Question: This exercises requires conversions from field to SI units: 1 4 5 psi = 1 MPa = 1 0 bar 1 g / cm 3
This exercises requires conversions from field to SI units:
psi MPa bar
gcm psift or psifeet gcm
psi MPa
millistrain strain
The design of the platform to produce the Heriot field requires an estimate of the seabed subsidence resulting from hydrocarbon production over yrs
Top of Heriot is located at m SS with a water depth of m The derrick floor elevation is m Average sea water density is gcm
Heriot reservoir characteristics:
vertical thickness m; radius m
composed of flatlying unconsolidated sands with porosity between and
samples taken from good quality, clean sands
between sands are lowpermeable mudrocks; average NG is
average overburden density is gcc; reservoir pore fluid pressure before production is MPa and; a MPa depletion planned over a period of years.
Lab tests:
vertical samples from core in a vertical producer well through central part of the reservoir deformed in the laboratory
pores were connected to atmospheric pressure
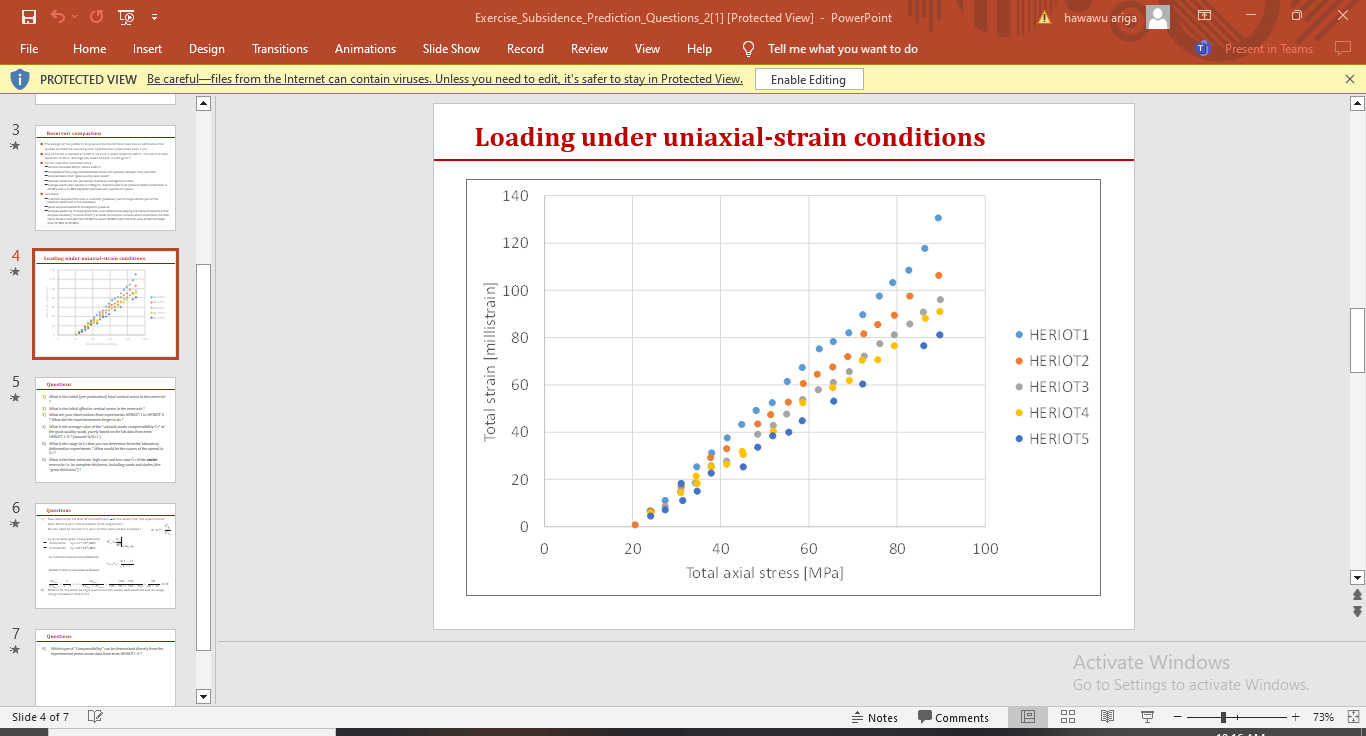
samples loaded by increasing the total axial stress while keeping the radial dimension of the samples constant uniaxial strain In order to maintain uniaxialstrain conditions, the total radial stress increased from MPa to about MPa when the total axial stress increased from MPa to MPa.
What is the initial preproduction total vertical stress in the reservoir
What is the initial effective vertical stress in the reservoir
What are your observations from experiments HERIOT to HERIOT What did the experimentators forget to do
What is the average value of the uniaxialstrain compressibility Cm of the goodquality sands, purely based on the lab data from tests HERIOTassume NG
What is the range in Cm that you can determine from the laboratory deformation experiments What would be the causes of the spread in Cm
What is the bestestimate, highcase and lowcase Cm of the entire reservoir, ie its complete thickness, including sands and shales the gross thickness
Now determine the BiotWillis coefficient a of the sands from the experimental data. What is your interpretation of its magnitude
Do you need to include it in your further poroelastic analyses
Cg is the solidgrain compressibility
Pure quartz: Cg MPa
Pure calcite: Cg MPa
Cbc is the bulk volume compressibility
Poissons ratio is calculated as follows:
Determine the static Youngs modulus of the sands, bestestimate and its range, using a Poissons ratio of
Which type of Compressibility can be determined directly from the experimental stressstrain data from tests HERIOTPROTECTED VIEW Be carefulfiles from the Internet can contain viruses. Unless you need to edit, it's safer to stay in Protected View.
Enable Editing
Present in Teams
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


