Question: This is using Java Create the following abstract classes and regular classes from the UML diagram. In this exercise Animal is an abstract class, which
This is using Java
Create the following abstract classes and regular classes from the UML diagram.
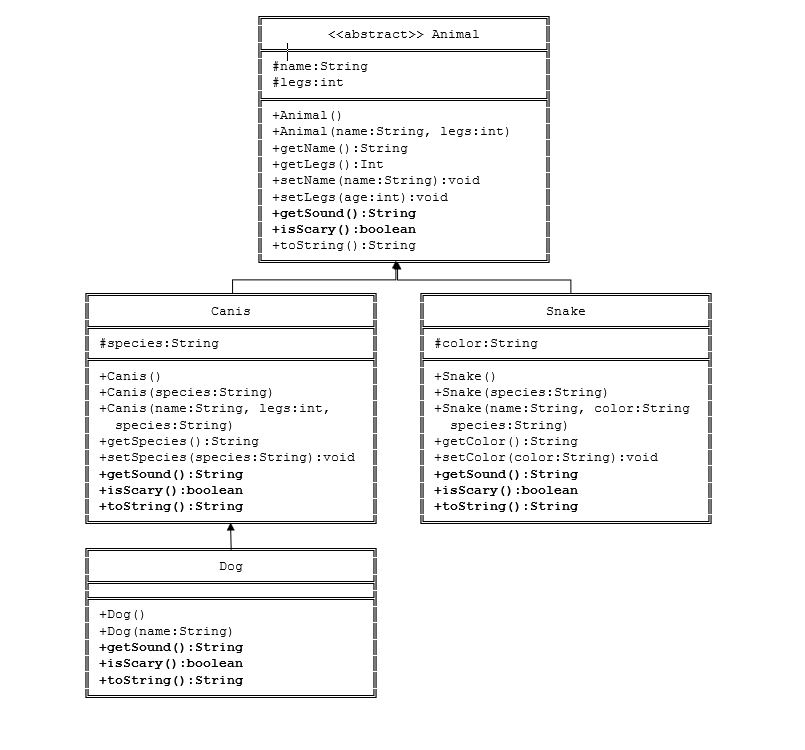
In this exercise Animal is an abstract class, which contains;
Two protected instance variables name(String) and legs(int). The protected variables can be accessed by its subclasses and classes in the same package. They are denoted with a '#' sign in the class diagram.
Getter and setter for all the instance variables, and toString().
Two abstract methods getSound() and isScary() (shown in italics in the class diagram).
Default values or animal are as follows; Name is Animal, and Legs is 0.
Details for Canis;
Default species is Canis
Canis is not scary when overriding the isScary method.
Details for Snake
Default color is Green.
Snake is scary when overriding the isScary method.
Details for Dog
Default species for dog is familiaris.
Default legs for dog is 4
Dog is not scary when overriding the isScary method
Write a test class to test these statements involving polymorphism and explain the outputs. Some statements may trigger compilation errors.
Explain the errors, if any [5 Points].
Animal s1 = new Snake("Snek", "Red", "Noodle"); // Upcast Snake to Animal
System.out.println(s1); // which version?
System.out.println(s1.getSound()); // which version?
System.out.println(s1.isScary()); // which version?
System.out.println(s1.getName());
System.out.println(s1.getLegs());
System.out.println(s1.getColor());
Snake c1 = (Snake)s1; // Downcast back to Snake
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c1.getSound());
System.out.println(c1.isScary());
System.out.println(c1.getName());
System.out.println(c1.getLegs());
System.out.println(c1.getColor());
Animal s2 = new Animal();
Animal s3 = new Canis("Wolf", 4, "Lupus"); // Upcast
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s3.getSound());
System.out.println(s3.isScary());
System.out.println(s3.getName());
System.out.println(s3.getSpecies());
Canis r1 = (Canis)s3; // downcast
System.out.println(r1);
System.out.println(r1.getSound());
System.out.println(r1.getName());
System.out.println(r1.getSpecies());
Animal s4 = new Dog("Goodboye"); // Upcast
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println(s4.getSound());
ab 3 tract>> Animal I #name: String +Animal () | +Animal (name:String, legs:int) I +getName () :String +getLegs Int I +setName (name:String) :void I +setLegs (age:int) :void I +getSound () :String tisScary ) :boolean | +toString ():String Canis Snake #species : String 1 1 #color:String +Canis) I +Canis (species:String) I +Canis (name:String, legs:int, +Snake (name:String, color:string | +Snake () +Snake (species:String) cies:String) I species:String) +getColor ):String I +getSpecies ):String I +setSpecies (species:String) :void +setcolor (color:String) :void I +getSound () :String tisScary) :boolea | +tostring) :String I getSonnd) :string +isscary ( :boolean |+tostring ) :String Dog I +Dog () l +Dog (name:String) |+getsound () :String tisScary ) :boolean I +tostring) :String
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


