Question: This is in C not C++ phone.c #include #include #include #include #include phone.h /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void printNumber(long val) { return; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// MultiLinkedList *add(MultiLinkedList *list, char
This is in C not C++

phone.c
#include
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void printNumber(long val) { return; }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
MultiLinkedList *add(MultiLinkedList *list, char *first, char *last, long num) {
// allocate a new node Node *newNode = malloc ( sizeof(Node) ); newNode->first = malloc ( strlen(first) + 1 ); strcpy(newNode->first, first); newNode->last = malloc ( strlen(last) + 1 ); strcpy(newNode->last, last); newNode->number = num; // add this new node at the head of the "byFirst" list newNode->nextFirst = list->headFirstName; list->headFirstName = newNode; // add this new node at the head of the "byLast" list newNode->nextLast = list->headLastName; list->headLastName = newNode; // return the multi-list object with updated head pointers return list; }
int size(MultiLinkedList *list) { // return the number of names in the list return -1; }
void printByFirst(MultiLinkedList *list) { // print (traverse the byFirst list) return; }
void printByLast(MultiLinkedList *list) { // print (traverse the byLast list) return; }
int lookup(MultiLinkedList *list, char *name) { // print all instances of name (as either a first name or a last name) return -1; }
void updatePhone(MultiLinkedList *list, char *first, char *last, long number) { // update the phone number for the individual specified return; }
MultiLinkedList *removeItem(MultiLinkedList *list, char *first, char *last) { // remove the individual specified from the list return NULL; }
MultiLinkedList *updateFirst(MultiLinkedList *list, char *first, char *last, char *newFirst) { // update the first name of the individual specified return NULL; }
MultiLinkedList *updateLast(MultiLinkedList *list, char *first, char *last, char *newLast) { // update the last name of the individual specified return NULL; }
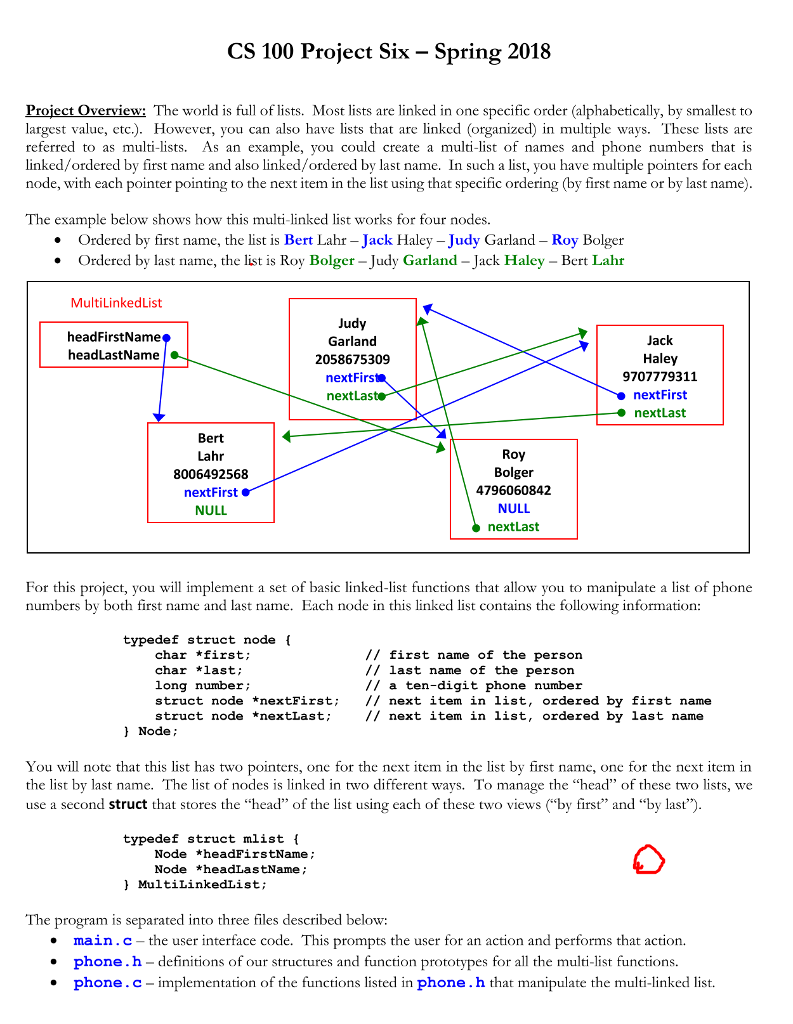
CS 100 Project Six - Spring 2018 Proiect Overview: The world is full of lists. Most lists are linked in one specific order (alphabetically, by smallest to largest valuc, etc.). However, you can also have lists that are linked (organized) in multiple ways. These lists are referred to as multi-lists. As an example, you could create a multi-list of names and phone numbers that is linked/ordered by first name and also linked/ordered by last name. In such a list, you have multiple pointers for each node, with each pointer pointing to the next item in the list using that specific ordering (by first name or by last name) The example below shows how this multi-linked list works for four nodes. Ordered by first name, the list is Bert Lahr - Jack Haley - Judy Garland - Roy Bolger Ordered by last name, the list is Roy Bolger - Judy Garland - Jack Haley - Bert Lahr * . MultiLinkedList headFirstName headLastName Garlang 2058675309 nextFirs nextLas Jack Haley 9707779311 nextFirst nextLast Bert Lahr 8006492568 nextFirst NULL Roy 4796060842 NULL nextLast For this project, you will implement a set of basic linked-list functions that allow you to manipulate a list of phone numbers by both first name and last name. Each node in this linked list contains the following information: typedef struct node char *first; char *last; long number; struct node *nextFirst; I next item in list, ordered by first name struct node *nextLast; // first name of the person // last name of the person // a ten-digit phone number // next item in list, ordered by last name ] Node, You will note that this list has two pointers, one for the next item in the list by first name, one for the next item in the list by last name. The list of nodes is linked in two different ways. To manage the "head" of these two lists, we use a second struct that stores the "head" of the list using each of these two views ("by first" and "by last"). typedef struct mlist Node *headFirstName; Node *headLastName l MultiLinkedList; The program is separated into three files describ ed below: * main.c -the user interface code. This prompts the user for an action and performs that action. . phone.h definitions of our structures and function prototypes for all the multi-list functions. * phone.c-implementation of the functions listed in phone.h that manipulate the multi-linked list
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


