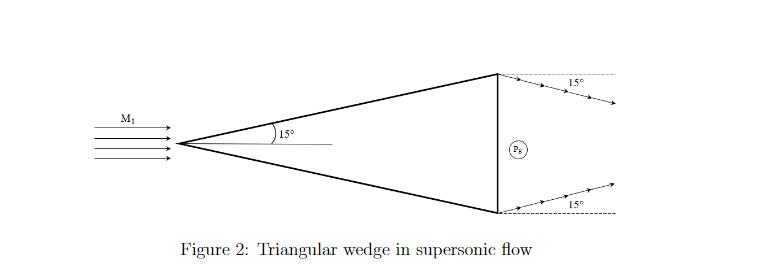
The triangular wedge shown in Figure 2 resides in air moving at M = 3. Making the assump- tions that (1) the flow separates at the corners, with the streamlines trailing downstream of the corners deflected toward the base at an angle of 15 degrees from the horizontal and (2) the base pressure PB is the arithmetic average between the pressure downstream of the expansion waves, and the free-stream pressure P. Pdownstream + P 2 PB Find the drag coefficient of the triangular wedge. M 15 (Pg Figure 2: Triangular wedge in supersonic flow 15 15
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Solutions Step 1 The drag coefficient of the triangular wedge is 1 This can be found by analyzing th... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


