Question: This is the SLinkedList.h in the github / Code from: // Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, Goodrich, Tamassia, and Mount, 2nd Ed., 2011. //
This is the SLinkedList.h in the github
/ Code from: // Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, Goodrich, Tamassia, and Mount, 2nd Ed., 2011. //
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
template class SLinkedList; // forward declaration to be used when declaring SNode
template class SNode { // singly linked list node private: E elem; // linked list element value SNode *next; // next item in the list friend class SLinkedList; // provide SLinkedList access };
template class SLinkedList { // a singly linked list public: SLinkedList(); // empty list constructor ~SLinkedList(); // destructor bool empty() const; // is list empty? E& front(); // return front element void addFront(const E& e); // add to front of list void removeFront(); // remove front item list int size() const; // list size private: SNode* head; // head of the list int n; // number of items };
template SLinkedList::SLinkedList() // constructor : head(NULL), n(0) { }
template bool SLinkedList::empty() const // is list empty? { return head == NULL; // can also use return (n == 0); }
template E& SLinkedList::front() // return front element { if (empty()) throw length_error("empty list"); return head->elem; }
template SLinkedList::~SLinkedList() // destructor { while (!empty()) removeFront(); }
template void SLinkedList::addFront(const E& e) { // add to front of list SNode* v = new SNode; // create new node v->elem = e; // store data v->next = head; // head now follows v head = v; // v is now the head n++; }
template void SLinkedList::removeFront() { // remove front item if (empty()) throw length_error("empty list"); SNode* old = head; // save current head head = old->next; // skip over old head delete old; // delete the old head n--; }
template int SLinkedList::size() const { // list size return n; }
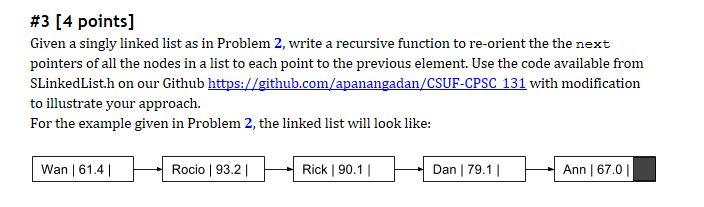
#3 [4 points] Given a singly linked list as in Problem 2, write a recursive function to re-orient the the next pointers of all the nodes in a list to each point to the previous element. Use the code available from SLinkedListh on our Github https://github.com/apanangadan/CSUF-CPSC 131 with modification to illustrate your approach. For the example given in Problem 2, the linked list will look like: I wan l 61.4 1 ! Rocio | 93.2 | Dan 79.1Ann | 67.0 |




