Question: This is what i have so far Here is the auto grading. The first 3 tests passed but the last 4 didnt, I am not
This is what i have so far
Here is the auto grading. The first 3 tests passed but the last 4 didnt, I am not sure what I have wrong? (Python please)
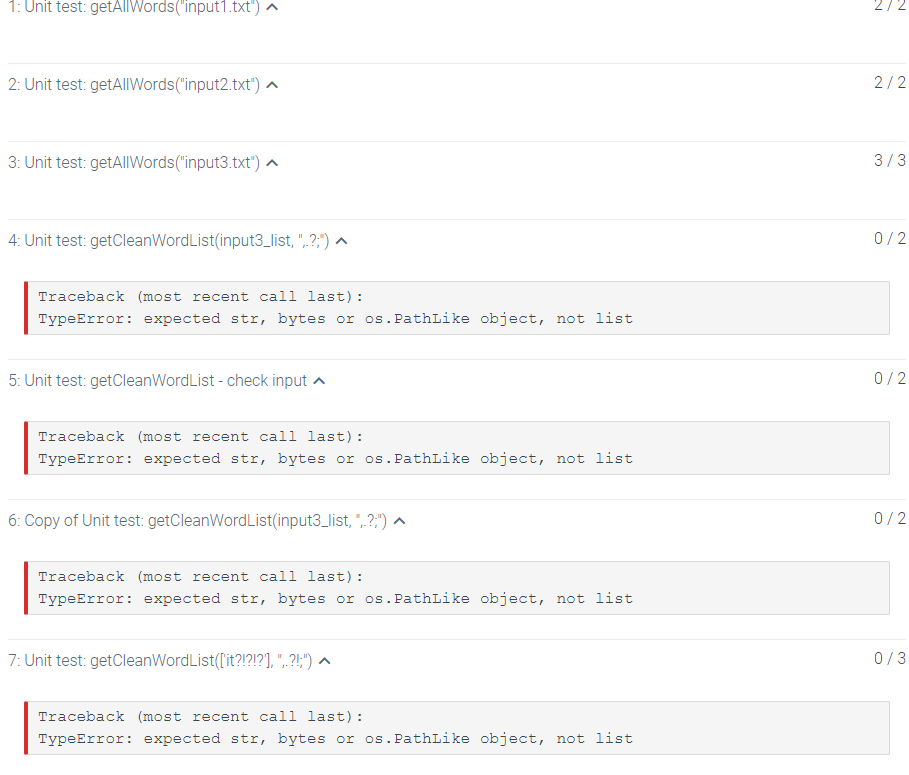
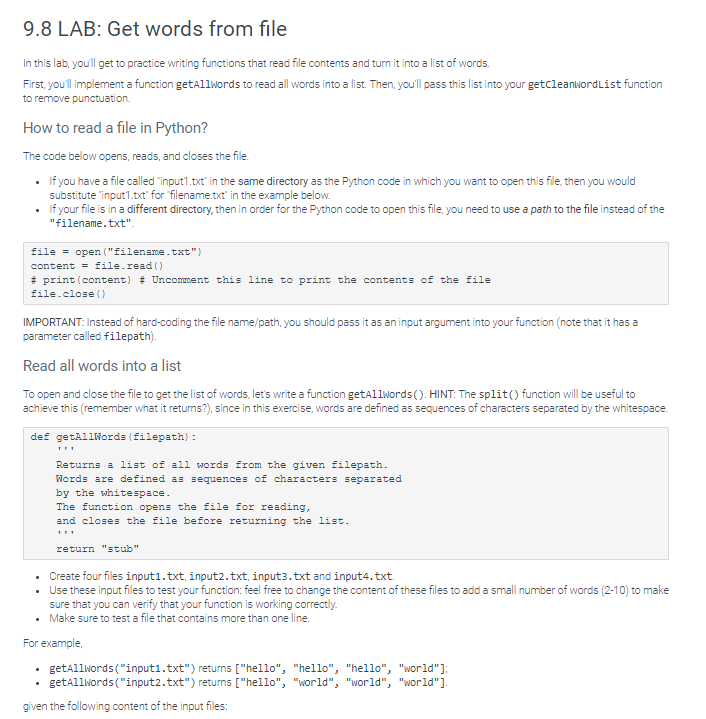
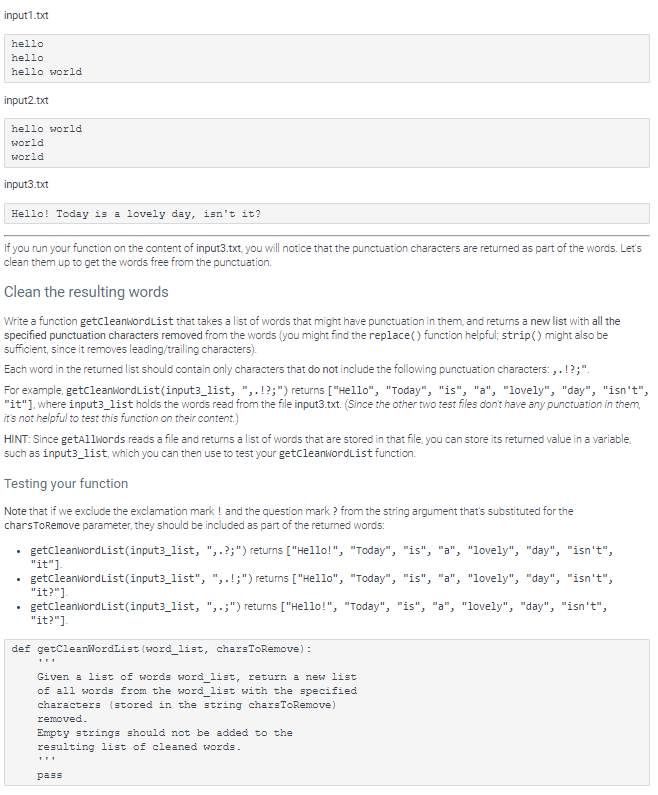
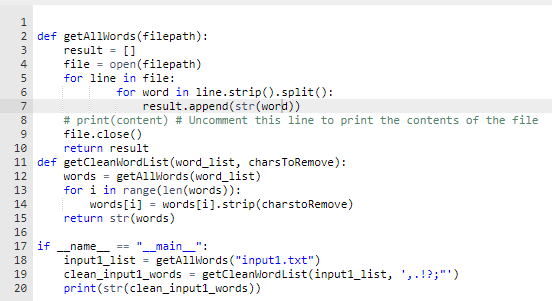
9.8 LAB: Get words from file In this lab, you'll get to practice writing functions that read file contents and turn it into a list of words. First, you'll implement a function getallwords to read all words into a list. Then, you'll pass this list into your getcleanwordList function to remove punctuation How to read a file in Python? The code below opens, reads, and closes the file. If you have a file called "input1.txt" in the same directory as the Python code in which you want to open this file, then you would substitute "input1.txt' for "filename.txt" in the example below. If your file is in a different directory, then in order for the Python code to open this file, you need to use a path to the file instead of the "filename.txt" file = open("filename.txt") content = file.read() # print (content) # Uncomment this line to print the contents of the file file.close() IMPORTANT: Instead of hard-coding the file name/path, you should pass it as an input argument into your function (note that it has a parameter called filepath) Read all words into a list To open and close the file to get the list of words, let's write a function getallwords(). HINT: The split() function will be useful to achieve this (remember what it returns?), since in this exercise, words are defined as sequences of characters separated by the whitespace. def getallWords (filepath) : Returns a list of all words from the given filepath. Words are defined as sequences of characters separated by the whitespace. The function opens the file for reading, and closes the file before returning the list. return "stub" . . Create four files inputi.txt, input2.txt inputs.txt and input4.txt. Use these input files to test your function: feel free to change the content of these files to add a small number of words (2-10) to make sure that you can verify that your function is working correctly. Make sure to test a file that contains more than one line. For example, getallwords ("inputi.txt") returns ["hello", "hello", "hello", "world"]; getAllwords("input2.txt") returns ["hello", "world", "world", "world"]. given the following content of the input files: input1.txt hello hello hello world input2.txt hello world world world input3.txt Hello! Today is a lovely day, isn't it? If you run your function on the content of input3.txt, you will notice that the punctuation characters are returned as part of the words. Let's clean them up to get the words free from the punctuation. Clean the resulting words Write a function getCleanwordlist that takes a list of words that might have punctuation in them, and returns a new list with all the specified punctuation characters removed from the words (you might find the replace() function helpful; strip() might also be sufficient, since it removes leading/trailing characters) Each word in the returned list should contain only characters that do not include the following punctuation characters...!?;". For example, getcleanwordList(input3_list, "..!?;") returns ["Hello", "Today", "is", "a", "lovely", "day", "isn't", "it"), where input3_list holds the words read from the file input3.txt. (Since the other two test files don't have any punctuation in them, it's not helpful to test this function on their content.) HINT: Since getallwords reads a file and returns a list of words that are stored in that file, you can store its returned value in a variable, such as input3_list, which you can then use to test your getcleanwordList function Testing your function Note that if we exclude the exclamation mark ! and the question mark ? from the string argument that's substituted for the charsToRemove parameter, they should be included as part of the returned words: getcleanwordList(input3_list, "..?;") returns ["Hello!", "Today", "is", "a", "lovely", "day", "isn't", "it") getcleanWordList(input3_list", "..!;") returns ["Hello", "Today", "is", "a", "lovely", "day", "isn't", "it?"] getCleanwordList(input3_list, ",.;") returns ["Hello!", "Today", "is", "a", "lovely", "day", "isn't", "it?"] def getCleanwordList (word_list, charsToRemove): Given a list of words word_list, return a new list of all words from the word_list with the specified characters stored in the string charsToRemove) removed. Empty strings should not be added to the resulting list of cleaned words. pass HM000) 1 2 def getAllWords(filepath): 3 result = [] 4 file = open(filepath) 5 for line in file: 6 for word in line.strip().split(): 7 result.append(str(word)) 8 # print(content) # Uncomment this line to print the contents of the file file.close() 10 return result 11 def getCleanWordList (word_list, charsToRemove): 12 words = getallwords (word_list) 13 for i in range(len(words)): 14 words[i] = words[i].strip(charstoRemove) 15 return str(words) 16 17 if -_name "__main_": 18 input1_list = getAllWords ("input1.txt") 19 clean_input1_words = getCleanbiordList(input1_list, ',.!?;"') print(str(clean_input1_words)) 20 1: Unit test: getAllWords("input1.txt") 2: Unit test:getAllWords("input2.txt") ^ 2/2 3: Unit test: getAllWords("input3.txt") ^ 3/3 4: Unit test: getCleanWordList(input3_list,"?:) ^ 0/2 Traceback (most recent call last): TypeError: expected str, bytes or os. Pathlike object, not list 5: Unit test: getCleanWordList-check input ^ 0/2 Traceback (most cent call last): TypeError: expected str, bytes or os. PathLike object, not list 6: Copy of Unit test: getCleanWordList(input3_list, :,-?:") ^ 0/2 Traceback (most recent call last): TypeError: expected str, bytes or os. PathLike object, not list 7: Unit test: getCleanWordList([it?!?!?], ", 21;") ^ 0/3 Traceback (most recent call last): TypeError: expected str, bytes or os. Pathlike object, not list
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


