Question: This project is the second project for this term where every student will work on his/her own. The objective of this project is to help
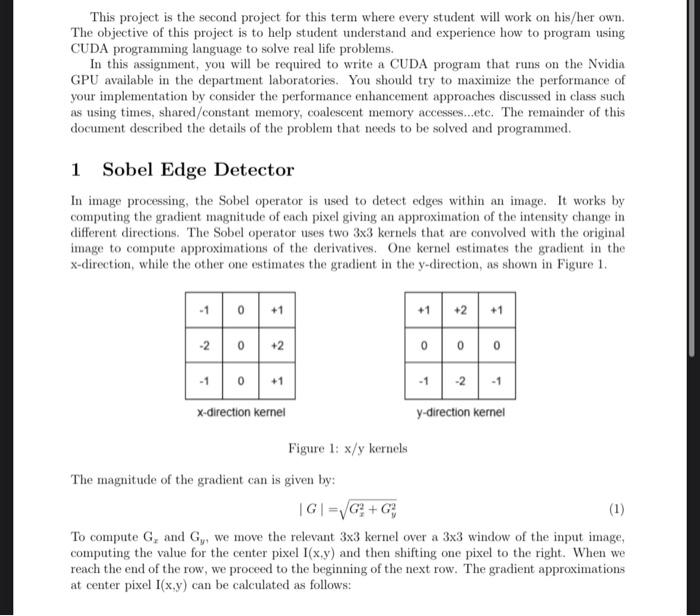
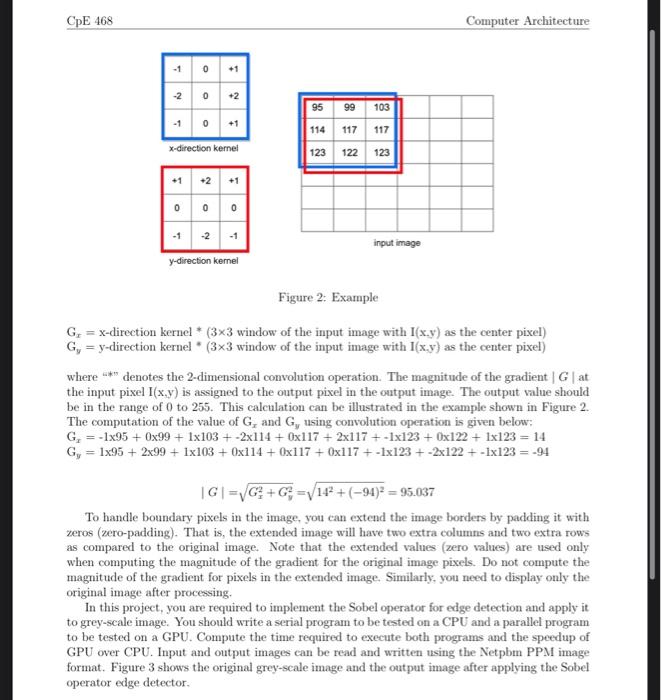
This project is the second project for this term where every student will work on his/her own. The objective of this project is to help student understand and experience how to program using CUDA programming language to solve real life problems. In this assignment, you will be required to write a CUDA program that runs on the Nvidia GPU available in the department laboratories. You should try to maximize the performance of your implementation by consider the performance enhancement approaches discussed in class such as using times, shared/constant memory, coalescent memory accesses...etc. The remainder of this document described the details of the problem that needs to be solved and programmed. 1 Sobel Edge Detector In image processing, the Sobel operator is used to detect edges within an image. It works by computing the gradient magnitude of each pixel giving an approximation of the intensity change in different directions. The Sobel operator uses two 33 kernels that are convolved with the original image to compute approximations of the derivatives. One kernel estimates the gradient in the x-direction, while the other one estimates the gradient in the y-direction, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1: x/y kernels The magnitude of the gradient can is given by: G=Gx2+Gy2 To compute Gx and Gy, we move the relevant 33 kernel over a 33 window of the input image, computing the value for the center pixel I(x,y) and then shifting one pixel to the right. When we reach the end of the row, we proced to the beginning of the next row. The gradient approximations at center pixel I(x,y) can be calculated as follows: Figure 2: Example Gx=x-direction kernel * (33 window of the input image with I(x,y) as the center pixel) Gy=y-direction kernel * (33 window of the input image with I(x,y) as the center pixel) where 6" denotes the 2-dimensional convolution operation. The magnitude of the gradient G at the input pixel I(x,y) is assigned to the output pixel in the output image. The output value should be in the range of 0 to 255 . This calculation can be illustrated in the example shown in Figure 2. The computation of the value of Gx and Gy using convolution operation is given below: Gx=195+099+1103+2114+0117+2117+1123+0122+1123=14Gy=195+299+1103+0114+0117+0117+1123+2122+1123=94 G=Gx2+Gy2=142+(94)2=95.037 To handle boundary pixels in the image, you can extend the image borders by padding it with zeros (zero-padding). That is, the extended image will have two extra columns and two extra rows as compared to the original image. Note that the extended values (zero values) are used only when computing the magnitude of the gradient for the original image pixels. Do not compute the magnitude of the gradient for pixels in the extended image. Similarly, you need to display only the original image after processing. In this project, you are required to implement the Sobel operator for edge detection and apply it to grey-scale image. You should write a serial program to be tested on a CPU and a parallel program to be tested on a GPU. Compute the time required to execute both programs and the speedup of GPU over CPU. Input and output images can be read and written using the Netpbm PPM image format. Figure 3 shows the original grey-scale image and the output image after applying the Sobel operator edge detector
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


