Question: This assignment gives you practice with basic game theory tools. Real background Before Canada legalized recreational cannabis in 2018, some observers expected the new legal
This assignment gives you practice with basic game theory tools. Real background Before Canada legalized recreational cannabis in 2018, some observers expected the new legal industry would provide a goldrush of profits, jobs, and taxes. After legalization, however, competition between licensed cannabis firms pushed down prices and profits; consequently, many firms are struggling to stay in business. These firms want governments to reduce the excise taxes charged on cannabis. On dried cannabis, for example, the federal-provincial excise tax is fixed at $1 per gram, regardless of the products retail price or the retailers profitability. Hypothetical story A cannabis retailers association would like the government to reduce its cannabis excise tax. A tax reduction would give the retailers 3 options for improving their profits: Charge the current retail prices and sell the same amount of product but with higher margins. Charge slightly lower prices and sell slightly more product at slightly higher margins. Charge much lower prices and sell much more product at the current margins. Although the government wants retailers to be profitable, it also wants the tax revenue, and it worries that lower prices could encourage excessive cannabis usage. Consequently, the government is considering 3 policy options: Maintain the existing $1 per gram fixed tax. Decrease the fixed tax amount from $1 per gram to $0.50 per gram. Replace the fixed dollar amount by a percentage of the products price, so that discount products incur less tax while premium products incur more. The table below shows the payoffs for each combination of decisions. The first number represents the governments popularity on opinion surveys, in percentage points; the second number is the average retailers monthly pre-tax profit, in thousands of dollars.
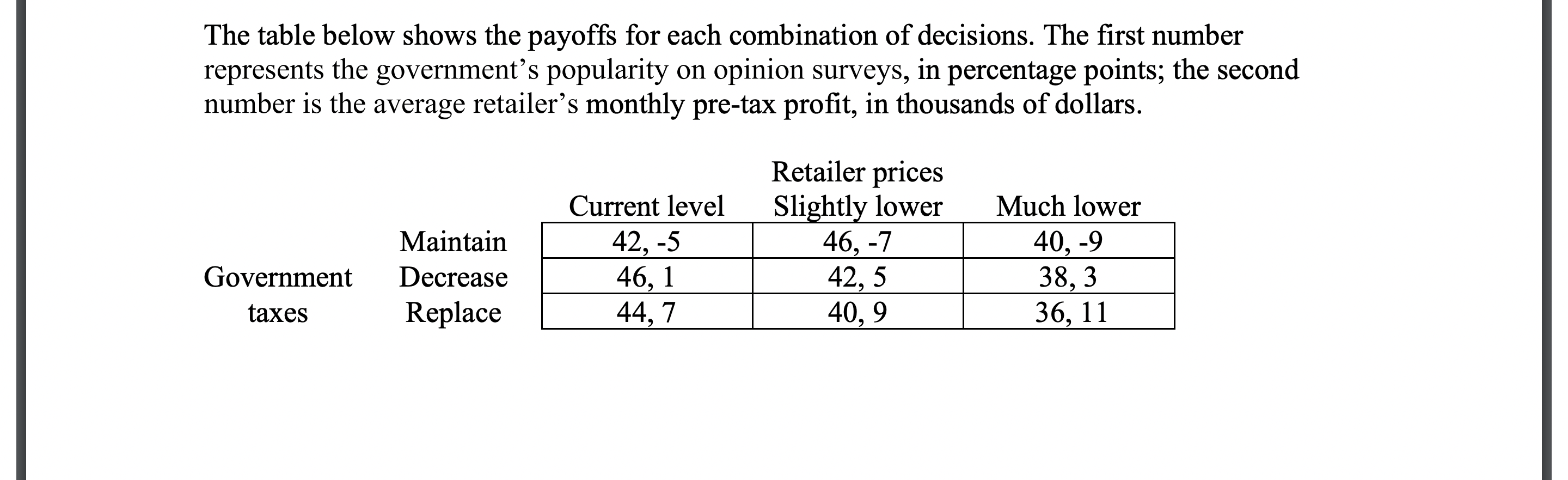
Questions 1. First, treat this situation as a simultaneous-move game between the government and the retailers. i. Analyze the table by applying concepts like dominance, best responses, etc. For each player, can any actions be ruled out, and/or does one strategy dominate all the others? What are the Nash equilibria, if any? ii. Is this game zero-sum, constant-sum, or variable sum? Which category of classic games, if any, does this game best fit? iii. If players use their maximin strategies, which actions will they choose? iv. Based on your analysis, what do you expect the government and the retailers to do? Given those two actions, what will be the expected payoff for each player?
2. Next, treat this situation as a sequential-move game where the government moves first. i. Model the situation by drawing the extensive form game tree. ii. What is the complete rollback equilibrium strategy for each player? iii. Based on your analysis, what should we expect the government and the retailers to do? Given those two actions, what will be the expected payoff for each player?
The table below shows the payoffs for each combination of decisions. The first number represents the government's popularity on opinion surveys, in percentage points; the second number is the average retailer's monthly pre-tax profit, in thousands of dollars
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


