Question: This code in Sound.java will apply to the next question 1: public void bumpRight() 2: { 3: SoundSample[] pA = this.getSamples(); 4: for (int i
This code in Sound.java will apply to the next question 1: public void bumpRight() 2: { 3: SoundSample[] pA = this.getSamples(); 4: for (int i = 1; i
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. If the pixel array contains: [2,3,4,5] what is the pixel array after calling bumpRight()?
2. In images, it is often useful to detect corners where corners are defined as the intersection of two edges. A very strong example of a corner would be: black black black black black white white white black white white white black white white white
This is an open-ended question for you to think about. Assume you are working with a grayscale image to make the problem easier. To solve this problem, multiple approaches are feasible. Think about how you might program corner detection (try some implementations and see). In general, to detect corners, you will need to look at the difference between the color of the center pixel and the color of the pixels above, below, to the left, and to the right. How would you define a corner in terms of colors? How would you write the code to then find the corners based on that definition? If you wish to code it - assume you have a Picture object p. Write a function in Picture.java called cornerDetect which takes an integer parameter threshold (perhaps used to with colorDistance to see if pixel colors are far apart) and returns a Picture object. The Picture returned should the same size as the original that has all corners white and all non-corners black based on your definition of a corner. If you wish to test your method on a picture try drawing a solid rectangle (you can easily draw one) and see if your approach correctly catches all 4 corners (and just those 4 corners).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3. We are creating a new Zoo class. The zoo can only hold elephants and lions. It has the following instance variables: int numElephants; int numLions; int numAnimals; If we have a Zoo(int elephants, int lions, int animals) constructor, write one constructor that ensures the legitimacy of the parameters (like you did with your weight and height ).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. Draw the memory model and output for the following code: public static void main(String[] args){ World myWorld=new World(200,200); Turtle john; Turtle mary; Turtle sara; john=new Turtle(100,100,myWorld); mary=new Turtle(75,150,myWorld); john.forward(25); mary.forward(25); sara=john; sara.forward(25); sara=mary; sara.turnLeft(); john=mary; sara.forward(25); mary=sara; john.turnRight(); john.forward(50); john=new Turtle(150,50,myWorld); sara.forward(25); mary.turnLeft(); mary.forward(50); john.forward(25); }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. What does this do? X%(1
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. What is the resulting value if X is 27?
7. Draw the image shown by this code: import java.awt.Color; public class PictureManip{ public static void main(String[] args){ Picture pic=new Picture(100,100); Pixel[] pixelArray=pic.getPixels(); for (int i=0;i
8. Write a method in the Sound class (including its header) named clipIntoFromEnd. This method takes two parameters: an integer (nsamples) and a Sound (other), in that order. The method should copy the first nsamples SoundSample values from other (the parameter Sound object) into the calling objects SoundSample array, but these SoundSample values should be positioned at the end of the calling objects SoundSample array. The method doesnt return anything to the caller and it does not modify the parameter Sound object. If either the parameter object OR the calling object (or both) has fewer samples than nsamples, then the method should not copy any samples at all. It should print a message that states Not enough samples and then return, leaving the calling object unchanged. Here is an example: If nsamples is 2, then the value of the first 2 samples in the parameter object are copied into the the last 2 samples in the calling objects SoundSample array. SoundSamples are kept in the same order when they are copied. This example is shown here:
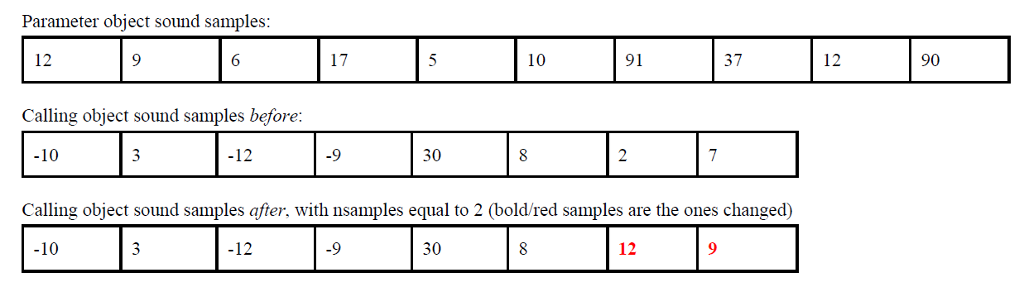
Your code should also do errorchecking for null references from the Sound parameter. If the Sound parameter is null, your method should simply return.
Please help me #1 - #8 questions!
Thanks in advance! :-)
#java programming
Parameter object sound samples: 37 10 91 Calling object sound samples before: -10 -12 -9 30 Calling object sound samples after, with nsamples equal to 2 (boldvred samples are the ones changed) -12 -10 30 12 12 90 Parameter object sound samples: 37 10 91 Calling object sound samples before: -10 -12 -9 30 Calling object sound samples after, with nsamples equal to 2 (boldvred samples are the ones changed) -12 -10 30 12 12 90
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


