Question: This is a python program done in wing 101. I need get_distance_to_inspector and find_closest_inspector functions Thank you import csv import math from typing import List,
This is a python program done in wing 101. I need get_distance_to_inspector and find_closest_inspector functions
Thank you
import csv import math from typing import List, TextIO
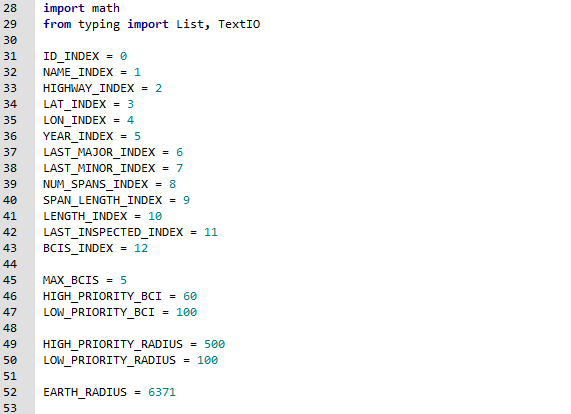
ID_INDEX = 0 NAME_INDEX = 1 HIGHWAY_INDEX = 2 LAT_INDEX = 3 LON_INDEX = 4 YEAR_INDEX = 5 LAST_MAJOR_INDEX = 6 LAST_MINOR_INDEX = 7 NUM_SPANS_INDEX = 8 SPAN_LENGTH_INDEX = 9 LENGTH_INDEX = 10 LAST_INSPECTED_INDEX = 11 BCIS_INDEX = 12
MAX_BCIS = 5 HIGH_PRIORITY_BCI = 60 LOW_PRIORITY_BCI = 100
HIGH_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 500 LOW_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 100
EARTH_RADIUS = 6371
### SAMPLE DATA TO USE IN DOCSTRING EXAMPLES ####
THREE_BRIDGES_UNCLEANED = [ ['1 - 32/', 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', '43.167233', '-80.275567', '1965', '2014', '2009', '4', 'Total=64 (1)=12;(2)=19;(3)=21;(4)=12;', '65', '04/13/2012', '72.3', '', '72.3', '', '69.5', '', '70', '', '70.3', '', '70.5', '', '70.7', '72.9', ''], ['1 - 43/', 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', '43.164531', '-80.251582', '1963', '2014', '2007', '4', 'Total=60.4 (1)=12.2;(2)=18;(3)=18;(4)=12.2;', '61', '04/13/2012', '71.5', '', '71.5', '', '68.1', '', '69', '', '69.4', '', '69.4', '', '70.3', '73.3', ''], ['2 - 4/', 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', '45.036739', '-81.33579', '1958', '2013', '', '1', 'Total=16 (1)=16;', '18.4', '08/28/2013', '85.1', '85.1', '', '67.8', '', '67.4', '', '69.2', '70', '70.5', '', '75.1', '', '90.1', ''] ]
THREE_BRIDGES = [[1, 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', 43.167233, -80.275567, '1965', '2014', '2009', 4, [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012', [72.3, 69.5, 70.0, 70.3, 70.5, 70.7, 72.9]], [2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4, [12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, '04/13/2012', [71.5, 68.1, 69.0, 69.4, 69.4, 70.3, 73.3]], [3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', 45.036739, -81.33579, '1958', '2013', '', 1, [16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013', [85.1, 67.8, 67.4, 69.2, 70.0, 70.5, 75.1, 90.1]] ]
####### BEGIN HELPER FUNCTIONS ####################
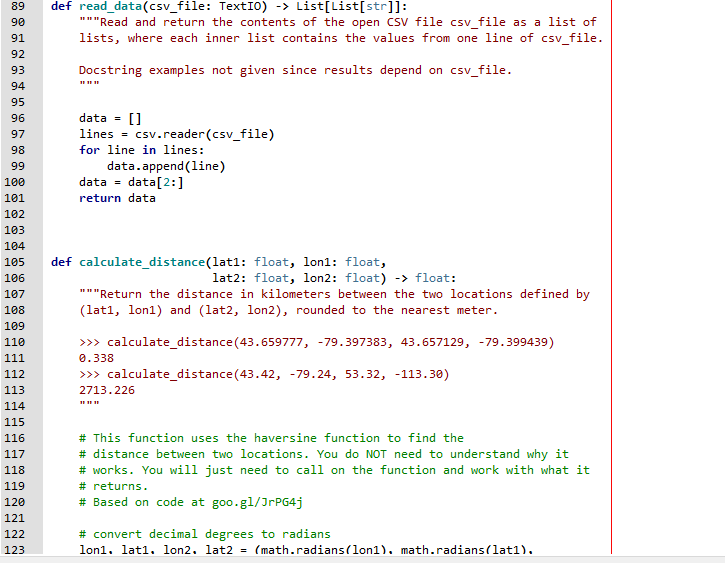
def read_data(csv_file: TextIO) -> List[List[str]]: """Read and return the contents of the open CSV file csv_file as a list of lists, where each inner list contains the values from one line of csv_file.
Docstring examples not given since results depend on csv_file. """
data = [] lines = csv.reader(csv_file) for line in lines: data.append(line) data = data[2:] return data
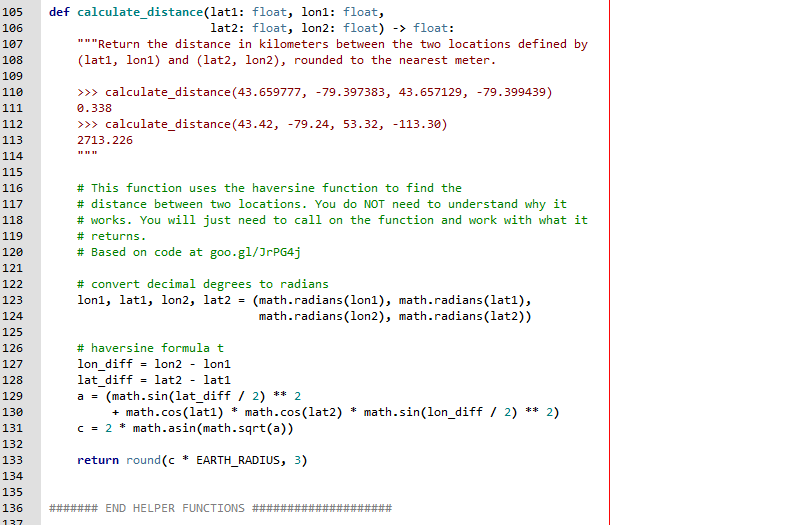
def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float, lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float: """Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by (lat1, lon1) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter. >>> calculate_distance(43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439) 0.338 >>> calculate_distance(43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30) 2713.226 """
# This function uses the haversine function to find the # distance between two locations. You do NOT need to understand why it # works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it # returns. # Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j
# convert decimal degrees to radians lon1, lat1, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians(lon1), math.radians(lat1), math.radians(lon2), math.radians(lat2))
# haversine formula t lon_diff = lon2 - lon1 lat_diff = lat2 - lat1 a = (math.sin(lat_diff / 2) ** 2 + math.cos(lat1) * math.cos(lat2) * math.sin(lon_diff / 2) ** 2) c = 2 * math.asin(math.sqrt(a)) return round(c * EARTH_RADIUS, 3)
####### END HELPER FUNCTIONS ####################
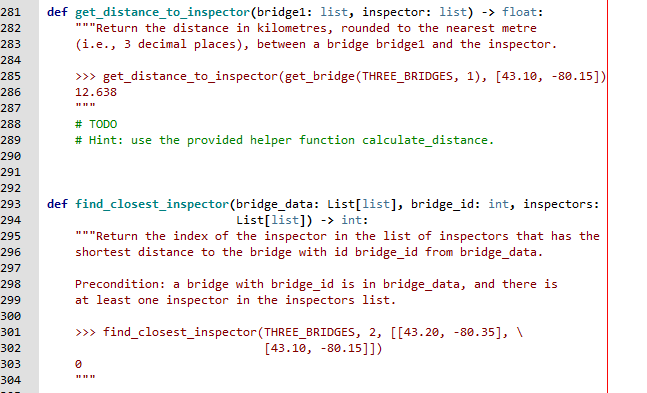
def get_distance_to_inspector(bridge1: list, inspector: list) -> float: """Return the distance in kilometres, rounded to the nearest metre (i.e., 3 decimal places), between a bridge bridge1 and the inspector. >>> get_distance_to_inspector(get_bridge(THREE_BRIDGES, 1), [43.10, -80.15]) 12.638 """ # TODO # Hint: use the provided helper function calculate_distance.
def find_closest_inspector(bridge_data: List[list], bridge_id: int, inspectors: List[list]) -> int: """Return the index of the inspector in the list of inspectors that has the shortest distance to the bridge with id bridge_id from bridge_data. Precondition: a bridge with bridge_id is in bridge_data, and there is at least one inspector in the inspectors list. >>> find_closest_inspector(THREE_BRIDGES, 2, [[43.20, -80.35], \ [43.10, -80.15]]) 0 """ # TODO
if __name__ == '__main__': pass

Each list item contain a meaning stated below: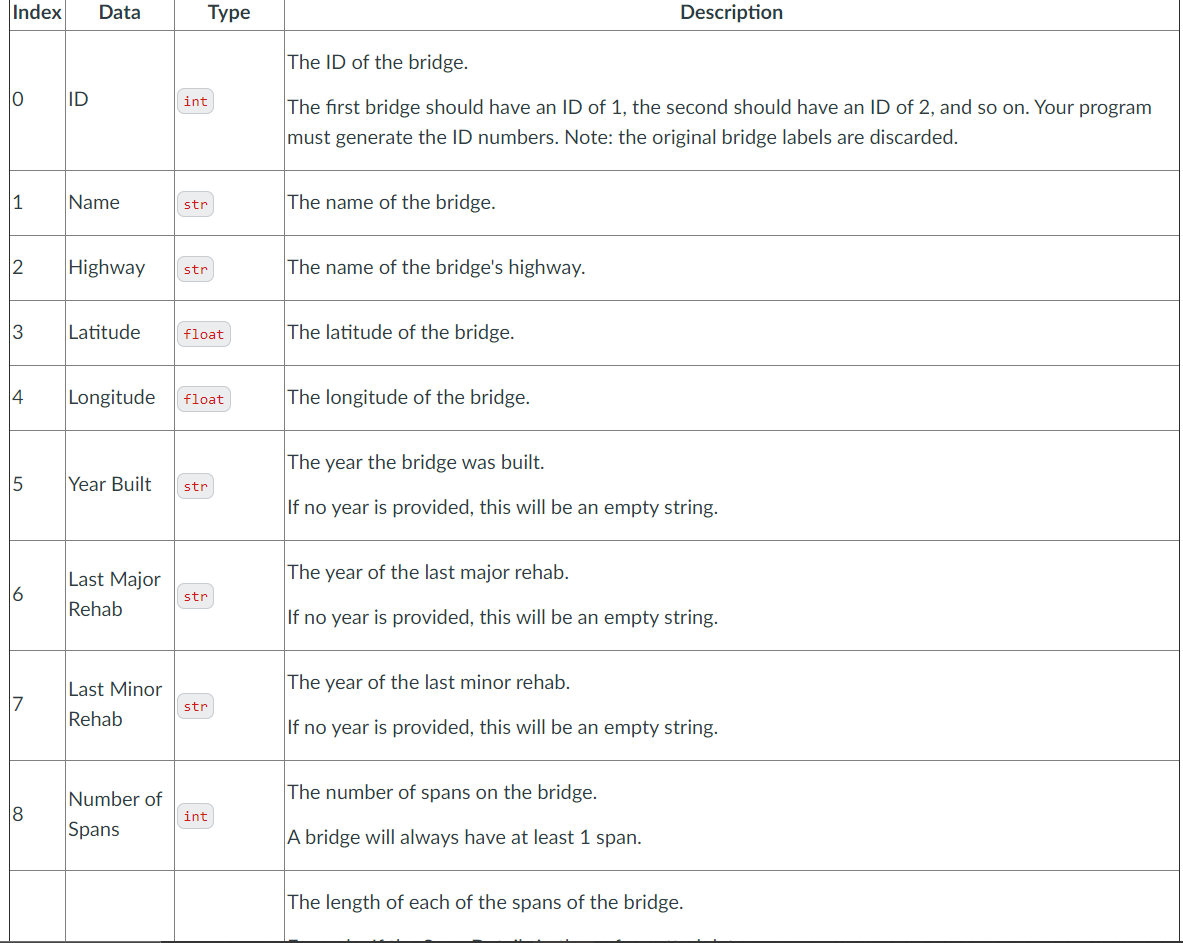

28 import math from typing import List, TextIO 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 ID_INDEX = 0 NAME_INDEX = 1 HIGHWAY_INDEX - 2 LAT_INDEX = 3 LON_INDEX = 4 YEAR_INDEX = 5 LAST_MAJOR_INDEX = 6 LAST_MINOR_INDEX = 7 NUM_SPANS_INDEX = 8 SPAN_LENGTH_INDEX - 9 LENGTH_INDEX = 10 LAST_INSPECTED_INDEX = 11 BCIS_INDEX - 12 MAX_BCIS - 5 HIGH_PRIORITY_BCI - 60 LOW_PRIORITY_BCI = 100 HIGH_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 500 LOW_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 100 EARTH_RADIUS - 6371 ### SAMPLE DATA TO USE IN DOCSTRING EXAMPLES #### = 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 THREE_BRIDGES_UNCLEANED [ ['1 - 32/', 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', '43.167233', -80.275567', '1965', '2014', '2009', '4', 'Total=64 (1)=12; (2)=19; (3)=21; (4)=12;', '65', '04/13/2012', '72.3', '', '72.3', '', '69.5', '', '70', '', '70.3', '', '70.5', '', '70.7', '72.9', "'], ['1 - 43/', 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', '43.164531', '-80.251582', '1963', '2014', '2007', '4', 'Total=60.4 (1)=12.2; (2)=18; (3)=18; (4)=12.2;', '61', '04/13/2012', '71.5', '', '71.5', '', '68.1', '', '69', '', '69.4', '', '69.4', '', '70.3', '73.3', ''], ['2 - 4/', 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', '45.036739', -81.33579', '1958', 2013', '', 'l', 'Total=16 (1)=16;', '18.4', '08/28/2013', '85.1', , '67.8', '', '67.4', '', '69.2', '70', '70.5', '75.1', '90.1', ''] ] 85.1', THREE_BRIDGES [[1, 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', 43.167233, -80.275567, '1965', '2014', '2009', 4, [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012', [72.3, 69.5, 70.0, 70.3, 70.5, 70.7, 72.9]], [2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4, [12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, 04/13/2012', [71.5, 68.1, 69.0, 69.4, 69.4, 70.3, 73.3]], [3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', 45.636739, -81.33579, '1958', 2013', '', 1, [16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013', [85.1, 67.8, 67.4, 69.2, 70.0, 70.5, 75.1, 90.1]] ] ####### BEGIN HELPER FUNCTIONS def read_data(csv_file: Text10) -> List[List[str]]: **"Read and return the contents of the open csv file csv_file as a list of lists, where each inner list contains the values from one line of csv_file. Docstring examples not given since results depend on csv_file. data = u lines = csv.reader(csv_file) for line in lines: data.append(line) data = data[2:] return data 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float, lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float: ***"Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by (lati, lonl) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter. >>> calculate_distance (43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439) 0.338 >>> calculate_distance (43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30) 2713.226 # This function uses the haversine function to find the # distance between two locations. You do NOT need to understand why it # works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it # returns. # Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j # convert decimal degrees to radians lon1, lati, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians(lon1), math.radians(lati), def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float, lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float: ***"Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by (lati, lonl) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter. >>> calculate_distance (43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439) 0.338 >>> calculate_distance (43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30) 2713.226 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 # This function uses the haversine function to find the # distance between two locations. You do not need to understand why it # works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it # returns. # Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j # convert decimal degrees to radians loni, lati, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians (lon1), math.radians(lat), math.radians (lon2), math.radians(lat2)) # haversine formula t lon_diff - lon2 - lon1 lat_diff - lat2 - lati (math.sin(lat_diff / 2) ** 2 + math.cos(lati) * math.cos(lat2) c = 2 * math.asin(math.sqrt(a)) math.sin(lon_diff / 2) ** 2) return round(c * EARTH_RADIUS, 3) ####### END HELPER FUNCTIONS ######## -- def get_distance_to_inspector(bridge1: list, inspector: list) -> float: **"Return the distance in kilometres, rounded to the nearest metre (i.e., 3 decimal places), between a bridge bridgel and the inspector. >>>get_distance_to_inspector(get_bridge (THREE_BRIDGES, 1), [43.10, -80.15)) 12.638 # TODO # Hint: use the provided helper function calculate_distance. 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 def find_closest_inspector(bridge_data: List[list], bridge_id: int, inspectors: List[list]) -> int: "Return the index of the inspector in the list of inspectors that has the shortest distance to the bridge with id bridge_id from bridge_data. Precondition: a bridge with bridge_id is in bridge_data, and there is at least one inspector in the inspectors list. >>> find_closest_inspector(THREE_BRIDGES, 2, [[43.20, -80.35], [43.10, -80.15]]) Index Data Type Description The ID of the bridge. 0 ID int The first bridge should have an ID of 1, the second should have an ID of 2, and so on. Your program must generate the ID numbers. Note: the original bridge labels are discarded. 1 Name str The name of the bridge. 2 Highway str The name of the bridge's highway. 3 Latitude float The latitude of the bridge. 4. Longitude float The longitude of the bridge. The year the bridge was built. 5 Year Built str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. The year of the last major rehab. 6 Last Major Rehab str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. The year of the last minor rehab. 7 Last Minor Rehab str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. Number of The number of spans on the bridge. 8 int Spans A bridge will always have at least 1 span. The length of each of the spans of the bridge. 19 Span Details List[float] Total=64 (1)=12; (2)=19; (3)=21; (4)=12; And the bridge had 4 spans, then the formatted version should be the following list: [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0] The length of the bridge. 10 Bridge Length float If no length is provided, this will be 0.0. The date of the last inspection (in MM/DD/YYYY format). 11 Last Inspected Date str If no date is provided, this will be an empty string. A list of the BCls from the most recent to the least. 12 BCIS List[float] If the bridge has no BCls, then this should be an empty list. After applying the format_data function to the example list, it should look like: [ [1, "Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', 43.167233, -80.275567, 1965', '2014', '2009', 4, [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012', [72.3, 69.5, 70.0, 70.3, 70.5, 70.7, 72.9]], [2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4, [12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, 04/13/2012', [71.5, 68.1, 69.0, 69.4, 69.4, 70.3, 73.3]], [3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', 45.036739, -81.33579, 1958', '2013', '', 1, [16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013', [85.1, 67.8, 67.4, 69.2, 70.0, 70.5, 75.1, 90.1]] ] Before you write the format_data function body, please note: 28 import math from typing import List, TextIO 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 ID_INDEX = 0 NAME_INDEX = 1 HIGHWAY_INDEX - 2 LAT_INDEX = 3 LON_INDEX = 4 YEAR_INDEX = 5 LAST_MAJOR_INDEX = 6 LAST_MINOR_INDEX = 7 NUM_SPANS_INDEX = 8 SPAN_LENGTH_INDEX - 9 LENGTH_INDEX = 10 LAST_INSPECTED_INDEX = 11 BCIS_INDEX - 12 MAX_BCIS - 5 HIGH_PRIORITY_BCI - 60 LOW_PRIORITY_BCI = 100 HIGH_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 500 LOW_PRIORITY_RADIUS = 100 EARTH_RADIUS - 6371 ### SAMPLE DATA TO USE IN DOCSTRING EXAMPLES #### = 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 THREE_BRIDGES_UNCLEANED [ ['1 - 32/', 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', '43.167233', -80.275567', '1965', '2014', '2009', '4', 'Total=64 (1)=12; (2)=19; (3)=21; (4)=12;', '65', '04/13/2012', '72.3', '', '72.3', '', '69.5', '', '70', '', '70.3', '', '70.5', '', '70.7', '72.9', "'], ['1 - 43/', 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', '43.164531', '-80.251582', '1963', '2014', '2007', '4', 'Total=60.4 (1)=12.2; (2)=18; (3)=18; (4)=12.2;', '61', '04/13/2012', '71.5', '', '71.5', '', '68.1', '', '69', '', '69.4', '', '69.4', '', '70.3', '73.3', ''], ['2 - 4/', 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', '45.036739', -81.33579', '1958', 2013', '', 'l', 'Total=16 (1)=16;', '18.4', '08/28/2013', '85.1', , '67.8', '', '67.4', '', '69.2', '70', '70.5', '75.1', '90.1', ''] ] 85.1', THREE_BRIDGES [[1, 'Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', 43.167233, -80.275567, '1965', '2014', '2009', 4, [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012', [72.3, 69.5, 70.0, 70.3, 70.5, 70.7, 72.9]], [2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4, [12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, 04/13/2012', [71.5, 68.1, 69.0, 69.4, 69.4, 70.3, 73.3]], [3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', 45.636739, -81.33579, '1958', 2013', '', 1, [16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013', [85.1, 67.8, 67.4, 69.2, 70.0, 70.5, 75.1, 90.1]] ] ####### BEGIN HELPER FUNCTIONS def read_data(csv_file: Text10) -> List[List[str]]: **"Read and return the contents of the open csv file csv_file as a list of lists, where each inner list contains the values from one line of csv_file. Docstring examples not given since results depend on csv_file. data = u lines = csv.reader(csv_file) for line in lines: data.append(line) data = data[2:] return data 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float, lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float: ***"Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by (lati, lonl) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter. >>> calculate_distance (43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439) 0.338 >>> calculate_distance (43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30) 2713.226 # This function uses the haversine function to find the # distance between two locations. You do NOT need to understand why it # works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it # returns. # Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j # convert decimal degrees to radians lon1, lati, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians(lon1), math.radians(lati), def calculate_distance(lat1: float, lon1: float, lat2: float, lon2: float) -> float: ***"Return the distance in kilometers between the two locations defined by (lati, lonl) and (lat2, lon2), rounded to the nearest meter. >>> calculate_distance (43.659777, -79.397383, 43.657129, -79.399439) 0.338 >>> calculate_distance (43.42, -79.24, 53.32, -113.30) 2713.226 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 # This function uses the haversine function to find the # distance between two locations. You do not need to understand why it # works. You will just need to call on the function and work with what it # returns. # Based on code at goo.gl/JrPG4j # convert decimal degrees to radians loni, lati, lon2, lat2 = (math.radians (lon1), math.radians(lat), math.radians (lon2), math.radians(lat2)) # haversine formula t lon_diff - lon2 - lon1 lat_diff - lat2 - lati (math.sin(lat_diff / 2) ** 2 + math.cos(lati) * math.cos(lat2) c = 2 * math.asin(math.sqrt(a)) math.sin(lon_diff / 2) ** 2) return round(c * EARTH_RADIUS, 3) ####### END HELPER FUNCTIONS ######## -- def get_distance_to_inspector(bridge1: list, inspector: list) -> float: **"Return the distance in kilometres, rounded to the nearest metre (i.e., 3 decimal places), between a bridge bridgel and the inspector. >>>get_distance_to_inspector(get_bridge (THREE_BRIDGES, 1), [43.10, -80.15)) 12.638 # TODO # Hint: use the provided helper function calculate_distance. 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 def find_closest_inspector(bridge_data: List[list], bridge_id: int, inspectors: List[list]) -> int: "Return the index of the inspector in the list of inspectors that has the shortest distance to the bridge with id bridge_id from bridge_data. Precondition: a bridge with bridge_id is in bridge_data, and there is at least one inspector in the inspectors list. >>> find_closest_inspector(THREE_BRIDGES, 2, [[43.20, -80.35], [43.10, -80.15]]) Index Data Type Description The ID of the bridge. 0 ID int The first bridge should have an ID of 1, the second should have an ID of 2, and so on. Your program must generate the ID numbers. Note: the original bridge labels are discarded. 1 Name str The name of the bridge. 2 Highway str The name of the bridge's highway. 3 Latitude float The latitude of the bridge. 4. Longitude float The longitude of the bridge. The year the bridge was built. 5 Year Built str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. The year of the last major rehab. 6 Last Major Rehab str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. The year of the last minor rehab. 7 Last Minor Rehab str If no year is provided, this will be an empty string. Number of The number of spans on the bridge. 8 int Spans A bridge will always have at least 1 span. The length of each of the spans of the bridge. 19 Span Details List[float] Total=64 (1)=12; (2)=19; (3)=21; (4)=12; And the bridge had 4 spans, then the formatted version should be the following list: [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0] The length of the bridge. 10 Bridge Length float If no length is provided, this will be 0.0. The date of the last inspection (in MM/DD/YYYY format). 11 Last Inspected Date str If no date is provided, this will be an empty string. A list of the BCls from the most recent to the least. 12 BCIS List[float] If the bridge has no BCls, then this should be an empty list. After applying the format_data function to the example list, it should look like: [ [1, "Highway 24 Underpass at Highway 403', '403', 43.167233, -80.275567, 1965', '2014', '2009', 4, [12.0, 19.0, 21.0, 12.0], 65.0, '04/13/2012', [72.3, 69.5, 70.0, 70.3, 70.5, 70.7, 72.9]], [2, 'WEST STREET UNDERPASS', '403', 43.164531, -80.251582, '1963', '2014', '2007', 4, [12.2, 18.0, 18.0, 12.2], 61.0, 04/13/2012', [71.5, 68.1, 69.0, 69.4, 69.4, 70.3, 73.3]], [3, 'STOKES RIVER BRIDGE', '6', 45.036739, -81.33579, 1958', '2013', '', 1, [16.0], 18.4, '08/28/2013', [85.1, 67.8, 67.4, 69.2, 70.0, 70.5, 75.1, 90.1]] ] Before you write the format_data function body, please
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


