Question: this is a physics assignment having to do with motion and free fall acceleration due to gravity, the only thing necessary is the chart that
this is a physics assignment having to do with motion and free fall acceleration due to gravity, the only thing necessary is the chart that i provided below and i also added the notes in the beginning to properly understand what to do better please answer everything that was asked at the bottom in full detail thank you!
Acceleration Due To Gravity:
The following value was given to us during our kinematics calculations:
Ag=32 ft/s^2 or ag=9.8 m/s^2 (10m/s^2)
In this section you will be experimentally calculating the acceleration due to gravity (and comparing it to the real value)
Introducing the Lab:
Any motion in a straight line can be measured using a ticker timer. A ticker timer is a device that has a set frequency (usually 60 hz) and it places a dot on a piece of paper every 1/60 of a second. This is useful because we know the time it takes for each dot to be placed (1/60 s or roughly 0.01667 seconds) and it allows us to measure the distance between points.
The pattern that is created on our ticker tape tells us a lot about the motion that is occurring. Not only does it tell us the type of motion (uniform or non uniform) but it allows us to calculate things (velocities or......acceleration).
In order to perform this lab all you would need is a ticker timer apparatus and an object that you can drop. You simply connect the tape to the object and drop it. You will be able to calculate everything you need based on the dots on the tape.
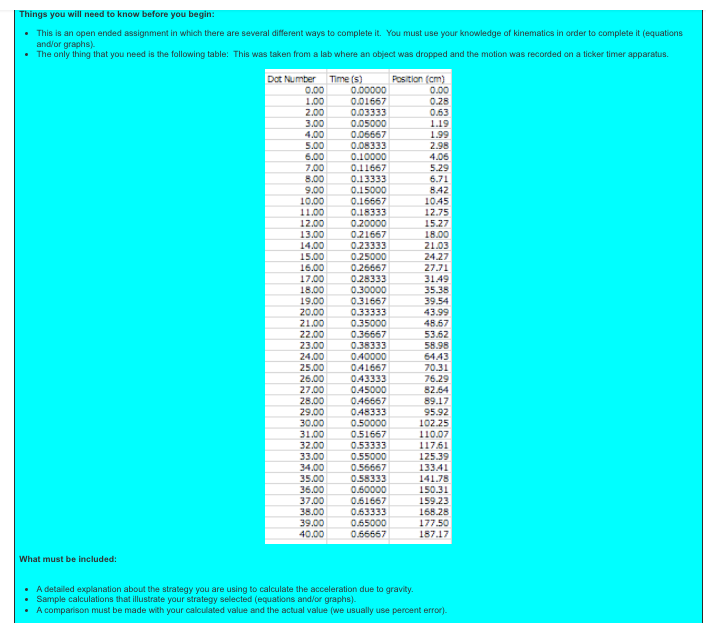
Things you will need to know before you begin: . This is an open ended assignment in which there are several different ways to complete it. You must use your knowledge of kinematics in order to complete it (equations andlor graphs The only thing that you need is the following table: This was taken from a lab where an object was dropped and the motion was recorded on a ticker timer apparatus. Dot Number Time (5) Position (cm) 0.00 0.00000 0.00 1.00 0.01667 0.28 2.00 0.03333 0.63 3.00 0.05000 1.19 4.00 0.06567 1.99 5.00 0.08333 2.98 6.00 0.10000 4.06 7.00 0.11867 5.29 8.00 0.13333 6.71 9.00 0.15000 6.42 10.00 0.15567 10.45 1 1.00 0.18333 12.75 12.00 0.20000 15.27 13.00 0.21667 15.00 14.00 0.23333 21.03 15.00 0.25000 24.27 16.00 0.26467 27.71 17.00 0.28333 31.49 15.00 0.30000 35.35 19.00 0.31567 39.54 20.00 0.33333 43.99 21.00 0.35000 45.67 22.00 0.36567 53.62 23.00 0.38333 58.95 24.00 040000 64.43 25.00 0.41567 70.31 26.00 0.43333 76.29 27.00 0.45000 82.64 25.00 0.45657 89.17 29.00 0.45333 95.92 30.00 0.50000 102.25 31.00 0.51667 110.07 32.00 0.53333 117.61 33.00 0.55000 125.39 34.00 0.56567 13341 35.00 0.58333 141.78 36.00 0.40000 150.31 37.00 0.61867 159.23 35.00 0.63333 168.28 39.00 0.65000 177.50 40.00 0.56567 187.17 What must be included: A detailed explanation about the strategy you are using to calculate the acceleration due to gravity. Sample calculations that illustrate your strategy selected (equations and/or graphs). A comparison must be made with your calculated value and the actual value (we usually use percent error)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


