Question: This is important, please Consider a binomial tree model for the stock price S,. Let So = 50 and let the price rise by 10%
This is important, please
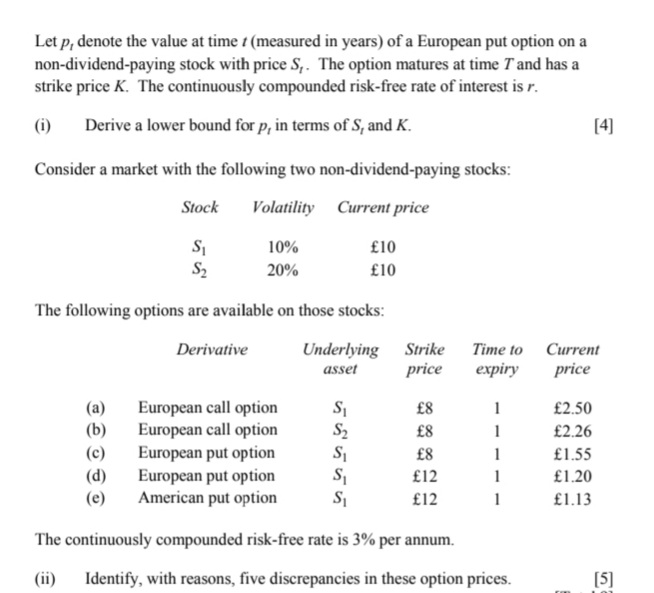
Consider a binomial tree model for the stock price S,. Let So = 50 and let the price rise by 10% or fall by 5% each month for the next three months. Assume also that the risk-free rate is 5% per annum continuously compounded. (i) State the conditions under which the market is arbitrage free. [2] (ii) Calculate the price at time / = 0 of a European call option on this stock, which expires in three months and is struck at-the-money (i.e. strike price K = 50). [4] A special option, called a knock-out barrier option, goes out of existence (i.e. expires without any payoff or value) if the underlying asset reaches a pre-specified barrier b > 0 either from above (down-and-out) or from below (up-and-out). The down-and-out call has the following payoff at time T: max(ST - K,0) if min S, 2b, OSIST 0 otherwise. Assume this special option is written on the given stock, has the same strike price and maturity as the European call option described in part (ii) and the barrier b is fixed at 48. (iii) Calculate the price of this contract using the binomial tree model and risk- neutral valuation. [3] (iv) Determine the price of the down-and-out contract when b = 40, without performing any further calculations. [21In order to model the seasonality of a particular data set an actuary is asked to consider the following model: (1-B 2)(1-(a +B)B +aBB? )X, = &, where B is the backshift operator and &, is a white noise process with variance o-. The actuary intends to apply a seasonal difference V, X, = Y,- (i) Explain why s should be 12 in this case (i.e. Y, = X - X1-12). [1] (ii) Determine the range of values for o and B for which the process will be stationary after applying this seasonal difference. [3] Assume that after the appropriate seasonal differencing the following sample autocorrelation values for observations of Y, are p, =0 and p2 =0.09. (iii) Estimate the parameters o and B. [5] The actuary observes a sequence of observations X1, X2, ..., Xy of X,, with > 12. (iv) Derive the next two forecasted values for next two observations x7+, and Xia, as a function of the existing observations. [4]Let p, denote the value at time / (measured in years) of a European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock with price S,. The option matures at time 7 and has a strike price K. The continuously compounded risk-free rate of interest is r. (i) Derive a lower bound for p, in terms of S, and K. [4] Consider a market with the following two non-dividend-paying stocks: Stock Volatility Current price S1 10% f10 S2 20% $10 The following options are available on those stocks: Derivative Underlying Strike Time to Current asset price expiry price (a) European call option S1 (2.50 (b) European call option S2 $2.26 (C) European put option $1.55 (d) European put option S f12 f1.20 e) American put option S f12 f1.13 The continuously compounded risk-free rate is 3% per annum. (ii) Identify, with reasons, five discrepancies in these option prices. [5]