Question: There's going to be several screenshots, but please note I have answered most of them. I'm having trouble at the end and there's one incorrect
There's going to be several screenshots, but please note I have answered most of them. I'm having trouble at the end and there's one incorrect number I put in....I realized for the first number I got wrong I got the 7 and 3 mixed up, there's one further down that's incorrect and I'm not sure why. I need help on the last couple of screenshots filling that information out as well.
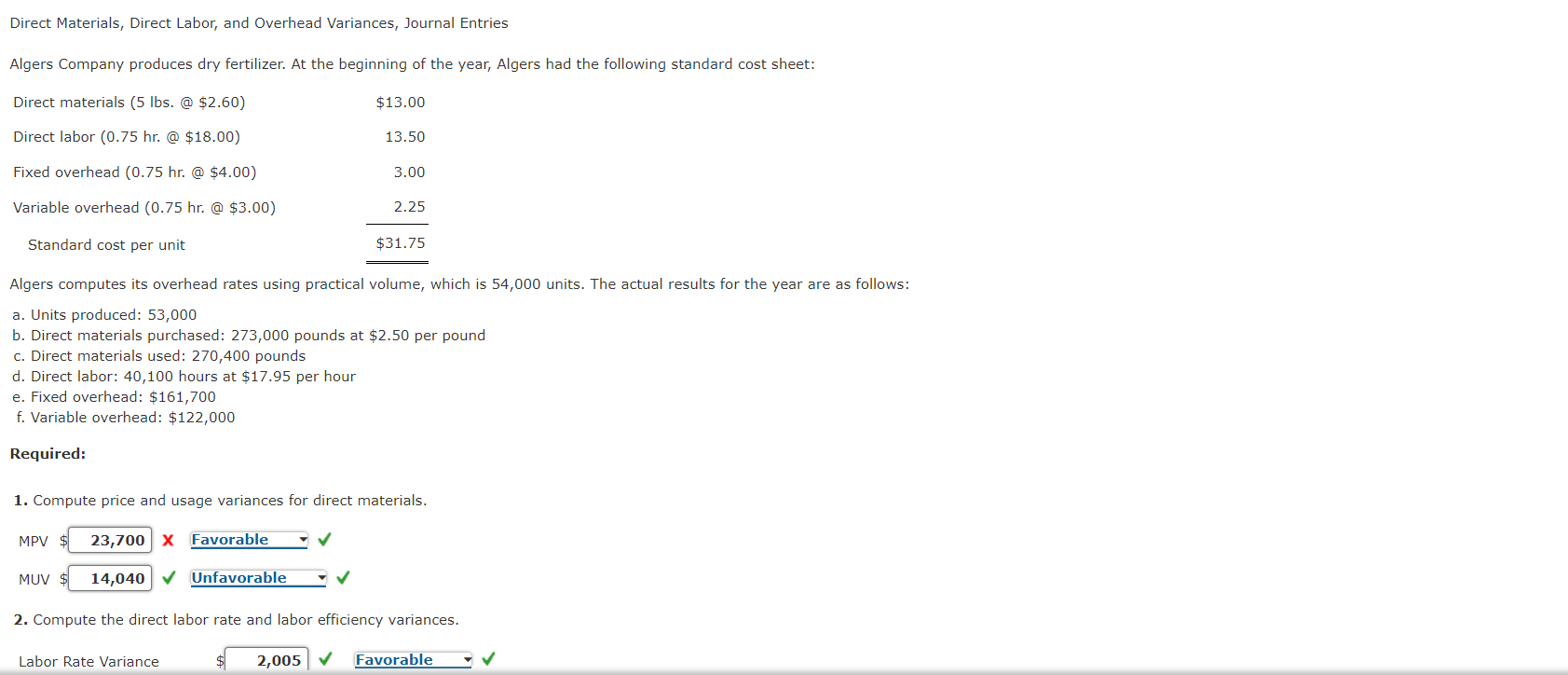
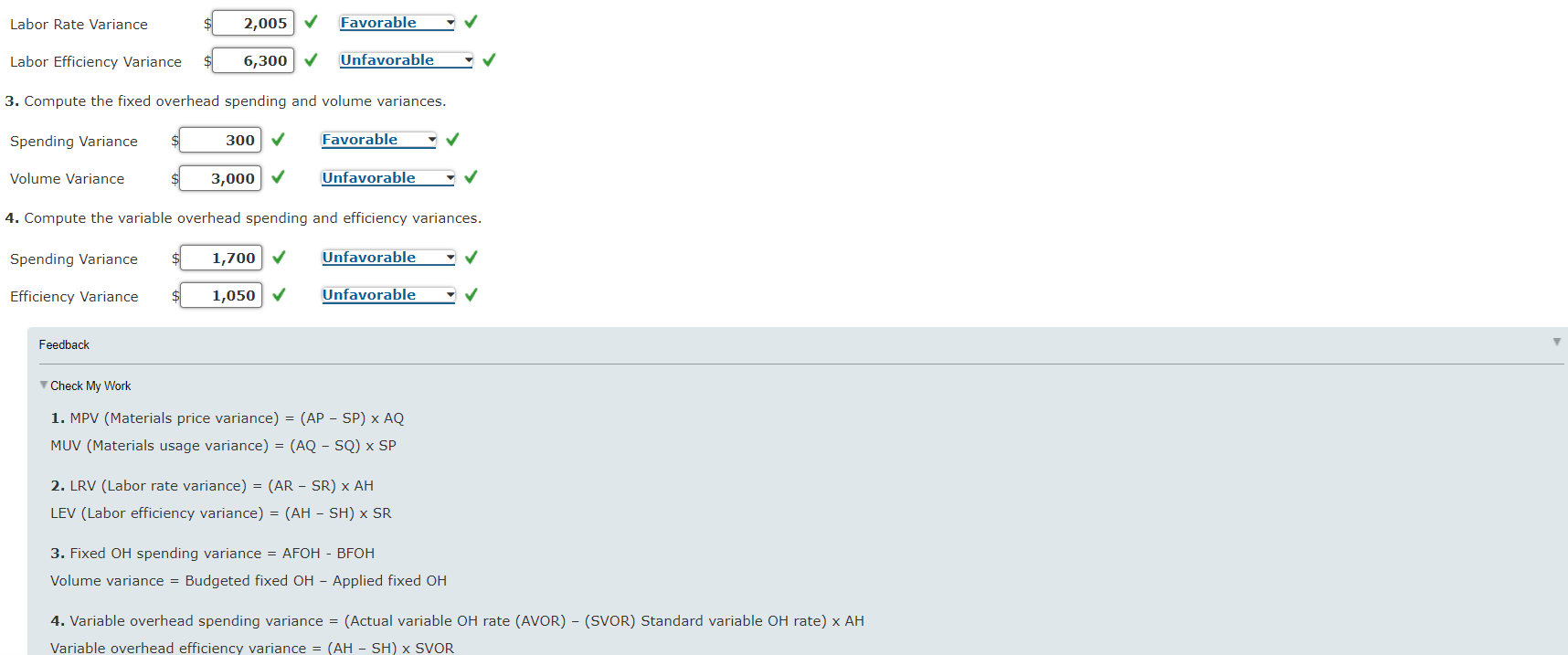
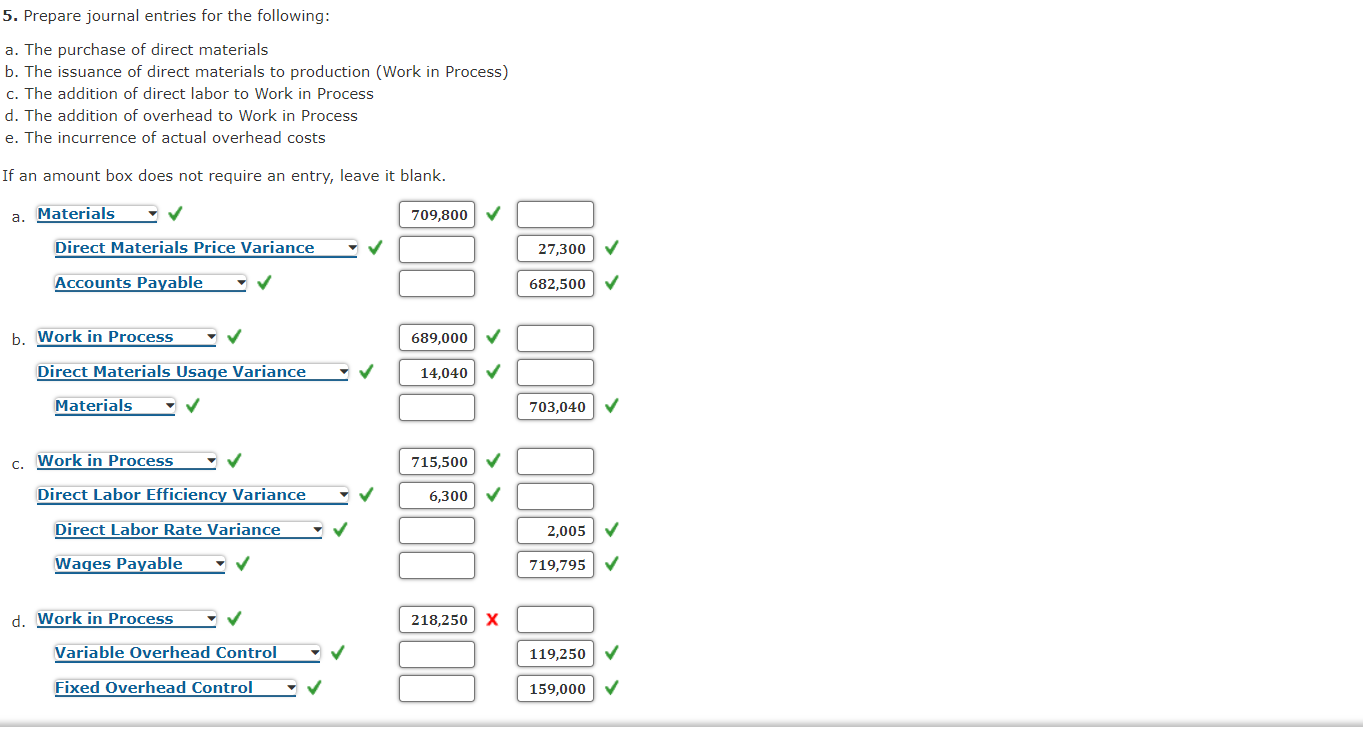
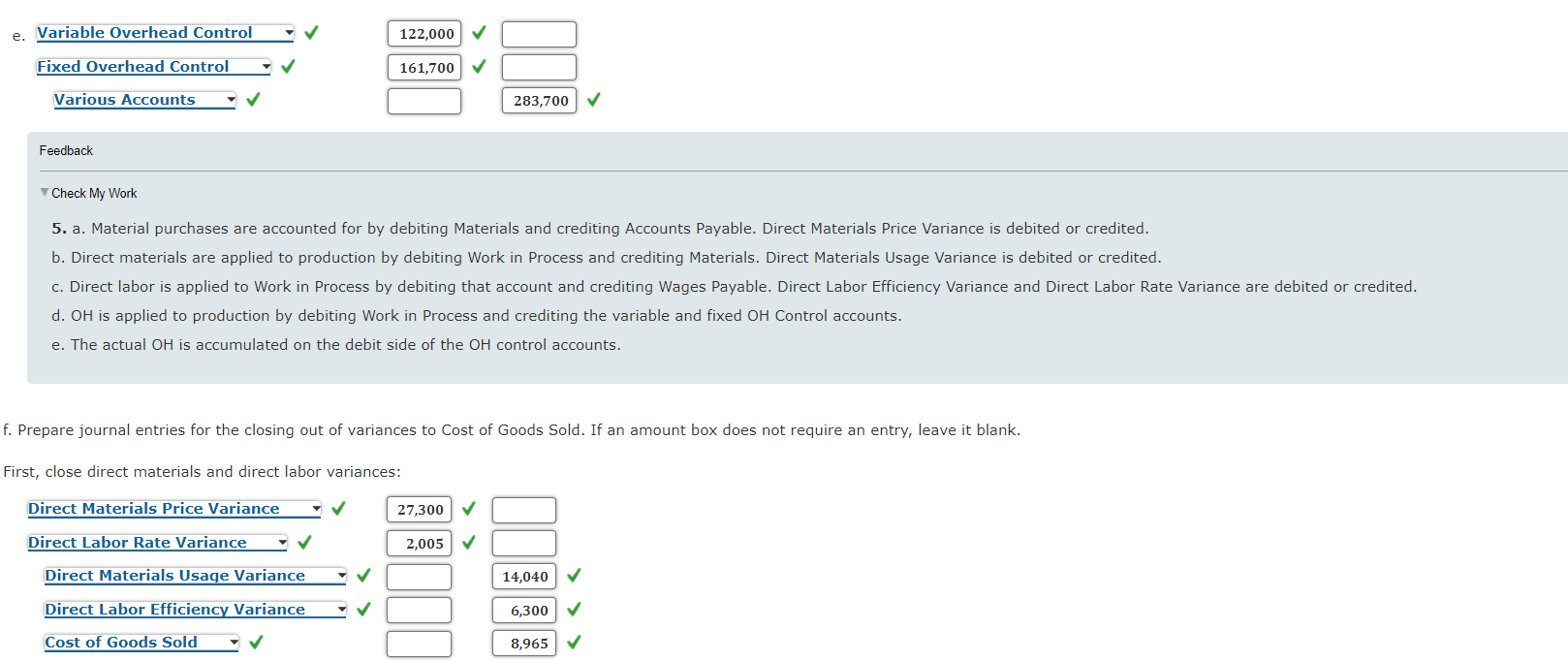
Direct Materials, Direct Labor, and Overhead Variances, Journal Entries Algers Company produces dry fertilizer. At the beginning of the year, Algers had the following standard cost sheet: Direct materials (5 lbs. @ $2.60) $13.00 Direct labor (0.75 hr. @ $18.00) 13.50 Fixed overhead (0.75 hr. @ $4.00) 3.00 Variable overhead (0.75 hr. @ $3.00) 2.25 Standard cost per unit $31.75 Algers computes its overhead rates using practical volume, which is 54,000 units. The actual results for the year are as follows: a. Units produced: 53,000 b. Direct materials purchased: 273,000 pounds at $2.50 per pound c. Direct materials used: 270,400 pounds d. Direct labor: 40,100 hours at $17.95 per hour e. Fixed overhead: $161,700 f. Variable overhead: $122,000 Required: 1. Compute price and usage variances for direct materials. MPV 23,700 X Favorable MUV 14,040 Unfavorable 2. Compute the direct labor rate and labor efficiency variances. Labor Rate Variance $ 2,005 Favorable Labor Rate Variance 2,005 Favorable Labor Efficiency Variance 6,300 Unfavorable 3. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. Spending Variance 300 Favorable Volume Variance 3,000 Unfavorable 4. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. Spending Variance 1,700 Unfavorable Efficiency Variance 1,050 Unfavorable Feedback Check My Work 1. MPV (Materials price variance) = (AP - SP) x AQ MUV (Materials usage variance) = (AQ - SQ) x SP 2. LRV (Labor rate variance) = (AR - SR) x AH LEV (Labor efficiency variance) = (AH - SH) x SR 3. Fixed OH spending variance = AFOH - BFOH Volume variance = Budgeted fixed OH Applied fixed OH 4. Variable overhead spending variance = (Actual variable OH rate (AVOR) - (SVOR) Standard variable OH rate) x AH Variable overhead efficiency variance = (AH - SH) X SVOR 5. Prepare journal entries for the following: a. The purchase of direct materials b. The issuance of direct materials to production (Work in Process) c. The addition of direct labor to Work in Process d. The addition of overhead to Work in Process e. The incurrence of actual overhead costs If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. a. Materials 709,800 Direct Materials Price Variance 27,300 Accounts Payable 682,500 b. Work in Process 689,000 Direct Materials Usage Variance 14,040 Materials 703,040 c. Work in Process 715,500 Direct Labor Efficiency Variance 6,300 Direct Labor Rate Variance 2,005 Wages Payable 719,795 d. Work in Process 218,250 X Variable Overhead Control 119,250 Il Fixed Overhead Control 159,000 e. Variable Overhead Control 122,000 Fixed Overhead Control 161,700 Various Accounts 283,700 Feedback Check My Work 5. a. Material purchases are accounted for by debiting Materials and crediting Accounts Payable. Direct Materials Price Variance is debited or credited. b. Direct materials are applied to production by debiting Work in Process and crediting Materials. Direct Materials Usage Variance is debited or credited. c. Direct labor is applied to Work in Process by debiting that account and crediting Wages Payable. Direct Labor Efficiency Variance and Direct Labor Rate Variance are debited or credited. d. OH is applied to production by debiting Work in Process and crediting the variable and fixed OH Control accounts. e. The actual OH is accumulated on the debit side of the OH control accounts. f. Prepare journal entries for the closing out of variances to Cost of Goods Sold. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. First, close direct materials and direct labor variances: Direct Materials Price Variance 27,300 Direct Labor Rate Variance 2,005 Direct Materials Usage Variance 14,040 Direct Labor Efficiency Variance 6,300 Cost of Goods Sold 8,965 Check My Work 5. f. The OH variances are disposed of by closing them to Cost of Goods Sold if they are not material or by prorating them among Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold Second, recognize the overhead variances: If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Feedback Check My Work Incorrect Third, close the overhead variances: Note: Close the variances with a debit balance first. For compound entries, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Check My Work Incorrect Third, close the overhead variances: Note: Close the variances with a debit balance first. For compound entries, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Feedback Check My Work Incorrect Feedback Check My Work Partially correct
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


