Question: this is reaction engineering, please show all the steps Below graph is a thermodynamic calculation of G (change in free energy) for dry reforming of
this is reaction engineering, please show all the steps
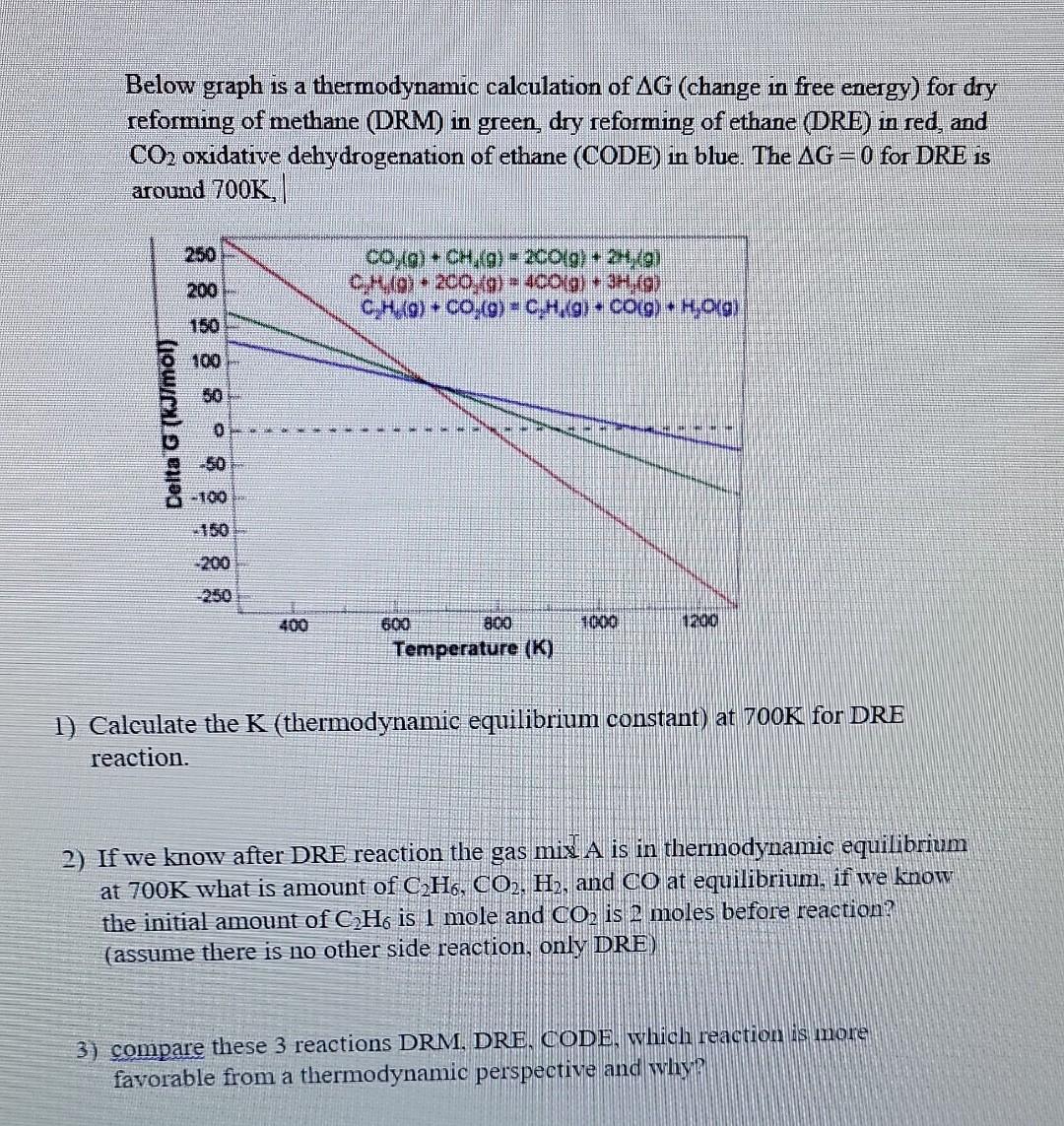
Below graph is a thermodynamic calculation of G (change in free energy) for dry reforming of methane (DRM) in green, dry reforming of ethane (DRE) in red, and CO2 oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane (CODE) in blue. The C=0 for DRE is around 700K, 1) Calculate the K (thermodynamic equilibrium constant) at 700K for DRE reaction. 2) If we know after DRE reaction the gas mix A is in thermodynamic equilibrium at 700K what is amount of C2H6,CO2,H2, and CO at equilibrium, if we know the initial amount of C2H6 is 1 mole and CO2 is 2 moles before reaction? (assume there is no other side reaction, only DRE) 3) compare these 3 reactions DRM, DRE, CODE, which reactiom is more favorable from a thermodynamic perspective and why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


