Question: This is a math numerical method problem. Plz do this in matlab thank you very much..Plz see the requirementsAnd the problem is clear enough, dont
This is a math numerical method problem. Plz do this in matlab thank you very much..Plz see the requirementsAnd the problem is clear enough, dont say it is not clear plz. 
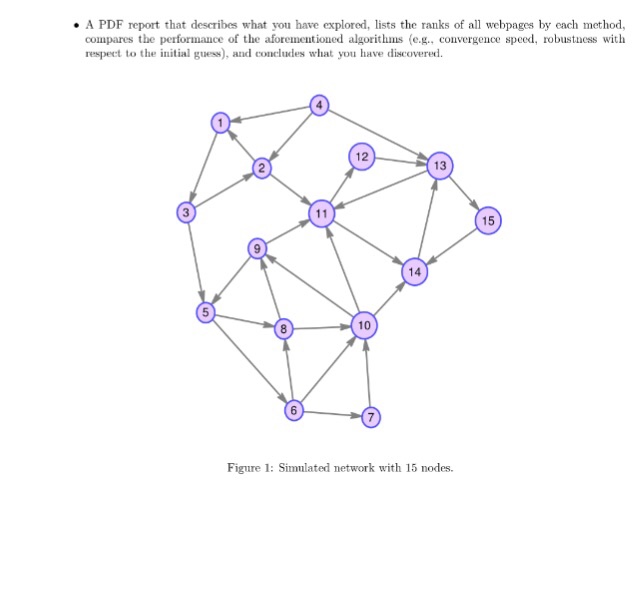
The goal of this part is to implement the PageRank algorithm of the Google search engine with the Power method and its variants, and apply them to a simplified graph simulating the World Wide Web. The ranking is based on finding the dominant eigenvector of a matrix which describes the connection of all webpages in one network. We start with some basic concepts from the graph theory. A directed graph is a set of vertices connected by edges where each edge has a direction. For example, the internet with various webpages can be considered as a directed graph where each vertex and directed edge stand for a webpage and a link, respectively. The adjacency matrix of a directed graph is defined as an n x matrix B whose entries are if there is a link from the page i to the page j: 0, otherwise. From B. we can construct a modified adjacency matrix M (my) which tells us the probability of visiting the webpage j from the webpage i. Suppose that when vising a webpage, one surfer clicks one link this webpage with probability p and jumps to a completely random webpage in the network with probability 1-p The probability p is also known as the damping factor in the PageRank theory and is usually set around 0.85 Furthermore, if there are n pages in the graph, we define the modified adjacency matrix M whose entries are In fact, M is a stochastic matrix satisfying that 1 and thereby 1 is the dominant eigenvalue of M with algebraic multiplicity 1 by the Pemon's Theorem. The Markov theory states that if with C LIvl 1 is a left dominant eigenvector of M associated with the eigenvalue 1, i.e., M iti then vi is the probability that one visits t page i at the stationary state independent of the starting page, which determines the rank of the ith webpage. Now we use the power method, scaled power method and inverse power method to find the left dominant eigenvector of Al, respectively. The initial vector can be randomly generated by randn (n, 1) Requirements Submit to CCLE a file lastnane firstname-hw8.zip containing the following files: A MATLAB function p that implements the Power Method with norm scaling, power2.m implements the Power Method with h-norm scaling, invpower.n that implements the Inverse Power Method, and a MATLAB script nain.m that finds the rank of each webpage in the network shown in Figure 1 with 15 webpages. (Hint: Use the graph to construct the corresponding adjacency matrix B first and then build the modified adjacency matrix M. The exact eigenwalues can be obtained via eig.) ihttp://www.mathworks.coe/helpatlabvreffrande.htnl. The goal of this part is to implement the PageRank algorithm of the Google search engine with the Power method and its variants, and apply them to a simplified graph simulating the World Wide Web. The ranking is based on finding the dominant eigenvector of a matrix which describes the connection of all webpages in one network. We start with some basic concepts from the graph theory. A directed graph is a set of vertices connected by edges where each edge has a direction. For example, the internet with various webpages can be considered as a directed graph where each vertex and directed edge stand for a webpage and a link, respectively. The adjacency matrix of a directed graph is defined as an n x matrix B whose entries are if there is a link from the page i to the page j: 0, otherwise. From B. we can construct a modified adjacency matrix M (my) which tells us the probability of visiting the webpage j from the webpage i. Suppose that when vising a webpage, one surfer clicks one link this webpage with probability p and jumps to a completely random webpage in the network with probability 1-p The probability p is also known as the damping factor in the PageRank theory and is usually set around 0.85 Furthermore, if there are n pages in the graph, we define the modified adjacency matrix M whose entries are In fact, M is a stochastic matrix satisfying that 1 and thereby 1 is the dominant eigenvalue of M with algebraic multiplicity 1 by the Pemon's Theorem. The Markov theory states that if with C LIvl 1 is a left dominant eigenvector of M associated with the eigenvalue 1, i.e., M iti then vi is the probability that one visits t page i at the stationary state independent of the starting page, which determines the rank of the ith webpage. Now we use the power method, scaled power method and inverse power method to find the left dominant eigenvector of Al, respectively. The initial vector can be randomly generated by randn (n, 1) Requirements Submit to CCLE a file lastnane firstname-hw8.zip containing the following files: A MATLAB function p that implements the Power Method with norm scaling, power2.m implements the Power Method with h-norm scaling, invpower.n that implements the Inverse Power Method, and a MATLAB script nain.m that finds the rank of each webpage in the network shown in Figure 1 with 15 webpages. (Hint: Use the graph to construct the corresponding adjacency matrix B first and then build the modified adjacency matrix M. The exact eigenwalues can be obtained via eig.) ihttp://www.mathworks.coe/helpatlabvreffrande.htnl
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


