Question: This question explores the behavior of polymer chains. We use a simple model to generate numerous polymer conformations in two dimensions. You will convince yourself
This question explores the behavior of polymer chains. We use a simple model to generate numerous polymer conformations in two dimensions. You will convince yourself that the random coil is the most likely macrostate, whereas the fully stretched chain represents a very unlikely macrostate.
The polymer consists of 100 beads linked by bonds that are 1 nm long. Bead 1 is located in the origin of an x/y coordinate system (at 0/0). Beads 2 - 100 are located in random positions.
The x-coordinate of each new bead is calculated based on the x-coordinate of the previous bead: xi+1 = xi + x, where x is chosen randomly as -1, 0, or 1.
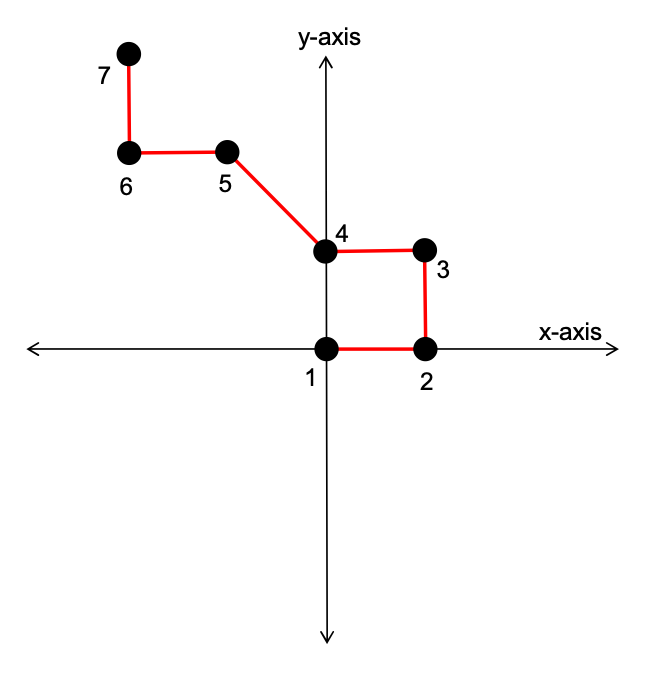
The y-coordinate of each new bead is calculated based on the y-coordinate of the previous bead: yi+1 = yi + y, where y is chosen randomly as -1, 0, or 1. Make sure that y values are independent of x values. Here is a possible conformation (only 7 beads are shown):
(a) Generate an Excel spreadsheet to calculate and plot the chains. Use the RAND BETWEEN() function.
Provide plots of three different random structures. Use the range -20 nm ... 20 nm for both x and y, with chart type scatter with straight lines and markers. Your plot areas should be square , not rectangular to ensure that the conformations are undistorted.
(b) Figure out how to calculate the chain end distance using Excel. Use the spreadsheet from (a) to determine the chain end distances of 100 random coils.
Generate a histogram that shows the frequency distribution of the 100 chain end distances. Use a bin width of 3 nm. The histogram x-axis should cover the range between 1 and 100 nm.
In your histogram, indicate with an arrow where the fully stretched chain would be located. Did you observe any fully stretched chains in this computer experiment?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


