Question: This needs to be done with MATLAB Thank you! Part II. Solving Equations Exercise 3 (5 points) Difficulty: Moderate In this exercise, you will be


This needs to be done with MATLAB
Thank you!
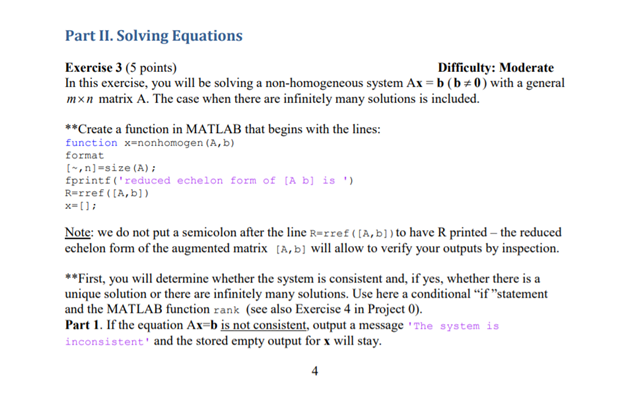
Part II. Solving Equations Exercise 3 (5 points) Difficulty: Moderate In this exercise, you will be solving a non-homogeneous system Ax=b (b=0) with a general mxn matrix A. The case when there are infinitely many solutions is included. **Create a function in MATLAB that begins with the lines: function x=nonhomogen (A,b) format [n]=size (A); fprintf("reduced echelon form of (A b] is ') R-rref([A,b]) x=0); Note: we do not put a semicolon after the line Rerref((A,b]) to have R printed - the reduced echelon form of the augmented matrix (A,b] will allow to verify your outputs by inspection. **First, you will determine whether the system is consistent and, if yes, whether there is a unique solution or there are infinitely many solutions. Use here a conditional "f "statement and the MATLAB function rank (see also Exercise 4 in Project 0). Part 1. If the equation Ax=b is not consistent, output a message 'The system is inconsistent' and the stored empty output for x will stay. 4 Part 2. If the equation is consistent and the solution is unique, output a message 'The system has a unique solution and use MATLAB backslash operator, , to output and display the solution x. Part 3. If the equation is consistent and there are infinitely many solutions, output a message: disp('There are infinitely many solutions) In this case, we will represent the general solution x of a non-homogeneous system as a sum of the general solution of the corresponding homogeneous system and particular solution p of the non-homogeneous system. To get the output x, you will need to construct another function in the file [C,p] - homobasis_b(A,b) which is a modification of the function c - homobasis (A) created in Project1, Exercise 5. Here is a description how to create the function homobasis_b: Referring to Exercise 5 of Project I, we can represent the general solution of a homogeneous system as a Span of the columns of the matrix C, where is the output matrix of the function homobasis. The Span of the columns of C is called the column space of C and denoted Col(C). **To create the function (C,p] - homobasis_b(A,b), which will output the matrix C and the vector p, you will need to modify the code for homobasis in the following way: (1) Remove the part of the code that deals with a system having only the trivial solution. (2) Leave only those commands that determine and output the free variables and the matrix C. Display C with the message: fprintf('a basis for the solution set of the homogeneous system ') fprintf('is formed by the columns of the matrix') (3) Add a few lines to the code that would generate and output particular solution p of the non-homogeneous system. It can be done in a way similar to creating the matrix C but with some adjustments: we use the matrix R-rref ([A,b]) and obtain the vector p by modifying the last column of that matrix. Hint: You might find it helpful, first, write the solution of a sample non-homogeneous system on paper using the reduced echelon form R-rref ((A,b]), and then, proceed with the coding of the output p in your function. You may notice that the ordered entries of p whose indexes correspond to the non-pivot columns of A are zero, and the ordered entries of p whose indexes correspond to the pivot columns of A come from the last column of the matrix Rurre (A,b]). Display vector p with a message: disp('particular solution of the non-homogeneous system is the vector) This will be the end of your function C.pl - homobasis_b(A,b) Here is the final part of your function x-nonhomogen (A,b) **After you created function homobasis_b and saved it in the Current Folder in MATLAB, insert the line [C,p] - homobasis_b(A,b); into the function nonhomogen for Part 3 after the message disp('There are infinitely many solutions) 5 and complete the code for the function nonhomogen with these lines: fprintf("the general solution of the non-homogeneous system is ") fprintf('the column space of the matrix C translated by the vector p') x-Col(C) +p The first line in the fragment above introduces symbolic variables, the second and third lines display a message, and the last line represents the output x in terms of symbolic variables. **Type in the Live Script format compact **Print the functions homobasis_b and nonhomogen in your Live Script. **Run the function x-nonhomogen (A,b); as indicated below: (a)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


