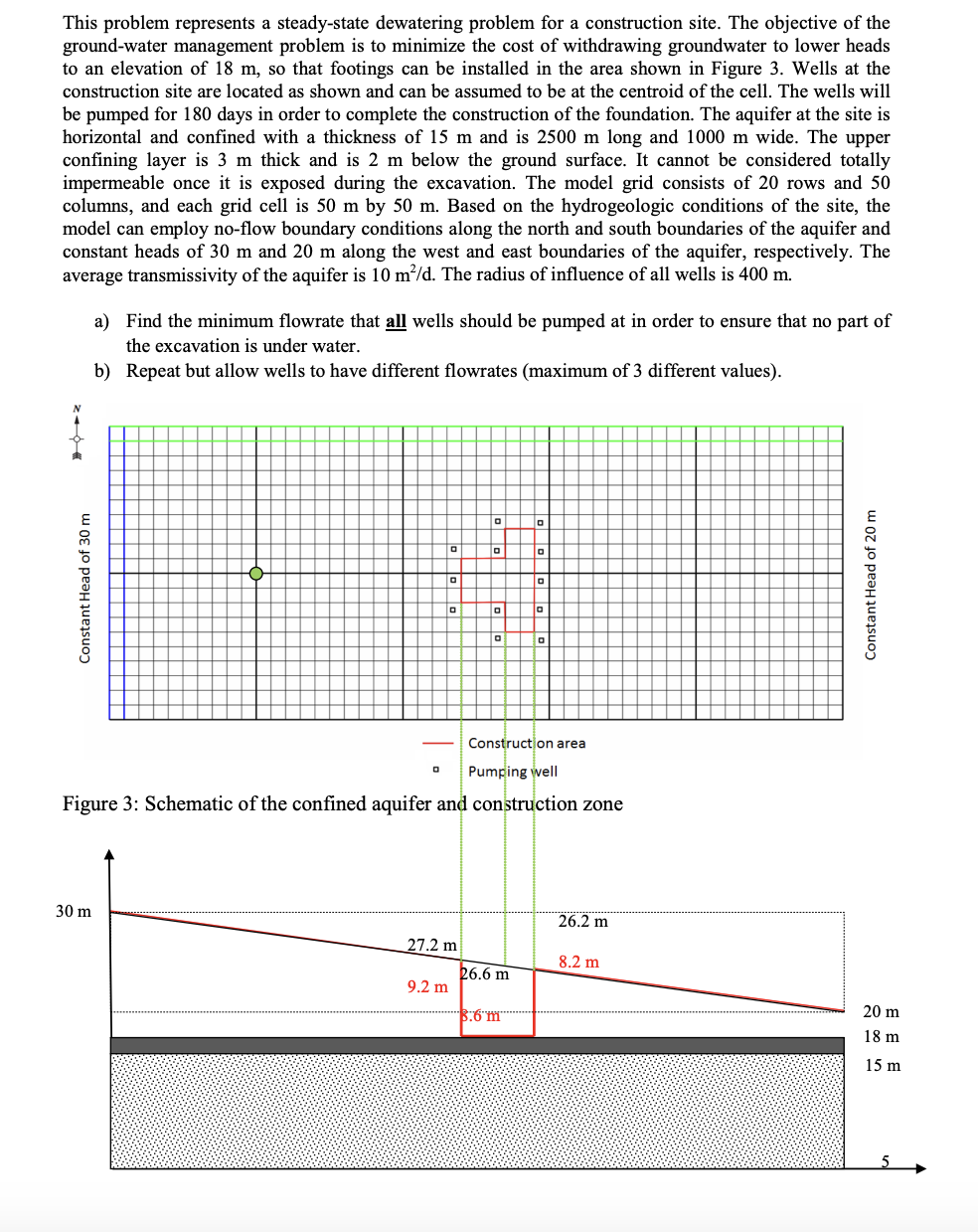
Question: This problem represents a steady - state dewatering problem for a construction site. The objective of the ground - water management problem is to minimize
This problem represents a steadystate dewatering problem for a construction site. The objective of the
groundwater management problem is to minimize the cost of withdrawing groundwater to lower heads
to an elevation of so that footings can be installed in the area shown in Figure Wells at the
construction site are located as shown and can be assumed to be at the centroid of the cell. The wells will
be pumped for days in order to complete the construction of the foundation. The aquifer at the site is
horizontal and confined with a thickness of and is long and wide. The upper
confining layer is thick and is below the ground surface. It cannot be considered totally
impermeable once it is exposed during the excavation. The model grid consists of rows and
columns, and each grid cell is by Based on the hydrogeologic conditions of the site, the
model can employ noflow boundary conditions along the north and south boundaries of the aquifer and
constant heads of and along the west and east boundaries of the aquifer, respectively. The
average transmissivity of the aquifer is The radius of influence of all wells is
a Find the minimum flowrate that all wells should be pumped at in order to ensure that no part of
the excavation is under water.
b Repeat but allow wells to have different flowrates maximum of different values
Figure : Schematic of the confined aquifer and construction zone
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


